* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
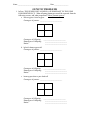
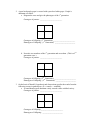
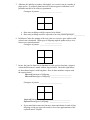
Name ____________________________________ Date ________________ GENETIC PROBLEMS 1. In Peas, THE GENES FOR TALLNESS (t) IS DOMINANT TO THE GENE FOR SHORTNESS (T). What offspring phenotypes would be expected from the following crosses, and what proportions? Show punnett squares! a. heterozygous x heterozygous Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring: Phenotypes of Offspring: Ratios: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ b. hybrid x homozygous tall Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring: Phenotypes of Offspring: Ratios: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ c. homozygous short x pure bred tall Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring: Phenotypes of Offspring: Ratios: _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ 2. A pure bred purple grape is crossed with a pure bred white grape. Purple is dominant over white. a. Diagram the cross and give the phenotypes of the 1st generation. Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring, (1st Generation):_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: (1st Generation): _______________________ b. Next take two members of the 1st generation and cross them. (This is a 2nd generation cross.) Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring, (2nd Generation):_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: (2nd Generation): _______________________ 3. On the basis of Mendel’s hypothesis and observations, predict the results from the following crosses in garden peas: (R = round, r = wrinkled) a. A round homozygous dominant variety crossed with a wrinkled variety. Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ b. The offspring of problem ‘a’ self-pollinated, (crossed with itself). Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ c. The offspring of problem ‘a’ crossed with the original round parent. Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ d. The offspring from problem ‘a’ crossed with the original wrinkled parent variety. Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ 4. If blue eye color in humans is recessive to the other colors, could: a. 2 brown-eyed parents have a blue-eyed child? __________________ b. 2 blue-eyed parents have a brown-eyed child? __________________ 5. Albinism, the inability to produce chlorophyll, is a recessive trait in a number of plant species. If a tobacco plant known to be heterozygous for albinism is selfpollinated and 600 of its seeds are germinated: Genotypes of parents: _________________________ a. How many seedling would be expected to be albino?_______________ b. How many seedlings would be expected to have the parental genotype?____________ 6. In Holstein Cattle, the spotting of the coat is due to a recessive gene while a solid colored coat is dominant. What types of offspring might be produced by a cross between two spotted animals? ___________________ Genotypes of parents: _________________________ 7. In cats, the gene for short hair is dominant over the gene for long hair, (Angora). A short-haired tomcat is mated with an Angora female. She bears eight kittens, six short-haired and two with long hairs. How do these numbers compare with the expected ratio? Observed Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Observed Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Expected Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Expected Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________ a. If you mated these same cats four more times and obtained a total of forty offspring would you expect the results to be a close approximation of the expected ration? Explain. 8. A women has a rare abnormality of the eyelids called ptosis, which makes it impossible for her to open her eyes completely. The condition has been found to depend on a single dominant gene (P). The women’s father has ptosis, but her mother had normal eyelids. Her father’s mother had normal eyelids. Use small (p) for normal. a. What are the probable genotypes of the woman, her father, and mother? i. Woman’s genotype: ____________________ ii. Her father’s genotype: ____________________ iii. Her mother’s genotype: ____________________ b. Show a pedigree, (family tree of genotypes), of the family’s traits. c. What proportion of her children will be expected to have ptosis if she marries a man with normal eyelids? Genotypes of parents: _________________________ Genotypes of Offspring:_________________________ Phenotypes of Offspring: _______________________