* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework Set 2
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
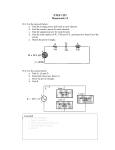
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science EEL4205 Electric Machinery Homework Set No. 2 Names: ____________________; _____________________; ____________________; Problem 1. The following figure shows a simple single phase AC power system with three loads. The voltage source is V 2400 V , and the impedances of three loads are Z1 1030 , Z 2 1045 , Z 3 10 90 (1) Assume that the switch shown in the figure is initially open. Calculate the current I, the power factor, and the real, reactive, and apparent power being supplied by the source. (2) How much real, reactive, and apparent power is being consumed by each load with the switch open? (3) Assume that the switch shown in the figure is now closed. Calculate the current I, the power factor, and the real, reactive, and apparent power being supplied by the source. (4) How much real, reactive, and apparent power is being consumed by each load with the switch closed? (5) What happened to the current flowing from the source when the switch is closed? Why? Answer: (1) (4) MatLab code: (2) (5) (3) Problem 2. The following figure shows a three phase power system with two loads. The connected generator is producing a line voltage of 480 V, and the line impedance is 0.09+j0.16 . Load 1 is Y connected with a phase impedance of 2.536.87 o . Load 2 is connected with a phase impedance of 5 20o . (1) What is the line to line voltage of two loads? (2) What is the voltage drop on the transmission line? (3) Find the real and reactive powers supplied to each load. (4) Find the real and reactive power loss in the transmission line. (5) Find the real power, reactive power and power factor supplied by the generator. Answer: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) MatLab code: Problem 3. The following figure shows a one line diagram of a simple power system containing a single 480 V generator and three loads. Assume that the transmission lines in this power system are lossless. (1) Assume that Load 1 is Y connected. What are the phase voltage and currents in that load? (2) Assume that Load 2 is connected. What are the phase voltage and currents in that load? (3) What real, reactive and apparent power does the generator supply when the switch is open? (4) What is the total line current IL when the switch is open? (5) What real, reactive and apparent power does the generator supply when the switch is closed? (6) What is the total line current IL when the switch is closed? (7) How does the total line current IL compared to the sum of three individual current I1 I 2 I 3 ? If they are not equal, why not? Answer: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) MatLab code: Problem 4. Find the magnitudes and angles of each line and phase voltage and current on the load shown in the following figure. Answer: MatLab code: Problem 5. The following figure shows a one-line diagram of a small 480 V (terminal voltage or line to line voltage) distribution system in an industrial plant. An engineer working at the plant wishes to calculate the current that will be drawn from the power utility company with and without the capacitor bank (for power factor correction) switched into the system. For the purposes of this calculation, the engineer will assume that the lines in the system have zero impedance. (1) If the switch shown is open, find the real, reactive and apparent powers in the system. Find the total current supplied to the distribution system by the utility. (2) Repeat part (a) if the switch closed. (3) What happened to the total current supplied by the power system when the switch closed? Why? What conclusion can you draw? Answer: (1) (2) (3) MatLab code: Problem 6. The linear machine shown in the figure has the following characteristics: B = 0.5 T into page, R=0.5l = 0.7m, VB=110V. (1) What’s the machine’s maximum starting current? How much is the induced force at starting? Which direction does this force pointing to? (2) What is the steady state velocity at no load? How much is the current at steady state? (3) Suppose a 40N force pointing to the right is applied to the bar. What’s the steady state velocity? How much is the current at steady state? Which direction is the current? How much power would the battery be providing or consuming? Is this device a generator or motor? (4) Suppose a 40N force pointing to the left is applied to the bar. What’s the steady state velocity? How much is the current at steady state? Which direction is the current? How much power would the battery be providing or consuming? Is this device a generator or motor? Answer: (1) (2) (3) (4) MatLab code: