* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 3.4 Basic Functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
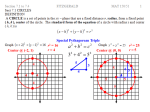
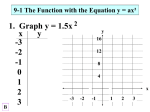
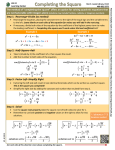
Special Pythagorean Triple r2 = 16 a2 b2 c2 r=4 Center @ (0, 0) Center @ (-2, 1) 32 4 2 5 2 5 4 3 5 4 3 4 4 r2 = 25 r=5 34 4 5 5 4 5 (___, 0) Substitute in 0 for y and solve for x. x 22 0 12 16 x 22 1 16 x 22 15 x 2 15 x 2 15 2 2 15,0 15 ,0; 2 15 ,0 (0, ___) Substitute in 0 for x and solve for y. 0 22 y 12 16 2 4 y 1 16 y 12 12 y 1 12 y 1 2 3 0,1 2 3 0,1 2 3 ; 0,1 2 3 ( h, k ) x h2 y k 2 r 2 x 12 y 22 r 2 x 12 y 22 r 2 4 12 2 22 r 2 32 42 r 2 9 16 25 r 2 Substitute in h and k as 1 and -2. Substitute in x and y as 4 and 2. Solve for r2. x 12 y 22 25 Write the standard equation of a circle with the endpoints of the diameter as ( -2, 7) and ( -14, -9). ( x, y ) GENERAL FORM OF THE EQUATION OF A CIRCLE: Graph x y 4 x 6 y 9 0 Convert to Group x terms and y terms together and move the constant to the other side. 2 2 x h2 y k 2 r 2 by completing the square. x 2 4 x y 2 6 y 9 Complete the square of the x’s and y’s. (+2)2 y 2 6 y ___ (-3)2 9 ___ 4 ___ 9 x 2 4 x ___ x y x y x 22 y 32 4 Graph Center @ (-2, 3) 2 x 2 2 y 2 12 x 8 y 24 0 r2 = 4 r=2 Divide everything by 2. Why? x 2 y 2 6 x 4 y 12 0 (-3)2 y 2 4 y ___ (-2)2 12 ___ 9 ___ 4 x 2 6 x ___ x x 32 y 22 25 y Center @ (3, 2) x x 2 y 2 ax by c 0 y r2 = 25 r=5 x 0 y a x 2 y (-a) x x y a 0 y a 2 2 2 2 2 Square both sides to remove radical. x2 y a y a FOIL the binomials. x 2 y 2 2ay a 2 y 2 2ay a 2 2 Focus Cancel like terms on each side. a a 2a x 2 2ay 2ay Solve for x2. 4a a -a -a Directrix 2 x 2 4ay Graph the following equations. y 12 x 2 x=-3 The y is squared and the coefficient on the x is positive, the parabola opens to the right. 4a = 12, a = 3 and the vertex is at (0, 0). 6 V 3 F 6 Graph the following equations. x 2 16 y The x is squared and the coefficient on the y is negative, the parabola y=4 opens down. 4a = -16, a = -4 and the vertex is at (0, 0). V 4 8 F 8 Graph the following equations. y 2 8 x x=2 The y is squared and the coefficient on the x is negative, the parabola opens to the left. 4a = -8, a = -2 and the vertex is at (0, 0). 4 F V 2 4 Graph the following equations. x 2 2 8 y 1 The x is squared and the coefficient on the y is positive, the parabola opens up. 4a = 8, a = 2 and the vertex is at (2, -1). 4 F 2 y=-3 V 4 Graph the following equations. y 2 2 y 4 x 17 0 x=3 We need to complete the square of the y-terms to put in graphing form. Isolate the y-terms. 1 y 2 2 y (-1) ___2 4 x 17 ___ y 1 2 4 x 16 Factor out the 4 as the GCF. y 1 2 4x 4 The y is squared and the coefficient on the x is positive, the parabola opens to the right. 4a = 4, a = 1 and the vertex is at (4, 1). V 2 F 2 Graph the following equations. x2 6x 4 y 1 0 We need to complete the square of the x-terms to put in graphing form. Isolate the x-terms. 9 x 2 6 x (+3) ___2 4 y 1 ___ x 3 2 4y 8 Factor out the 4 as the GCF. x 3 2 4 y 2 2 F y=-3 The x is squared and the coefficient on the y is positive, the parabola opens up. 4a = 4, a = 1 and the vertex is at (-3, -2). V 2 Equation format is ... …plug in x & y to solve for 4a. Draw a rough graph. (2,3) Draw a rough graph. V V(-4, ?) 9 4a 2 9 4a 2 Equation format is ... …distance from V to F is 1, a = 1, 2 y k 4a x h and plug in the vertex values. F Draw a rough graph. F(-4, 4) 3 y = -2 32 4a2 y 2 4ax 9 2 y x 2 Equation format is ... x h 2 4a y k 4–3=1 V(-4, 1) y 22 41x 1 y 22 4x 1 …distance from F to the directrix line is 6, V is halfway, so a = 3. Plug in a and the vertex values. x 42 43 y 1 x 42 12 y 1