* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fiscal policy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
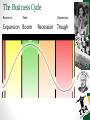
HEALTH of an ECONOMY PIE Production = P Income = I Employment = E The Business Cycle • The term business cycle refers to economywide fluctuations in production, trade and economic activity in general over several months or years in an economy organized on free-enterprise principles. • The business cycle is the upward and downward movements of levels of GDP (gross domestic product) and refers to the period of expansions and contractions in the level of economic activities around its long-term growth trend. The Business Cycle Recovery Peak Expansion Boom Depression Recession Trough Economic TOOLS Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy FISCAL POLICY Fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection (taxation) and expenditure (spending) to influence the economy. The two main instruments of fiscal policy are changes in the level and composition of taxation and government spending in various sectors. FISCAL POLICY Expansionary fiscal policy involves government spending exceeding tax revenue, and is usually undertaken during recessions. FISCAL POLICY Contractionary fiscal policy occurs when government spending is lower than tax revenue, and is usually undertaken to pay down government debt. MONETARY POLICY Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting a rate of INTEREST for the purpose of promoting economic growth and stability. MONETARY POLICY • An EXPANSIONARY monetary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual • Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering INTEREST RATES in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. MONETARY POLICY • A CONTRACTIONARY monetary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it • Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values. President Herbert Hoover NEW DEAL PROGRAMS •Relief •Recovery •Reform •President Roosevelt - 100 Days •FDR and Alphabet Soup NEW DEAL PROGRAMS •Relief - Immediate action taken to halt the economies deterioration. •Recovery - "Pump - Priming" Temporary programs to restart the flow of consumer demand. •Reform - Permanent programs to avoid another depression and insure citizens against economic disasters.

















![[MT445 | Managerial Economics] Unit 9 Assignment Student Name](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001525631_1-1df9e774a609c391fbbc15f39b8b3660-150x150.png)






