* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INTO THE PAGE
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear drip line wikipedia , lookup
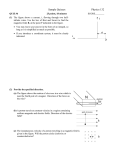
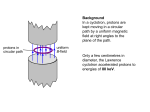
PHYS-1100 PHYSICS I QUIZ 3 APRIL 27, 2000 NAME ______________________________ INSTRUCTOR _________________ SEC #___ There are 5 different pages in this quiz. Check now to see that you have all of them. CREDIT PART A 40% PART B 20% PART C 40% TOTAL 100% GRADE All work and answers must be given in the spaces provided on these pages. PART A. Each question is worth 5%. In the space provided, to the left of the question number, write the letter corresponding to the best answer to the question. ___1. A projectile is fired straight upward from Earth’s surface with a speed that is half the escape speed. If R is the radius of Earth, and air resistance is ignored, the greatest distance from the center of Earth that the projectile will reach is: A. 5R/4 B. 4R/3 C. 3R/2 D. 2R E. 4R ___ 2. A planet travels in an elliptical orbit about a star as shown. At what pair of points is the speed of the planet the same? A. W and S B. P and T E. need to know where the star is C. P and R D. Q and U ___ 3. A positively charged insulating rod is brought close to an object that is suspended by a string. If the object is attracted toward the rod we can conclude: A. the object is positively charged D. the object is a conductor B. the object is negatively charged E. none of the above C. the object is an insulator 1 NAME ______________________________ INSTRUCTOR _________________ SEC #___ ___ 4. Two point charges are arranged as shown. In which region(s) is there a point, at a finite distance from the charges, where the net electric field due to the two charges is zero? A. I only B. II only C. III only D. I and III only E. II and III only ___ 5. In a region where the potential is not constant, a positively charged particle will be accelerated: A. from high potential to low potential D. some other direction B. from low potential to high potential E. there will be no electrostatic force C. tangent to an equipotential surface ___ 6. The figure below shows the path of an electron (with a negative charge) that passes through two regions containing uniform magnetic fields of magnitudes B1 and B2. Its path in each region is a half-circle. The directions of the two fields are: A. Both B1 and B2 are directed into the page. B. Both B1 and B2 are directed out of the page. C. B1 is directed into the page and B2 is directed out of the page. D. B1 is directed out of the page and B2 is directed into the page. E. There is no way to tell the directions of the fields. ___7. A uniform magnetic field is directed into the page. A charged particle, moving in the plane of the page, follows a clockwise spiral of decreasing radius as shown. A reasonable explanation is: A. B. C. D. E. The charge is positive and slowing down. The charge is negative and slowing down. The charge is positive and speeding up. The charge is negative and speeding up. None of the above. ___8. Two computer programs that are used in Physics I are WebCT, and WebAssign. Choose the correct statement concerning these programs. F. Both programs are Microsoft products. F. WebCT is used for homework and WebAssign is used for class quizzes. F. WebAssign is used for homework and WebCT is used for class quizzes. F. They are really the same program. F. I hate both programs. 2 NAME ______________________________ INSTRUCTOR _________________ SEC #___ PART B. 1. (20%)A satellite of mass m is placed in a circular orbit about Earth. The radius of the orbit is 2R where R is the radius of Earth (R = 6.37 × 106 m). A rocket then moves the satellite to a new orbit of radius 4R. a) (4%) In which orbit is the period of the satellite greater? (Circle the correct answer.) THE PERIOD IS GREATER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 2R THE PERIOD IS GREATER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 4R THE PERIOD IS THE SAME IN BOTH ORBITS b) (4%) In which orbit is the kinetic energy of the satellite higher (more positive)? (Circle the correct answer.) THE KINETIC ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 2R THE KINETIC ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 4R THE KINETIC ENERGY IS THE SAME IN BOTH ORBITS c) (4%) In which orbit is the potential energy of the satellite higher (more positive)? (Circle the correct answer.) THE POTENTIAL ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 2R THE POTENTIAL ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 4R THE POTENTIAL ENERGY IS THE SAME IN BOTH ORBITS d) (4%) In which orbit is the total mechanical energy of the satellite higher (more positive)? (Circle the correct answer.) THE MECHANICAL ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 2R THE MECHANICAL ENERGY IS HIGHER IN THE ORBIT OF RADIUS 4R THE MECHANICAL ENERGY IS THE SAME IN BOTH ORBITS e) (4%) Is the work done by the rocket in moving the satellite from the radius of orbit 2R to the orbit of radius 4R positive or negative? (Circle the correct answer.) THE ROCKET DOES POSITIVE WORK THE ROCKET DOES NEGATIVE WORK THE ROCKET DOES ZERO WORK 3 NAME ______________________________ INSTRUCTOR _________________ SEC #___ PART C. You must show all your work or state your reasoning in order to receive credit. 1. (40%) The sketch show a proton traveling undeflected through a uniform magnetic field that is directed into the page, and perpendicular to the direction of the proton’s velocity. The proton is headed directly toward point P on a wall a distance d from the proton. There also is an electric field present that cancels the force produced by the magnetic field on the proton. a) (5%) The direction of the electric field that cancels the effect of the magnetic field is: (Circle the correct answer.) INTO THE PAGE OUT OF THE PAGE TOWARD THE TOP OF THE PAGE TOWARD THE BOTTOM OF THE PAGE SOME OTHER DIRECTION b) (5%) Imagine for a moment that the proton in the sketch is an electron. If the electron, instead of the proton, went undeflected through the field shown, the direction of the electric field would have to be: (Circle the correct answer.) THE SAME DIRECTION THAT IT WAS FOR THE PROTON OPPOSITE TO THE DIRECTION THAT IT WAS FOR THE PROTON SOME OTHER DIRECTION c) (7%) Now, back to the proton. The proton’s speed is v = 4.0 × 106 m/s. What is the proton’s kinetic energy, in electron volts. (The mass of a proton is m = 1.67 × 10-27 kg) K = ______________eV d) (8%) The magnitude of the magnetic field in the sketch is B = 0.50 T. What is the magnitude of the electric field that cancels the force produced by the magnetic field on the proton. E = __________________ units 4 NAME ______________________________ INSTRUCTOR _________________ SEC #___ Suddenly, the electric field is turned off, so only the force due to the magnetic field remains. The proton does not travel in a straight line, but is deflected by the magnetic force. e) (5%) The direction in which the proton is deflected is: (Circle the correct answer.) INTO THE PAGE OUT OF THE PAGE TOWARD THE TOP OF THE PAGE TOWARD THE BOTTOM OF THE PAGE SOME OTHER DIRECTION f) (10%) With the electric field turned off, and only the magnetic force present, does the proton reach the wall? The distance from the proton to the wall when the electric field is turned off is d = 0.20 m. (Circle the correct answer.) THE PROTON WILL REACH THE WALL THE PROTON WILL NOT REACH THE WALL If you circled THE PROTON WILL REACH THE WALL, how far will the point where the proton hits the wall be from point P? y = __________________ units If you circled THE PROTON WILL NOT REACH THE WALL, how close to the wall will the proton get? x = __________________ units 5