* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Down
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
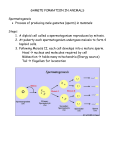
Unit # 4: Genetics Review Guide 1. Who is considered the “Father of Genetics”? What type of plant did he study? 2. How did Mendel set up his experiment, starting with the P1 generation to the F2 generation? 3. What does “true-breeding” mean? 4. Summarize Mendel’s 4 principles. 5. Be able to solve monohybrid and dihybrid story problems! a. What are the steps to solving dihybrid story problems? 6. Give 3 examples to show how dominant traits don’t necessarily mean that they are more prevalent in the population. 7. What are the 4 blood types? 8. For each blood type, know: a. The type of antigen (protein) present d. What type they can donate blood to b. Possible genotypes e. What type they can receive blood from c. Antibodies found 9. 10. 11. 12. What is the rH factor? Why is it important during pregnancy? What blood type is the universal donor? Why? What blood type if the universal recipient? Why? What is the most common blood type? Least common? Describe the following: a. Incomplete dominance (and give an d. Polygenic traits (give an example) example) e. Homologous chromosomes b. Codominance (give an example) f. Haploid (what type of cells are haploid) c. Multiple alleles (give an example) g. Diploid (what type of cells are diploid) 13. What is meiosis? 14. Know the steps of meiosis I and II. Be able to match drawings with descriptions. What is the end result of meiosis I? What is the end of meiosis II? 15. Complete the chart below: Mitosis Meiosis Is the original parent cell haploid or diploid? How many daughter cells are produced? ____sperm cell(s) are formed in males; ____egg cell(s) are formed in females. Are the daughter cells haploid or diploid? Are the daughter cells identical to the parent cell? yes or no Are the daughter cells identical to each other? yes or no What type of cell does this occur in? somatic or sex cells 16. How many viable sperm cells are created during meiosis? How many viable egg cells are created during meiosis? 17. What are polar bodies? How many form during female meiosis? 18. What is gametogenesis? a. What is oogenesis? Spermatogenesis? b. Explain how the egg cell in a female and a sperm cell in the male develop prior to the child’s birth. c. Explain what happens to the egg and sperm once the child reaches puberty. 19. Define the following words: a. Genotype c. Homozygous b. Phenotype d. Heterozygous 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. e. Segregation g. Punnett square f. Allele What is a karyotype? Be able to interpret a karyotype: a. What is the sex of the child? b. Label the autosomes. Label the sex chromosomes. c. Does the child display any disorders such as: i. Down Syndrome (trisomy 21) ii. Klinefelter Syndrome (47, XXY) iii. Turner Syndrome (45, X) iv. XYY Syndrome v. Trisomy X What is a pedigree? a. Be able to draw a pedigree based on given information. b. Be able to interpret a pedigree. Describe autosomal dominant genetic disorders. Be able to show how this type of disorder is passed on to offspring using a Punnett square. Describe autosomal recessive genetic disorders. Be able to show how this type of disorder is passed on to offspring using a Punnett square. Describe X-linked disorders. Be able to show how this type of disorder is passed on to offspring using a Punnett square. Refer to your poster about Genetic Disorders. Be able to match VERY general characteristics, causes, treatments, etc. to its appropriate genetic disorder. This will be matching on the test.