* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reconstruction Notes
Fourteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
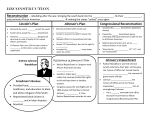
Reconstruction Notes Three Plans I. Reconstruction: Rebuilding the south economically and politically II. Issues A. How to help newly freed slaves B. How should former Confederate states be let back into the Union C. Replacing the Plantation System III. Abraham Lincoln’s Plan A. Lincoln wanted to be lenient toward the former Confederate states B. He wanted to heal the wounds of the Civil War as quick as possible C. Lincoln’s Plan 1. Statehood: As soon as 10% of a former Confederate States population swore an oath of allegiance to the U.S. they could set up a new state government. IV. Assassination of Abraham Lincoln A. John Wilkes Booth was a popular actor and Confederate spy. During the war, he originally tried to kidnap President Lincoln in a plan to exchange him for Confederate prisoners of war. His plan failed when Lincoln took a different road then where Booth and his fellow conspirators were waiting. When the war end Booth decided to try to assassinate Lincoln. He shot Lincoln while he was attending a play at Ford’s Theater. He and his fellow conspirators were later captured and executed. V. Andrew Johnson’s Plan A. Johnson was a Southern Democrat from Tennessee who had remained loyal to the Union during the Civil War. B. Northern Republicans controlled Congress. C. The Republicans wanted to punish the South for the Civil War. D. Johnson’s Plan 1. Pardoned all Southerners willing to take an oath of allegiance 2. A majority (over 51%) of voters would need to swear an oath of loyalty to the Union 3. State would need to ratify the 13th Amendment in order to rejoin the Union. 4. 13th Amendment 1865– Made Slavery Illegal VI. Radical Reconstruction A. Outrage by Johnson’s lenient treatment of the South the North elected over a 2/3 majority Radical Republicans to Congress. 1 B. With control over Congress the Radical Republican pushed through their own plan of reconstruction. With over a 2/3 majority in both houses they could override any presidential vetoes. C. The Republican Congress gets so fed up with Johnson that they impeach him and put him on trial in the Senate. Johnson wins the impeachment trial by one vote. 1. Impeach – to charge with wrong doing D. Republican Plan 1. Military Reconstruction Act –The law divided the south into five military districts. 2. No state could be readmitted to the Union with out creating a new constitution that guaranteed suffarage (right to vote) to African Americans. 3. They states also had to ratify the 14th Amendment. 4. 14th Amendment 1866– Gave African Americans citizenship and equal protection under the law. 5. Former confederate Soldiers could not hold an elected office VII. President Ulysses S. Grant A. Grant won the election of 1868. His administration was one of the most corrupt in history. B. Hiram Revels & Blanch Bruce were the first African Americans elected to the U.S. Senate. C. 15th Amendment 1870 – All men (over 21) were granted the right to vote. No state could deny any man the right to vote due to race, religion, or previous condition of servitude. D. Many Southern States got around the 15 Amendment by using literacy tests and poll taxes. 1. Literacy Test- People would have to pass a test in order to be allowed to vote. 2. Poll Tax – People would have to pay a tax in order to vote. 3. Grandfather Clause – Gave people the right to vote if their grandfathers voted. Even if they could not pass the literacy test or pay the poll tax. This law allowed many poor white southerners to vote. VIII. Effects of Reconstruction A. Political Changes: “The Solid South” -The southern states become loyal to the Democratic Party, which supported segregation. B. Social Changes: Southern Whites deny African Americans their rights 1. Black Codes – laws passed in the south to keep African Americans in a slave like role 2 2. KKK – The Klu Klux Klan – A secret organization founded in 1866 to intimidate freed slaves through threats and acts of violence. Their goal was to prevent African Americans from voting. C. Economic Changes: The plantation system was replaced with sharecropping. 1. Sharecropping- A system in which a farmers rented a piece of property and agreed to give part of their crops (usually 1/2) to a Land Lord. They often borrowed money from the Land Lord to buy seeds, tools, and other equipment. If they did not grow enough food they sunk into debt owing the landlord money. 2. Industry started to develop in the South 3