* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
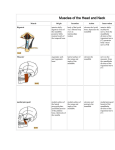
Download Superficial muscles of neck Platysma Attaches from inferior border of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Superficial muscles of neck o Platysma Attaches from inferior border of mandible to fascia covering superior parts of pec major and deltoid muscles Innervated by cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII) Draws corners of mouth inferiorly and widens it as in expressions of sadness and fright; draws skin of neck superiorly when teeth are clenched o Sternocleidomastoid Attaches from lateral surface of mastoid process of temporal bone and lateral half of superior nuchal line to anterior surface of manubrium of sternum (sternal head) and superior surface of medial third of clavicle (clavicular head) Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI, motor); C2 and C3 nerves Unilateral: tilts head to same side and rotates it so face is turned superiorly toward opposite side Bilateral: extends neck at atlanto occipital joints, flexes cervical vertebrae so chin approaches manubrium, extends superior cervical vertebrae while flexing inferior vertebrae so chin is thrus forward o Trapezius Attaches from medial third of superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, nuchal ligament, spinous processes of C7-T12 vertebrae, and lumbar and sacral spinous processes to lateral third of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI, motor); C2 and C3 Suprahyoid muscles o Mylohyoid Myohyloid line of mandible -> mylohyoid raphe and body of hyoid Innervated by nerve to mylohyoid; a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve (CN V3) Elevates hyoid, floor of mouth, and tongue during swallowing and speaking o Geniohyoid Inferior mental spine of mandible -> body of hyoid Innervated by C1 via hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) Pulls hyoid anterosuperiorly; shortens floor of mouth; widens pharynx o Stlyohyoid Styloid process of temporal bone -> body of hyoid Innervated by stylohyoid branch of facial nerve (CN VII) Elevates and retracts hyoid; elongates floor of mouth o Digastric Digastric fossa of mandible (anterior), mastoid notch of temporal bone (posterior) -> intermediate tendon to body and greater horn of hyoid Innervated by nerve to mylohyoid (anterior) and digastric branch of facial nerve (posterior) Depresses mandible against resistance; elevates and steadies hyoid during swallowing and speaking Infrahyoid muscles o Sternohyoid Manubrium of sternum and medial clavicle -> body of hyoid Innervated by C1-3 through a branch of ansa cervicalis Depresses hyoid after elevation during swallowing o Omohyoid Superior border of scapula near suprascapular notch -> inferior border of hyoid Innervated by C1-3 through a branch of ansa cervicalis Depresses, retracts, and steadies hyoid o Sternothyroid Posterior surface of manubrium -> oblique line of thyroid cartilage Innervated by C2-3 through branch of ansa cervicalis Depresses hyoid and larynx o Thyrohyoid Oblique line of thyroid cartilage -> inferior border of body and greater horn of hyoid Innervated by C1 via hypoglossal nerve Depresses hyoid and elevates larynx Prevertebral muscles o Anterior scalene Transverse processes of C4-6 -> 1st rib Cervical spinal nerves C4-6 Flex head o Levator scapulae Posterior tubercles of transverse processes C1-4 vertebrae -> superior part of medial border of scapula Dorsal scapular nerve C5 and cervical spinal nerves C3,4 Elevates scapula and tilts its glenoid cavity inferiorly o Middle scalene Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C4-6 -> superior border of 1st rib; posterior groove for subclavian artery Anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves Flexes neck laterally; elevates 1st rib during forced inspiration o Posterior scalene Posterior tubercles of transverse processes of C4-6 -> external border of 2nd rib Anterior rami of cervical spinal nerves C7,8 Flexes neck laterally; elevates 2nd rib during forced inspiration Muscles of face/scalp o Occipitofrontalis Frontal belly Epicranial aponeurosis -> skin and subcutaneous tissue of eyebrows and forehead Elevates eyebrows and wrinkles skin of forehead; protracts scalp (surprise) Temporal branch of parotid plexus Occipital belly Lateral two thirds of superior nuchal line -> epicranial aponeurosis Retracts scalp, increasing effectiveness of frontal belly Posterior auricular branch of CN VII o Orbicularis oculi Medial orbital margin; medial palpebral ligament; lacrimal bone -> skin around margin of orbit; superior and inferior tarsal plates Closes eyelids; palpebral does so weakly; oribital does so tightly Temporal and zygomatic branches of parotid plexus o Orbicularis oris Medial maxilla and mandible; deep surface of perioral skin; angle of mouth -> mucous membrane of lips Tonus closes rima oris; phasic contraction compresses and protrudes lips (kissing) or resists distension (blowing) Buccal branch of parotid plexus o Buccinator Mandible, alveolar processes of maxilla and mandible, pterygomandibular raphe -> angle of mouth; orbicularis oris Presses cheek against molar teeth; works with tongue to keep food between occlusal surfaces and out of oral vestibule; resists distension (blowing) Buccal branch of parotid plexus o Platysma Subcutaneous tissue of infraclavicular and supraclavicular regions -> base of mandible; skin of cheek and lower lip; angle of mouth; orbicularis oris Depresses mandible; tenses skin of inferior face and neck Extraocular muscles of the orbit o Levator palpebrae superioris Oculomotor nerve; deep layer is supplied by sympathetic fibers Elevates superior eyelid o Superior oblique Trochlear nerve (CN IV) Abducts, depresses, and medially rotates eyeball o Inferior oblique Oculomotor nerve (CN III) Abducts, elevates, and laterally rotates eyeball o Superior rectus Oculomotor nerve (CN III) Elevates, adducts, and rotates eyeball medially o Inferior rectus Oculomotor nerve (CN III) Depresses, adducts, and rotates eyeball medially o Medial rectus Oculomotor nerve (CN III) Adducts eyeball o Lateral rectus Abducent nerve (CN VI) Abducts eyeball Muscles of mastication o Temporal Floor of temporal fossa -> tip and medial surface of coronoid process and anterior border of ramus of mandible Mandibular nerve via deep temporal branches Elevates mandible; posterior, more horizontal fibers are primary retractors of mandible o Masseter Inferior border and medial surface of maxillary process -> angle and lateral surface of ramus of mandible Mandibular nerve via masseteric nerve Elevates mandible; superficial fibers make limited contribution to protrusion of mandible o Lateral pterygoid Infratemporal surface and crest of greater wing of sphenoid and lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate -> upper head attaches to joint capsule and articular disc of TMJ; inferior head attaches to pterygoid fovea on anteriomedial aspect of neck of condyloid process of mandible Mandibular nerve via lateral pterygoid nerves Bilaterally: protracts mandible and depresses chin; unilaterally: swings jaw towards contralateral side; large lateral chewing movements produced by alternating unilateral contractions o Medial pterygoid Medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate and pyramidal process of palatine bone and tuberosity of maxilla -> medial surface of ramus of mandible Mandibular nerve via medial pterygoid nerve Synergistic with masseter to elevate mandible; contributes to protrusion; small grinding movements produced by alternate unilateral activity Muscles of the soft palate o Tensor veili palatine Medial pterygoid nerve (branch of CN V3) via otic ganglion Tenses soft palate and opens mouth of pharyngotympanic tube during swallowing and yawning o Levator veli palatini Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve via pharyngeal plexus Elevates soft palate during swallowing and yawning o Palatoglossus Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve via pharyngeal plexus Elevates posterior part of tongue and draws soft palate onto tongue o Palatopharyngeus Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve via pharyngeal plexus Tenses soft palate and pulls walls of pharynx superiorly, anteriorly, and medially during swallowing o Musculus uvulae Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve via pharyngeal plexus Shortens uvula and pulls it superiorly Extrinsic muscles of the tongue o Genioglossus Tendon from superior part of mental spine of mandible -> entire dorsum of tongue; inferior most and posterior most fibers attach to body of hyoid bone Bilaterally: depresses tongue, especially central part causing a longitudinal furrow; posterior part pulls tongue anteriorly for protrusion; most anterior part retracts apex of protruded tongue; unilateral contraction deviates tongue to contralateral side Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) o Hyoglossus Body and greater horn of hyoid bone -> inferior aspects of lateral part of tongue Depresses tongue, especially pulling its sides inferiorly; helps shorten tongue Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) o Styloglossus Anterior border of distal styloid process; stylohyoid ligament -> sides of tongue posteriorly, interdigitating with hyoglossus Retrudes tongue and curls its sides working with genioglossus to form a central trough during swallowing Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) o Palatoglossus Palatine aponeurosis -> enters posterolateral tongue transversely, blending with intrinsic transverse muscles Capable of elevating posterior tongue or depressing soft palate; most commonly acts to constrict isthmus of fauces Vagus nerve Muscles of the larynx o Cricothyroid Anterolateral part of cricoids cartilage -> inferior margin and inferior horn of thyroid cartilage External laryngeal nerve (CN X) Stretches and tenses vocal ligament o Thyroarytenoid Lower half of posterior angle of thyroid laminae and cricothyroid ligament -> anterolateral arytenoid surface Inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal recurrent from CN X) Relaxes vocal ligament o Posterior cricoarytenoid Posterior surface of lamina of cricoids cartilage -> vocal process of arytenoid cartilage Inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal recurrent from CN X) Abducts vocal folds o Lateral cricoarytenoid Arch of cricoids cartilage -> vocal process of arytenoid cartilage Inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal recurrent from CN X) Adducts vocal folds (interligamentous portion) o Transverse and oblique arytenoids One arytenoid cartilage -> contralateral arytenoid cartilage Inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal recurrent from CN X) Adduct arytenoid cartilages (adducting intercartilagenous portion of vocal folds, closing posterior rima glottidis) o Vocalis Lateral surface of vocal process of arytenoid cartilage -> ipsilateral vocal ligament Inferior laryngeal nerve (terminal recurrent from CN X) Relaxes posterior vocal ligament while maintaining (or increasing) tension of anterior part Muscles of pharynx o External layer Superior constrictor Pterygoid hamulus, pterygomandibular raphe; posterior end of mylohyoid line of mandible and side of tongue -> pharyngeal tubercle on basilar part of occipital bone Pharyngeal branch of vagus Constrict walls of pharynx during swallowing Middle constrictor Stylohyoid ligament and greater and lesser horns of hyoid -> pharyngeal raphe o Pharyngeal branch of vagus + branches of external and recurrent laryngeals Constrict walls of pharynx during swallowing Inferior constrictor Oblique line of thyroid cartilage and side of cricoids cartilage -> pharyngeal raphe, cricopharyngeal part encircles pharyngoesophageal junction without forming a raphe Pharyngeal branch of vagus + branches of external and recurrent laryngeals Constrict walls of pharynx during swallowing Internal layer Palatopharyngeus Hard palate and palatine aponeurosis -> posterior border of lamina of thyroid cartilage and side of pharynx and esophagus Pharyngeal branch of vagus Elevate (shorten and widen) pharynx and larynx during swallowing and speaking Salpingopharyngeus Cartilaginous part of pharyngotympanic tube -> blends with palatopharyngeus Pharyngeal branch of vagus Elevate (shorten and widen) pharynx and larynx during swallowing and speaking Stylopharyngeus Styloid process of temporal bone -> posterior and superior borders of thyroid cartilage and palatopharyngeus Glossopharyngeal nerve Elevate (shorten and widen) pharynx and larynx during swallowing and speaking