* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Female anatomy Teacher Key 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
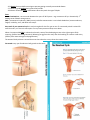
Name ___________XX_Chromosomes_____________________________ Class Period_____________________ Female Reproductive Anatomy – Teacher Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. The uterus is a muscular organ of the female reproductive system that holds a fetus during pregnancy. The woman’s sex cell is called an ovum. (also known as an egg) The ova, or eggs, are stored in organs called ovaries. The ovaries also make most of the primary female sex hormone, known as estrogen. An ovum, travels from an ovary to the uterus through a fallopian tube. The fallopian tube is not attached to the ovary. The ovum is drawn into the fallopian tube and carried toward the uterus by movements of the fallopian tubes. The lower part of the uterus, where the uterus meets the vagina, is the cervix. The vagina connects the outside of the body with the uterus. A woman’s breasts are also part of her reproductive system. (Easily digested, clean and warm, passess some immunities) Ovulation (Time a girl can get pregnant. 14th day following the 1st day of the last menstrual period) 11. Women are born with all of the ova they will ever have. (thousands of eggs in each ovary) 12. Beginning at puberty, one of the ovaries releases a mature ovum every month in a process called ovulation. 13. When the ovum is released, the fallopian tube draws the ovum into the tube. 14. Sweeping movement in the tube’s lining causes a current of fluid in the fallopian tube that carries the ovum toward the uterus. Menstruation (Period 4-5 days – discharge through the vagina from a nonpregnant uterus. Shedding of the membrane lining endometrium) 15. The lining of the uterus is called the endometrium. 16. If the ovum is fertilized by a sperm cell in the fallopian tube, the fertilized ovum will attach to the wall of the uterus and a pregnancy will begin. 17. If the ovum is not fertilized, the lining of the uterus will be shed. 18. When the lining is shed, blood & tissue leave the body through the vagina. 19. The monthly breakdown and shedding of the endometrium is called menstruation (period). 20. Ovulation and menstruation happen in a cycle that lasts about 28 days. 21. This cycle is known as the menstrual cycle. 22. The length of the menstrual bleeding can be affected by age, stress, diet, exercise, and illness. 23. Girls usually have their first menstrual period between the ages of 9 and 16. Some women have what are known as “cramps”. The cramping is caused by the contracting of the uterus to shed the lining during menstruation Problems of the female reproductive system PROBLEM DESCRIPTION Infection of the urinary tract Urinary Tract Infection Infection of the vagina by that causes itching, odor, Vaginitis Endometriosis Sexually Transmitted Diseases Toxic shock syndrome Cervical, uterine, & ovarian cancer Medical treatment required and/or discharge from the vagina Growth of tissue outside the uterus/ wrong place. Medical attention required Diseases passed one to another through sexual contact Medical treatment, abstain from sexual contact Bacterial infection caused by leaving tampons in the vagina for too long during menstruation. Uncontrolled growth of cells on the cervix, uterus, or ovaries. HPV increases chance of getting cervical cancer Immediate medical care required, change tampons every 4-6 hours Medical care required – surgery and/or chemotherapy may be required. Menopause – Ovaries stop producing eggs, produce less estrogen/progesterone Caring for the Female Body 24. Bathe everyday. 25. See a doctor regularly. PREVENTION & TREATMENT Medical treatment, antibiotics 26. Abstain from sex before marriage to prevent getting a sexually transmitted disease. 27. Maintain good hygiene during menstrual periods. 28. Women should do breast examinations when they reach the age of 30 plus. Extra Breast Examinations – once a month between the years of 30-50 years = avg. Increases at 65 yrs. Dramatically. 2nd leading cause of death among women. PMS – premenstrual syndrome, (PMS) occurs just before menstruation. It can include headaches, breast tenderness, fatigue, irritability, acne, and abnormal cramps. Keep track of your menstrual cycle. It may be irregular for the first year or two. If a menstrual period is missed for several months, or if there is severe pain or a very heavy menstrual flow, see a doctor. When a hormone called FSH is released each month, some of the developing ova are at the right stage to finish maturing. (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) (Releasing an egg from the ovary after the breaking of a mature small cavity (follicle). Also reases estrogen and progesterone) The woman’s body releases a second hormone that makes the ovary release the mature ovum. Get tested every year for abnormal cell growth on the cervix.