* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spring 2001
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
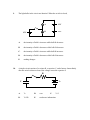
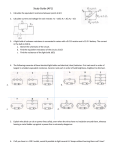
PHYS2424 – SPRIBG 2001 EXAM #1 – PART 1 Electric Force, Fields, Potential, Capacitance, and Circuits NAME ______________________________________________________ I. Basic Equation and Definitions ___________________ (50 points) II. Multiple Choice ___________________ (60 points) III. Short Problems ___________________ (30 points) IV. Units ___________________ (20 points) TOTAL PART 1 ___________________ (160 points) TOTAL PART 2 ___________________ (280 points) TOTAL POINTS ___________________ ( GRADE ___________________ ) I. Basic Equations and Definitions – ( 5 marks each) 1. Write Coulomb’s Law : 2. Write Gauss’s Law for Electric Fields 3. Mathematical formula used to find the electric field if one knows the electric potential function. 4. Lorentz Force Law For Electric Fields 5. The definition of circuit elements in parallel 6. Explain the difference between resistivity and resistance. 7. The equation that defines capacitance 8. The definition of circuit elements in series 9. The definition of an open circuit 10. The definition of a short circuit II. Multiple Choice ( 5 marks each) 1. A +4nC point charge is located at the center of conducting spherical shell, point A, as shown below. D A B C Given that the spherical shell has +4nC of charge on its outer surface, the electric field E will be zero at: A. point A only. B. points A and B only. C. points A,B, and C only. D. point D only. E. none of these 2. Consider a conducting sphere connected to a battery of voltage V. If we replace the sphere by a sphere of twice the radius, but also at the same voltage V which of the following change(s)? (choose all that apply) P V P V A. the electric field at point P B. the potential at point P C. the charge on the conductor D. the capacitance of the conductor E. none of these 3. 4. A parallel plate capacitor was used as an energy source. It was charged up, disconnected electrically, and then the plates allowed to move doing useful work. If the capacitance has been increased by a factor of 2.67 how much of the initial stored energy has been used up? A. 43% B. 25% D. 57% E. 63% C. 36% When two D batteries (1.5 V each) are connected in series with a 40 resistor, the resistor dissipates 0.2 W. What is the internal resistance of one of the D batteries? A. 1.21 B. 0.89 D. 0.67 E. 1.06 C. 0.08 5. Consider the three closed surfaces S1, S2, and S3 shown below. -2q S3 +2q S2 -q -q S1 Which surface has the greatest electric flux leaving its volume? 6. A. S1 B. S2 C. S3 D. S1 and S2 A small positive charge is placed at point P in the electric field shown below (represented by equipotential lines). Which way should the charge be moved if no work is to be done on it as it moves? 3V 2V 1V P 0V -1 V -2 V A. Along the 1 V equipotential. B. Perpendicular to the equipotential lines. C. You can't avoid doing work, unless you move the charge along the 0 V equipotential line. D. None of the above. 7. Consider the pair of charged metal spheres connected by a conducting wire shown below. The radius of sphere A is larger than that of sphere B. Which of the following quantities must be the same for both spheres? A B A. potential at the surface B. charge on the surface D. surface charge density E. more than one of the above 8. C. electric field at the surface Two identical conducting spheres, one with charge +4q and the other with charges –4q, are allowed to touch, and then they are separated. The force between the two bodies before and after contact will be A. repulsive before and attractive after contact. B. repulsive before and after contact. C. attractive before and after contact. D. attractive before and repulsive after contact. E. Attractive before contact, but no attraction or repulsive after contact. 9. The light bulbs in the circuit are identical. When the switch is closed, 15 V 10. A 12 V B 12 V A. the intensity of bulb A increases while bulb B decreases. B. the intensity of bulb A decreases while bulb B decreases. C. the intensity of bulb A increases while bulb B increases. D. the intensity of bulb A decreases while bulb B increases. E. nothing changes. A simple circuit consists of a resistor R, a capacitor C, and a battery. Immediately after the switch is thrown closed, the voltage across the capacitor is R Vo C A. Vo B. zero C. Vo/2 D. Vo/CR E. need more information 11. 12. Two copper wires have the same volume, but wire 2 is 20% longer than wire 1. The ratio of the resistances of the two wires R2/R1 is approximately A. 1.2 B. 0.83 D. 0.91 E. 1.4 C. 1.1 Charge flows through a light bulb. Suppose a wire is connected across the bulb as shown. When the wire is connected, I A. all the charge continues to flow through the bulb. B. half the charge flows through the wire, the other half continues through the bulb. C. all the charge flows through the wire. D. none of the above. III. Short Problems ( 15 marks each) 1. Draw and label the electric field lines and equipotential surfaces for the following charge distribution. +2 Q -4Q 2. Show that the voltage drop across a coaxial cable with an inner conductor of radius A surrounded by an outer annular conductor of inner radius B is given by λ A VBA ln . 2πε 0 B where is the linear charge density on the inner conducting cylinder B A (Hint: Start with Gauss' Law for a cylinder) IV. Units (2 points each) 1. Power 2. Permitivity ( ) ___________________________________ 3. Resitivity () ___________________________________ 4. Electrical Potential ___________________________________ 5. Charge __________________________________________ 6. Capacitance __________________________________________ 7. Time Constant ____________________________________ 8. Electric Field ____________________________________ 9. Electric Flux ___________________________________ 10. Resistance ____________________________________ _________________________________________