* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download S1 Photosynthesis and Biodiversity WYSK
Survey
Document related concepts
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
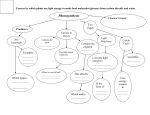
What You Should Know: Photosynthesis and Biodiversity Photosynthesis: Write a word equation for the process of photosynthesis and state that it is carried out in green plants. Light Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen Chlorophyll Water is taken in at the roots of the plant. Carbon dioxide is taken into the leaves of the plant through tiny holes called stomata. The green coloured chemical chlorophyll can absorb the energy of the sun light and uses this energy to make food molecules. Glucose is produced during photosynthesis and is converted into starch (which can be stored in the plant). Oxygen is released as a by-product. Testing a green leaf for starch: 1. 2. 3. Boil the leaf in water to break open the cells. Heat the leaf in alcohol in a test tube in the hot water to take the green coloured chlorophyll out of the leaf. Rinse the leaf and drop some iodine onto the leaf. If the iodine turns black this shows starch is present. Green plants depend on photosynthesis to make the food that gives them energy for life. Animals also depend on photosynthesis because they either eat plants or eat other animals which eat plants. Animals also depend on the oxygen that plants make. Biotic and Abiotic factors All living things are affected by things in the environment that can have a positive of negative affect on their survival chances. These are called biotic or abiotic factors. Biotic factors are living factors present in an ecosystem, which can affect a living organism’s survival. These include availability and competition for food, number of predators and diseases. Abiotic factors are non-living factors present in an ecosystem, which can affect living organisms’ distribution and survival. These include light intensity, temperature, moisture, pH, wind speed and oxygen content. Light intensity is measured by a light meter. Ensure no shadows are cast over the meter during measuring. Moisture is measured by a moisture meter. Ensure the probe is wiped clean between uses. Temperature is measured by a thermometer. Ensure thermometer is given time to settle before reading. The effect of Abiotic factors on organism distribution Some plants need high levels of light to grow and can not grow in shaded areas Other plants grow best in shaded area because there is less competition. Some organisms can not survive in acidic conditions. Some organisms like woodlice, need to live in moist conditions Biodiversity Biodiversity is a measure of the the variety of life on Earth and the essential interdependence of all living things Some habitats are more biodiverse than others e.g. the Amazon rainforest is more biodiverse than the Sahara desert. Scientists have identified more than 2 million species. Tens of millions remain unknown The tremendous variety of life on Earth is made possible by complex interactions among all living things including microscopic species like bacteria, algae and mites. Sampling We can measure how much biodiversity there is in a habitat by counting both the number of different species in the environment and how many individual animals or plant there are of each species. We do this by sampling. There are many ways of sampling in different habitats. Two examples are quadrats and pitfall traps: Quadrats Quadrats are squares used to estimate numbers of small ground living plants in an area. To find the how many plants of one (i.e. daisies) type are in a field. A quadrat is placed at several random sites in the field. We then count the number of squares that daisies are in. Not the individual daisies Pitfall Traps Soil level Beaker Pitfall traps are generally very simple traps dug into the earth. Pitfall traps catch small organisms, which are active on the ground. Camouflage such as leaves are used to cover the top of the cup/beaker at the soil surface allowing the organisms to fall into the trap unsuspectingly.