* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth`s 3 Layers 2 Types of Crust 2 Mantle Regions 2 Core Regions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
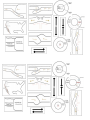
Part 4: Theory of Plate Tectonics Earth’s 3 Layers 2 Types of Crust 2 Mantle Regions 2 Core Regions Convergent Picture Divergent Picture Transform Picture What happens to the Plates? What happens to the Plates? What happens to the Plates? Picture of Convergent Oceanic-Oceanic Picture of Convergent Oceanic-Continental Picture of Convergent Continental-Continental Example on Earth: Example on Earth: Example on Earth: Picture of Divergent Oceanic Plates Picture of Divergent Continental Plates Picture of Transform Boundary Example on Earth: Example on Earth: Example on Earth: Plate Boundaries Describe the following features in a few sentences. Identify which feature belongs to which boundary. Use pages 258-264 in your textbook to help you. Continental rift: _________________________ boundary __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Continental volcanic arc: _________________________ boundary __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Ocean trenches: _________________________ boundary __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Ocean ridge/Rift valley: _________________________ boundary __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Volcanic island arc: _________________________ boundary __________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Use the following terms to fill in the blank: convergent, divergent, transform fault Crust is not created or destroyed ___________________________________ Crust is created _________________________________________________ Crust is destroyed _______________________________________________ Using what you know about plate boundaries, explain the tectonic movement that is occurring at the East African Rift Valley, and predict how the area may change in the future. Why are subduction zones not commonly found at convergent continental-continental boundaries? Explain why divergent plate boundaries are also called constructive plate margins. Label A-G in Figure 9-1. What type of plate boundary is illustrated in Figure 9-1? Evidence of Plate Tectonics Fill in the chart for the evidence of plate tectonics below (pages 265-268). Evidence Description Paleomagnetism Earthquake Patterns Ocean Drilling Hot Spots How does the pattern of earthquake foci support the theory of plate tectonics? Causes of Plate Motion Use pages269-270 to help you answer the following questions. 1. The main source of downward convection flow in the mantle is called ____. a. ridge-pull c. slab-push b. slab-pull d. ridge-push 2. The downward sliding characteristic of ridge-push is the result of ____. a. gravity c. paleomagnetism b. uneven heat distribution d. continental rifting 3. The thermal convection that drives plate motion is caused by ____. a. seafloor spreading c. gravity b. an unequal distribution of heat d. subduction 4. According to whole-mantle convection, ____. a. small amounts of material from the lower mantle move upward to the surface b. slabs of cold oceanic lithosphere move down and into the lower mantle c. large chunks of continental crust are pulled down into the lower mantle d. material from the inner core rises into the mantle to form super hot plumes