* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit1-KA3-Revision
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
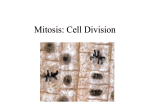
Unit1-Key area 3- Producing new cells 1-State the function of cell division 2-State the biological name for cell division 3-State what is the store of hereditary information? 4-What is meant by “chromosome complement”? 5-Describe how the daughter cells compare to the original cell 6-Explain why it is important that the chromosome complement of daughter cells in multi-cellular organisms is maintained To increase the number of cells in an organism so that growth and cell replacement/repair can take place. Mitosis Chromosomes, DNA Number of chromosomes characteristic to a species, e.g. humans have 46 chromosomes They have an identical set of chromosomes which carry the same information as the original cell. To obtain two identical sets of chromosomes, the genetic material contained in a nucleus is replicated (copied) before mitosis. If not, cells might die or grow and/or function abnormally. 1-Chromatids 2-Centromere (Keeps the chromatids together) 7 8-Recognise the stages of mitosis in an animal cell and in a plant cell 1- Duplicated chromosomes get shorter and fatter. The cell is ready for mitosis. 2- Chromosome are attached to spindle fibres at the centromere and positioned at the equator (plane at the centre of the cell). They can be seen to be made of two chromatids. 3- Spindle fibres contract, chromatids are pulled apart towards opposites poles. 4- Two nuclei form at each end of the cell 5- The cytoplasm starts to divide 6- Two daughter cells are formed Same as above except for 5: 5- New cell wall forms on a plane at the centre of a cell. What is meant by a “diploid cell” Diploid cells have two matching sets of chromosomes. Cell culture 1-Why is cell culture done? 2-What is needed for cell culture? 3-Explain how glassware can be sterilised 4-Explain how hands and surfaces need to be prepared before an experiment. 5-Explain how microbes can be prevented to contaminate an opened petri dish 6-Explain how the inoculating can be sterilized? 7-Why are lids held onto inoculated petri dishes with tape - Make food & drink (e.g. beer, wine). - Test antibiotic, vaccines, medicine. - Aseptic techniques. - Appropriate medium . - Control of other factors (e.g. availability of oxygen, temperature, pH). Heat glassware in an autoclave (pressure cooker) to 121oC. - Hands need to be washed before an experiment to remove microorganisms from skin. - Surfaces are disinfected before and after experiment to kill microbes on work area. Hold the lid over an opened petri dish. Flame the inoculating loop. To prevent entry OR exit of microbes from agar.