* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence for Evolution
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
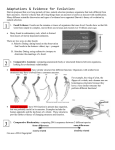
Review of Natural Selection Evidence for Evolution Evidence for Evolution Evidence for Evolution Darwin argued that living things have been evolving on Earth for millions of years. Evidence for this can be found in 1. 2. 3. 4. Fossil Records Geographic distribution of living things Homologous structure of organisms Similarities during development or (embryology) Evidence for Evolution 1. Fossil evidence provides an incomplete record of early life. Fossils can include any evidence of life, such as imprints and remains of organisms. Evidence for Evolution This evidence must be interpreted to form an overall picture of how species changed over time (evolved) By examining the fossil record, scientists have concluded that evolution happens in a simple to complex pattern and life emerged from sea to land. Evidence for Evolution Fossils must be dated to help establish a time frame for the existence of a species. There are two methods of determining the age of fossils. Evidence for Evolution In relative dating the exact age of the fossil cannot be determined, only the order of appearance as compared to other fossils found in nearby rocks. Fossils occur in layers of sedimentary rock. The fossils near the top will be more recent than fossils in lower layers of rock. Fill It In … Explanation of the fossil diagram: Evidence for Evolution Radioactive dating gives a more exact age using the natural decay of radioactive isotopes in organisms. Evidence for Evolution 2. Biochemical similarities include comparisons of DNA and the resulting amino acid sequences for certain, shared proteins. This is considered one of the most reliable and objective types of evidence used to determine evolutionary relationships. Evidence for Evolution In general, the fewer differences found between two species, the closer the evolutionary relationship. Evidence for Evolution Fill It In … Explanation of the amino acid sequence diagram: Evidence for Evolution 3. Shared anatomical structures supports some type of evolutionary relationship. Evidence for Evolution Structures with a similar bone arrangement are called homologous structures. A similar bone arrangement, even if the functions are different, supports evidence from a common ancestor. Homologous Structures Homologous Structures- different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissue Similar function Found on different species Thought to be inherited by a common ancestor Comparative Anatomy Vestigial organs- are no longer used by the organism Have shrunk in size May only be a trace left behind Why? Example- Whale Hip, Human tail bone Comparative Anatomy Analogous structure- Similar function Found in different species Inherited by a DIFFERENT ancestor Fill It In … Explanation of the bone diagram: Evidence for Evolution Structures that perform the same function (ex. flying) but are very different anatomically (ex. bird wing vs. butterfly wing) are called analogous structures. This supports evolution in similar habitats though not from a recent common ancestor Evidence for Evolution Vestigial structures (ex. Appendix or tail bone in human) are not functional in that organism, but may represent a link to a previous ancestor. Human Vestigial Organs Evidence for Evolution Fill It In … Example of vestigial structure: Embryology Embryology- is an organisms development ALL vertebrate embryos have gill pouches- thought to be inherited from a common ancestor Embryonic tissue develop in the same order http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evo lution/library/04/2/l_042_02.h tml Check Yourself! 1. Name the two methods by which fossils may be dated. 2. How do biochemical similarities support the theory of evolution? 3. What does similar bone structure (even if the function is different) suggest about two species? Check Yourself! 1. Name the two methods by which fossils may be dated. RELATIVE DATING & RADIOACTIVE DATING 2. How do biochemical similarities support the theory of evolution? 3. What does similar bone structure (even if the function is different) suggest about two species? Check Yourself! 1. Name the two methods by which fossils may be dated. RELATIVE DATING & RADIOACTIVE DATING 2. How do biochemical similarities support the theory of evolution? FEWER DIFFERENCES = CLOSER EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIP 3. What does similar bone structure (even if the function is different) suggest about two species? Check Yourself! 1. Name the two methods by which fossils may be dated. RELATIVE DATING & RADIOACTIVE DATING 2. How do biochemical similarities support the theory of evolution? FEWER DIFFERENCES = CLOSER EVOLUTIONARY RELATIONSHIP 3. What does similar bone structure (even if the function is different) suggest about two species? EVOLUTION FROM A COMMON ANCESTOR Does evolution still happen today? As long as variation, overproduction, competition, natural selection and mutations occur, evolution will occur. Because evolution leading to speciation happens over such a long period of time, speciation is not readily observable within a lab. Does evolution still happen today? Natural selection, one of the main mechanisms of evolution, is observable in some populations. For example, the evolution of resistance to chemicals: Resistance- Standard Resistance -TedTalk Does evolution still happen today? Farmers use pesticides to eliminate insects. In a population of insects, some individuals will possess genetic immunity to certain chemicals. Does evolution still happen today? When the chemicals are applied, the individuals with genetic immunity will survive and reproduce, passing this resistance to the next generation of offspring. Over time, more individuals are born with this immunity, rendering the pesticide useless. Does evolution still happen today? Antibiotics are drugs that fight bacterial infections. Within any population there is genetic variation. In the case of antibiotic resistance, some bacteria are genetically more resistant to the antibiotic than other bacteria Does evolution still happen today? If the amount of antibiotic delivered is too low or the full course not completed, only those least resistant will die. The surviving, resistant bacteria will reproduce. Does evolution still happen today? With future applications of antibiotics the population is selected to become more and more resistant. The overuse of antibiotics has led to many resistant strains of bacteria. Antibiotic resistance Brainpop- antibiotic resistance Fill It In … Definition of antibiotic resistance: CAUSE of resistance: EFFECT of resistance: CAN WE SEE EVOLUTION? 1. YES! Antibiotics are good for ridding us of bacteria but are agents of natural selection. They select out of a population the weaker bacteria while the more resilient (mutant) bacteria survive and reproduce. This can occur b/c some have medicine destroying enzymes or eat the drug as food. Some TB causing bacteria are resistant to all three drugs developed. http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evoluti on/library/10/4/l_104_07.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evoluti on/library/01/1/l_011_20.html http://www.pbs.org/wgb h/evolution/library/10/4/l _104_09.html Check Yourself! 1. What is a pesticide? 2. Why do some insects become resistant to pesticides? 3. What is an antibiotic? 4. What has led to the many resistant strains of bacteria? Check Yourself! 1. What is a pesticide? CHEMICAL USED TO ELIMINATE PESTS 2. Why do some insects become resistant to pesticides? 3. What is an antibiotic? 4. What has led to the many resistant strains of bacteria? Check Yourself! 1. What is a pesticide? CHEMICAL USED TO ELIMINATE PESTS 2. Why do some insects become resistant to pesticides? SOME POSSESS GENETIC IMMUNITY TO CERTAIN CHEMICALS 3. What is an antibiotic? 4. What has led to the many resistant strains of bacteria? Check Yourself! 1. What is a pesticide? CHEMICAL USED TO ELIMINATE PESTS 2. Why do some insects become resistant to pesticides? SOME POSSESS GENETIC IMMUNITY TO CERTAIN CHEMICALS 3. What is an antibiotic? DRUG THAT FIGHTS BACTERIAL INFECTIONS 4. What has led to the many resistant strains of bacteria? Check Yourself! 1. What is a pesticide? CHEMICAL USED TO ELIMINATE PESTS 2. Why do some insects become resistant to pesticides? SOME POSSESS GENETIC IMMUNITY TO CERTAIN CHEMICALS 3. What is an antibiotic? DRUG THAT FIGHTS BACTERIAL INFECTIONS 4. What has led to the many resistant strains of bacteria? THE OVERUSE OF ANTIBIOTICS