* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NAME________________________ (H) What Does it Start with
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
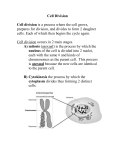
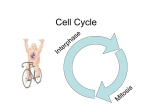
NAME________________________ (H) What Does it Start with? Review CHAPTER 10 & 11-4 Cell division in eukaryotes consists of two parts: M __ __ __ __ __ __ which divides the chromosomes and C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ which divides the cytoplasm. Bacteria divide using B __ __ __ __ __ F __ __ __ __ __ __ instead of mitosis. In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides once to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell; In M __ __ __ __ __ __ a cell divides twice to produce four genetically different daughter cells with one-half the number of chromosomes of a body cell, A C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is made up of two C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ arms joined in the middle by a C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. G1, S, and G2 combine to make up I __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , the non-dividing phase of the cell cycle. When cells like nerve cells are in G0, they leave the cell cycle and S __ __ __ dividing. DNA is copied during the S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ or S phase of interphase. P __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is the first phase of mitosis during which C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ scrunches into chromosomes, the C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ and S __ __ __ __ __ __ fibers appear to pull the chromosomes, and the N __ __ __ __ __ __ M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ and N __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ disappear. During M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ the chromosomes line up along the center of the cell. In A __ __ __ __ __ __ __ the chromatid arms separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. T __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is also called reverse P __ __ __ __ __ __ __ because all of the events that happen in prophase are “undone” in telophase. H __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ chromosomes are the same size and the same shape and carry genes for the same traits but are NOT identical. The region near the nucleus where the centrioles are found that helps organize the spindle fibers during cell division is called the C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are log-like structures that appear near the nucleus during cell division in an animal cell and move to opposite poles to pull the chromosomes apart. The S __ __ __ __ __ __ fibers are made of M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ and connect each chromosome to the centrioles. The family of proteins that regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells is called C __ __ __ __ __ __. When DNA and its attached proteins is spread out in the nucleus of non-dividing cells it is called C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . When it is scrunched up in dividing cells it is called C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. The disease in which one of the body’s own cells loses the ability to control division= C __ __ __ __ __ When animal cells undergo cytokinesis they use a C __ __ __ __ __ __ __ F __ __ __ __ __ to split their cytoplasm, but plant cells use a C __ __ __ P __ __ __ __ because their cell wall keeps them from pinching. The repeating steps a cell goes through during its lifetime are called the C __ __ __ C __ __ __ __. The spread of cancer cells to a new location in the body is called M __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. _T_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are the protective tips on the ends of chromosomes that shrink smaller every time the cell divides. _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are things that can damage DNA and cause cancer (like cigarette smoke, radiation, and some viruses) Crowded cells that stop dividing when they touch other cells are showing _C_ __ __ __ __ __ __ _I_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ . Cells that show _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ _D_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ can only divide when they are attached to other cells or to a surface. _T_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ is the process by which a normal cell changes into a cancer cell. Cancer cells have high levels of _T_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , the enzyme that adds the protective tips onto the ends of chromosomes.