* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 Test Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
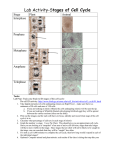
Chapter 8 Test Review Mitosis Question 1. As a cell grows – which grows fast – volume or surface area? 2. What are three reasons that cells divide? 3. What is true about the chromosomes of the new cells after cell division? 4. What two types of cells divide on a daily basis (fast)? 5. How do cells know when to stop growing? 6. When a group of cells has uncontrolled growth – what is this called? 7. What are the three (3) stages of cell division? 8. What is the difference between mitosis and cytokinesis? 9. What is the smallest form of genetic material 10. What is the largest form of genetic material before it is in the form of chromatin, visible only during cell division? 11. What is chromatin? 12. What phase doe mitosis happen 13. What are the special proteins that DNA coils around called? 14. How are sister chromatids joined? 15. What does #14 connect to during mitosis? 16. How many chromosomes does the human body cell contain? 17. When we say that the human body cell is diploid – what does this mean? 18. What are the 3 stages of interphase? 19. During which phase of interphase is there cell growth and protein production? 20. During which phase of interphase does the DNA replicate? 21. During which phase of interphase do the organelles replicate? 22. What form is the DNA in during interphase? 23. What are the two main parts of a chromosome 24. What are the two main stages of cell division Answer Volume Too large to get stuff in/out Low surface to volume ration Small cell can manage itself better The are duplicated so each new cell has a complete set Skin and digestive tract cells When they bump into each other STOP/OFF switch As a cut heals Cancer Interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis Mitosis is the nucleus dividing whereas cytokinesis is the whole cell dividing Double helix chromosome Condensed DNA M phase Histones By a centromere Spindle fibers 46 That it has the 2n number of chromosomes – 46 G1, S, and G2 G1 S G2 Chromatin chromatids Mitosis and cytokinesis 25. What are the 4 phases of mitosis(cell division) – in order? 26. What phase of mitosis is the longest? 27. What is the first phase of mitosis where chromosomes are visible? 28. During which phase of mitosis do centrioles start to move to the poles and spindle fibers appear? 29. During which phase of mitosis do chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers and line up in the middle? 30. During which phase of mitosis do the centromeres split and pull sister chromatids apart? 31. During which phase of mitosis do chromosomes uncoil and go back into chromatin? 32. During which phase of mitosis does a nuclear envelop form around each new nuclei? 33. What is present at the end of mitosis? 34. What process moves inward and pinches in the middle to form two cells? 35. What forms before the cell wall at the end of the cell cycle in plants? 36. What is the result of the cell cycle 37. What is the advantage of sexual reproduction? 38. In eukaryotes what regulates the timing of the cell cycle? 39. What is the chromosome number of a gamete 40. What is the chromosome number of a somatic cell 41. How many alleles do gametes have for each gene 42. What is meiosis? 43. The process of changing genetic information during prophase in meiosis? 44. Tetrads are formed during what phase of meiosis 45. What is the result of meiosis? 46. Which type of reproduction makes genetically identical offspring? 47. Female egg cells produce what chromosome? 48. Males can produce 50% each of what type of chromosome, what are they? 49. pre-programmed, deliberate cell death 50. A photographic inventory of homologous chromosomes Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase Prophase Prophase 51. What is a homologous chromosome? One that has the same size, shape and codes for the same trait. Super male Super female Klienfelter’s Turner’s 52. What do the following stand for? XYY XXX XXY Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Telophase One cell – two nuclei Cytokinesis Cell plate 2 new identical cells Genetic diversity cyclins n 2(n) 1 The production of gametes Crossing over prophase 4 genetically different haploid cells Asexual X X or Y apoptosis Karyotype XO 53. What is the failure of chromosomes to separate equally? nondisjunction