* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
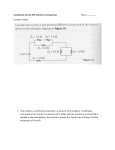
Download 1) Two identical aluminum objects are insulated from their
History of the battery wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
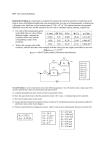
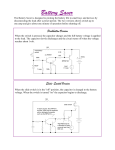
Physics Review Chapters 25 – 28 Name: _____________________ 1) Two identical aluminum objects are insulated from their surroundings. Object A has a net charge of excess electrons. Object B is grounded. Which object is at a higher potential? A) A B) B C) Both are at the same potential. D) cannot be determined without more information 2) For a proton moving in the direction of the electric field A) its potential energy increases and its electric potential decreases. B) its potential energy decreases and its electric potential increases. C) its potential energy increases and its electric potential increases. D) its potential energy decreases and its electric potential decreases. 3) A small charged ball is accelerated from rest to a speed v by a 500 V potential difference. If the potential difference is changed to 2000 V, what will the new speed of the ball be? A) v B) 2v C) 4v D) 16v 4) An equipotential surface must be A) parallel to the electric field at any point. B) perpendicular to the electric field at any point. C) Could be both of these. D) There is no specific direction. 5) The net work done in moving an electron from point A, where the potential is -50 V, to point B, where the potential is +50 V, is A) +1.6 × 10-17 J. B) -1.6 × 10-17 J. C) zero. D) none of the given answers 6) A 6.0-V battery maintains the electrical potential difference between two parallel metal plates separated by 1.0 mm. What is the electric field between the plates? A) 6.0 V/m B) 600 V/m C) 6000 V/m D) zero 7) How much energy is necessary to place three charges, each of 2.0 μC, at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 2.0 cm? A) 4.5 J B) 5.4 J C) 6.7 J D) 7.6 J 8) The resistance of a wire is A) proportional to its length and its cross-sectional area. B) proportional to its length and inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area. C) inversely proportional to its length and proportional to its cross-sectional area. D) inversely proportional to its length and its cross-sectional area. 9) Consider two copper wires. One has twice the length of the other. How do the resistivities of these two wires compare? A) Both wires have the same resistivity. B) The longer wire has twice the resistivity of the shorter wire. C) The longer wire has four times the resistivity of the shorter wire. D) none of the given answers 10) A coffee maker, which draws 13.5 A of current, has been left on for 10 min. What is the net number of electrons that have passed through the coffee maker? (e = 1.6x10 A) 1.5 × 1022 B) 5.1 × 1022 C) 1.8 × 103 D) 8.1 × 103 19 C) 11) A 110-V hair dryer is rated at 1200 W. What current will it draw? A) 0.090 A B) 1.0 A C) 11 A D) 12 A 12) A toaster is rated 800 W at 120 V. What is the resistance of its heating element? A) 16 Ω B) 18 Ω C) 6.7 Ω D) 0.15 Ω 13) Four 16 μF capacitors are connected in series. The equivalent capacitance of this combination is A) 64 μF. B) 16 μF. C) 8.0 μF. D) 4.0 μF 14) 1.0 μF, 2.0 μF, and 3.0 μF capacitors are connected in parallel across a 24-V battery. How much energy is stored in this combination when the capacitors are fully charged? A) 1.7 mJ B) 2.1 mJ C) 4.8 mJ D) 7.1 mJ 15) Two capacitors of 6.00 μF and 8.00 μF are connected in parallel. The combination is then connected in series with a 12.0V battery and a 14.0-μF capacitor. What is the voltage across the 6.00-μF capacitor? A) 4.00 V B) 5.00 V C) 6.00 V D) 12.0 V 16) A 2.0-μF capacitor is charged through a 50-kΩ resistor. How long does it take for the capacitor to reach 90% of full charge? A) 0.90 s B) 0.23 s C) 2.2 s D) 2.3 s 17. Points R and S are each the same distance d from two unequal charges, +Q and +2Q, as shown above. The work required to move a charge -Q from point R to point S is (A) dependent on the path taken from R to S (B) directly proportional to the distance between R and S (C) positive ( D) zero (E) negative 18. The five resistors shown below have the lengths and cross-sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same resistivity. Which has the greatest resistance? Questions 19-21 The batteries in each of the circuits shown above are identical and the wires have negligible resistance. 19. In which circuit is the current furnished by the battery the greatest? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 20. In which circuit is the equivalent resistance connected to the battery the greatest? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 21. Which circuit dissipates the least power? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Questions 22-24 refer to the circuit shown below. Assume the capacitor C is initially uncharged. The following graphs may represent different quantities related to the circuit as functions of time t after the switch S is closed 22. Which graph best represents the voltage versus time across the resistor R ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 23. Which graph best represents the current versus time in the circuit? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 24. Which graph best represents the voltage across the capacitor versus time? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)









![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)