* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download I. Introduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
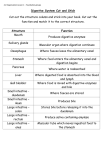
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole’s Human Anatomy and Physiology, 10 th ed. Chapter 17: Digestive System Chapter 17: Digestive System I. Introduction A. Digestion is ___________________________________________________________ B. Mechanical digestion breaks ______________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ C. Chemical digestion breaks _______________________________________________ D. The organs of the digestive system carry out the processes of ____________________ ________________________________________________________________________ E. The alimentary canal is composed of _______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ F. The accessory organs of the digestive system are ______________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ II. General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Introduction 1. The alimentary canal is a _______________________ tube that passes through __________________________________________________________________ 2. The structure of __________________, how it ___________________ , and its innervation are similar _______________________________________________ B. Structure of the Wall 1. The four layers of the alimentary wall are ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The mucosa is located ________________________________________ and is composed of _______________________________________________________ 3. The functions of the mucosa are _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The submucosa is located _____________________________________ and is composed of _______________________________________________________ 17-1 5. The functions of the submucosa are___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. The muscular layer is located __________________________________ and is composed of _______________________________________________________ 7. When the circular fibers contract, the diameter of the tube _________________ 8. When the longitudinal fibers contract, the tube __________________________ 9. The serosa layer is located _____________________________________ and is composed of _______________________________________________________ 10. The functions of the serosa are _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Movements of the Tube 1. The two types of motor functions of the alimentary canal are ______________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Mixing occurs when _______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Peristalsis is _____________________________________________________ 4. Peristalsis occurs when ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ D. Innervation of the Tube 1. Branches of _____________________________________________ innervate the alimentary canal. 2. The innervation of the alimentary canal maintains _______________________ and regulates _______________________________________________________ 3. The submucosal plexus is important for _______________________________ 4. The myenteric plexus is important for _________________________________ 5. The functions of parasympathetic impulses are __________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. The functions of sympathetic impulses are _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-2 III. Mouth A. Introduction 1. The functions of the mouth are ______________________________________ 2. Mastication is ____________________________________________________ 3. The mouth is surrounded by ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The oral cavity is _________________________________________________ 5. The vestibule of the mouth is ________________________________________ B. Cheeks and Lips 1. The cheeks form _______________________________________________ and consist of __________________________________________________________ 2. The lips surround ______________________________________________ and consist of __________________________________________________________ 3. The reddish color of lips is due to ____________________________________ C. Tongue 1. The tongue is located ______________________________________________ 2. _______________________________________ membranes cover the tongue. 3. The frenulum of the tongue is _______________________________________ 4. The body of the tongue is composed of ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Muscles of the tongue function to ____________________________________ 6. Papillae of the tongue are ___________________________________________ 7. Functions of papillae are ___________________________________________ 8. The root of the tongue is anchored to _________________________________ 9. Lingual tonsils are located __________________________________________ D. Palate 1. The palate forms ______________________________________________ and consists of _________________________________________________________ 2. The hard palate is formed by ________________________________________ 3. The soft palate is formed by_________________________________________ 4. The uvula is _____________________________________________________ 17-3 5. The function of the uvula is _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. Palatine tonsils are located __________________________________________ 7. Pharyngeal tonsils are located _______________________________________ E. Teeth 1. The primary teeth are ______________________________________________ 2. The secondary teeth are ____________________________________________ 3. The secondary teeth consist of _______________________________________ 4. The arrangement of secondary teeth are _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Wisdom teeth are _________________________________________________ 6. Chewing increases ________________________________________________ 7. Incisors are specialized to __________________________________________ 8. Cuspids are specialized to __________________________________________ 9. Bicuspids and molars are specialized to _______________________________ 10. The crown of a tooth is ___________________________________________ 11. The root of a tooth is _____________________________________________ 12. The neck of a tooth is _____________________________________________ 13. Enamel consists of _______________________________________________ 14. Dentin is _______________________________________________________ 15. The root canal is located _______________________________________ and contains ___________________________________________________________ 16. The pulp cavity is located ______________________________________ and contains ___________________________________________________________ 17. Cementum is ___________________________________________________ 18. A periodontal ligament is __________________________________________ IV. Salivary Glands A. Introduction 1. Salivary glands secrete _____________________________________________ 2. The functions of saliva are __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-4 3. The three pairs of major salivary glands are ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ B. Salivary Secretions 1. Two cell types of salivary glands are __________________________________ 2. Serous cells produce ______________________________________________ 3. Mucous cells produce _____________________________________________ 4. Amylase digests __________________________________________________ 5. Salivary glands are innervated by both ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. Sympathetic fibers stimulate the glands to _____________________________ 7. Parasympathetic fibers stimulate the glands to __________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Major Salivary Glands 1. The largest of the major salivary glands is _____________________________ 2. The parotid glands are located _______________________________________ 3. A parotid duct is located ___________________________________________ 4. The parotid glands secrete __________________________________________ 5. The submandibular glands are located _________________________________ 6. The submandibular glands secrete ____________________________________ 7. Ducts of submandibular glands open __________________________________ 8. The sublingual glands are located ____________________________________ 9. The sublingual glands secrete _______________________________________ 10. The ducts of sublingual glands open _________________________________ V. Pharynx and Esophagus A. Introduction 1. The pharynx is ___________________________________________________ 2. The pharynx and esophagus function in _______________________________ B. Structure of the Pharynx 1. The pharynx connects _____________________________________________ 2. The three divisions of the pharynx are _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-5 3. The nasopharynx is located _________________________________________ 4. The nasopharynx provides __________________________________________ 5. The oropharynx is located __________________________________________ 6. The oropharynx is a passageway for __________________________________ 7. The laryngopharynx is located _______________________________________ 8. The laryngopharynx is a passageway to _______________________________ 9. Constrictor muscles function to ______________________________________ C. Swallowing Mechanism 1. The events of the first stage of swallowing are __________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The events of the second stage of swallowing are ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The events of the third stage of swallowing are _________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The actions of the swallowing reflex are _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ D. Esophagus 1. The esophagus is a passageway for ___________________________________ 2. The esophagus propels food from _______________ to the ________________ 3. The esophagus descends through _____________________________________ 4. The esophageal hiatus is ___________________________________________ 5. ___________ glands are scattered throughout the submucosa of the esophagus. 6. The lower esophageal sphincter is located___________________________ and functions to ________________________________________________________ VII. Stomach A. Introduction 1. The shape of the stomach is _________________________________________ 2. The location of the stomach is _______________________________________ 3. Rugae are _______________________________________________________ 17-6 4. The functions of the stomach are _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ B. Parts of the Stomach 1. The four parts of the stomach are ____________________________________ 2. The cardiac region is ______________________________________________ 3. The fundic region is _______________________________________________ 4. The body of the stomach is _________________________________________ 5. The pyloric region is ______________________________________________ 6. The pyloric sphincter is located ___________________________________ and functions to ________________________________________________________ C. Gastric Secretions 1. Gastric pits are ___________________________________________________ 2. The three cell types of gastric glands are _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Mucous cells secrete ______________________________________________ 4. Chief cells secrete ________________________________________________ 5. Parietal cells secrete _______________________________________________ 6. Gastric juice is ___________________________________________________ 7. Pepsin is ________________________________________________________ 8. The function of pepsinogen is _______________________________________ 9. The function of hydrochloric acid in the stomach is ______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 10. The coating of the stomach is important for ___________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 11. The function of intrinsic factor is _____________________________ D. Regulation of Gastric Secretions 1. Somatostatin is produced ________________________________________ and functions to ________________________________________________________ 2. Parasympathetic innervation stimulates ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-7 3. Gastrin is produced ____________________________________________ and functions to ________________________________________________________ 4. The three stages of gastric secretion are _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. The events of the cephalic phase are __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. The events of the gastric phase are ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 7. The events of the intestinal phase are _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. Cholecystokinin is produced _____________________________________ and functions to ________________________________________________________ E. Gastric Absorption 1. The stomach absorbs ______________________________________________ 2. Most nutrients are absorbed in _______________________________________ F. Mixing and Emptying Actions 1. A stomachache results from _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Chyme is _______________________________________________________ 3. Peristaltic waves push chyme _______________________________________ 4. Stomach contractions push chyme a little at a time into ________________ and backwards into ______________________________________ , mixing it further. 5. The lower esophageal sphincter prevents ______________________________ 6. The rate at which the stomach empties depends on _______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 7. ________________________________ usually pass first through the stomach. 8. The enterogastric reflex is __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 9. Vomiting results from _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-8 VIII. Pancreas A. Structure of the Pancreas 1. The pancreas is located ____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Pancreatic acinar cells produce ___________________________________ and make up the ________________________________________________________ 3. Acini are ________________________________________________________ 4. The pancreatic ducts extends ________________________________________ __________________________ and empties into _________________________ 5. Hepatopancreatic ampulla is ________________________________________ 6. The hepatopancreatic sphincter is ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ B. Pancreatic Juice 1. Pancreatic juice contains ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The function of pancreatic amylase is _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The function of pancreatic lipase is ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The functions of trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase are __________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Zymogen granules are _____________________________________________ 6. The function of trypsinogen is _______________________________________ 7. The functions of nucleases are _______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Regulation of Pancreatic Secretion 1. Parasympathetic fibers cause the pancreas to ___________________________ 2. The function of secretin is __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The release of cholecystokinin is triggered by __________________________ 17-9 4. The action of cholecystokinin on the pancreas is ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ IX. Liver A. Introduction 1. The largest internal organ is the ______________________________________ 2. The liver is located ________________________________________________ B. Liver Structure 1. The two large lobes of the liver are ___________________________________ 2. The falciform ligament is __________________________________________ ` __________________________________________________________________ 3. The two small lobes of the liver are ___________________________________ 4. The porta hepatic is _______________________________________________ 5. The coronary ligament is ___________________________________________ 6. Hepatic lobules are ________________________________________________ 7. A hepatic lobule consists of _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. Hepatic sinusoids are ______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 9. Kupffer cells are __________________________________________________ 10. Bile canals are __________________________________________________ 11. Hepatic ducts are formed from _____________________________________ C. Liver Functions 1. The liver carries on many important __________________________ functions. 2. The liver plays a key role in carbohydrate metabolism by _________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The liver plays a key role in lipid metabolism by ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The liver plays a key role in protein metabolism by ______________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. The liver stores ___________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-10 6. Liver cells help destroy ____________________________________________ 7. The liver removes ____________________________________________ from the blood. 8. The liver’s role in digestion is _______________________________________ D. Composition of Bile 1. Bile is secreted by ________________________________________________ 2. Bile contains_____________________________________________________ 3. Hepatic cells use __________________________________ to make bile salts. 4. Bile pigments are products of _______________________________________ 5. Jaundice results from ______________________________________________ E. Gallbladder 1. The gallbladder is located __________________________________________ 2. The cystic duct is ______________________________________________ and opens into _________________________________________________________ 3. The common bile duct is formed from ________________________________ _______________________ and opens into _____________________________ 4. Gallstones form when _____________________________________________ F. Regulation of Bile Release 1. Cholecystokinin triggers the gallbladder to _____________________________ 2. Cholecystokinin is released in response to _____________________________ G. Functions of Bile Salts 1. Functions of bile salts are __________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Emulsification is _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Lack of bile salts results in__________________________________________ X. Small Intestine A. Introduction 1. The small intestine extends from _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The small intestine receives secretions from ____________________________ 17-11 __________________________________________________________________ 3. The functions of the small intestine are ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ B. Parts of the Small Intestine 1. The three parts of the small intestine are _______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The duodenum is located ___________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The jejunum is located _____________________________________________ 4. The ileum is located ________________________________________ 5. Mesentery is __________________________________________________ and supports ___________________________________________________________ 6. The greater omentum is ____________________________________________ 7. The functions of the omentum are ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Structure of the Small Intestinal Wall 1. The velvety appearance of the inner wall of the small intestine is due to ______ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Intestinal villi are _________________________________________________ 3. The functions of villi are ___________________________________________ 4. Each villus consists of _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. A lacteal is ______________________________________________________ 6. Microvilli increase ________________________________________________ 7. Intestinal glands are _______________________________________________ 8. Plicae circulares are _______________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ D. Secretions of the Small Intestine 1. Brunner’s glands are ____________________ and are located _____________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. Brunner’s glands secrete ___________________________________________ 17-12 3. The enzymes secreted by epithelial cells of the small intestine are ___________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The functions of peptidases are ______________________________________ 5. The functions of sucrase, maltase, and lactase are________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. The functions of intestinal lipase are __________________________________ E. Regulation of the Small Intestinal Secretions 1. ____________________________________________ stimulate the duodenal mucous glands to release large amounts of mucus. 2. Chyme stimulates _________________________________________________ 3. Distension of the intestinal wall stimulates _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ F. Absorption in the Small Intestine 1. The most important absorbing organ is the _____________________________ 2. Carbohydrate digestion begins ____________________________________ and is completed _______________________________________________________ 3. Monosaccharides are absorbed by ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. Protein digestion begins _________________________________________ and is complete ________________________________________________________ 5. Amino acids are absorbed by ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. Fat molecules are digested almost entirely by ___________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 7. Chylomicrons are _________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. Chylomicrons are carried to the blood by ______________________________ 9. The ions absorbed by the intestinal villi are ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 10. Water is absorbed by _____________________________________________ G. Movements of the Small Intestine 17-13 1. Segmentation is __________________________________________________ 2. Chyme moves______________________________ through the small intestine. 3. Parasympathetics enhance ____________________________ and sympathetics __________________________________________________________________ 4. A peristaltic rush is _______________________________________________ 5. Diarrhea results from ______________________________________________ 6. The ileocecal sphincter joins ________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ XI. Large Intestine A. Introduction 1. The large intestine is located ________________________________________ 2. The functions of the large intestine are ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ B. Parts of the Large Intestine 1. The parts of the large intestine are ____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The cecum is ____________________________________________________ 3. The vermiform appendix is located ________________________________ and consists of _________________________________________________________ 4. The four parts of the colon are _______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. The ascending colon is located ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 6. The transverse colon is located ______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 7. The descending colon is located _____________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. The sigmoid colon is ______________________________________________ 9. The rectum is ____________________________________________________ 10. The anal canal is_________________________________________________ 11. Anal columns are ________________________________________________ 17-14 12. The anus is _____________________________________________________ 13. Two sphincters of the anus are______________________________________ 14. The internal anal sphincter is composed of ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 15. The external anal sphincter is composed of ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ C. Structure of the Large Intestinal Wall 1. Teniae coli are ___________________________________________________ 2. Haustra are ______________________________________________________ 3. Epiploic appendages are ___________________________________________ D. Functions of the Large Intestine 1. Mucus secretion into the large intestine is controlled by ___________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The functions of mucus in the large intestine are ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. Chyme entering the large intestine contains ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. The large intestine can absorb _______________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. Intestinal flora is _________________________________________________ 6. The functions of intestinal flora are ___________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ E. Movements of the Large Intestine 1. The movements of the large intestine are _____________________ than those of the small intestine. 2. Mass movements are produced when _________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. The defecation reflex is triggered by __________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 17-15 4. The actions of the defecation reflex are ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. A person can inhibit defecation by ___________________________________ F. Feces 1. Feces are composed of _____________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 2. The pungent odor or feces results from ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ XII. Life-Span Changes A. Maintaining healthy teeth requires _________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ B. The effects of aging on teeth include _______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ C. Dry mouths in elderly people is usually a result of _____________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ D. Frequent heartburn may be the result of _____________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ E. Effects of aging on the small intestine include ________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ F. The effects of aging on the large intestine include _____________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ G. The effects of aging on the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder include _______________ ________________________________________________________________________ 17-16