* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Infection Control Unit 2
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
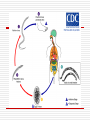
Infection Control Unit 2 Trotter Standard Precautions All patients treated the same Everyone is infected with infectious diseases Routine practice for all healthcare professionals PPE Biohazard containers Standard Precautions Handwashing Before and after gloving Between patients After using the bathroom After sneezing, coughing, using tissue Before eating After processing specimens, lab procedures Sharps Use extreme caution when handling sharps – needles, lancets, glass, sharp instruments Never recap, break or remove needles Use puncture-proof containers Look in/on beds, tables, counters Infectious Waste Proper container – biohazard symbol Red bags Minor – regular trash Treat with extreme caution Wear PPE Two greatest threats – HBV & HIV CDC recommendations Latex Allergies Swelling, rash, itching, dyspnea Can be life threatening Range of reactions Latex free items available Latex free carts Latex free exam room Always ask, always look Disease Prevention Changes began in the mid-1980’s OSHA – before AIDS CLIA – 1988 Federal regulations – law and safety for patients and healthcare workers Called Standard Precautions Fines for noncompliance Standard Precautions p- 538 Handwashing Gloves Eye protection Mask Gown Patient care equipment Environmental Control Linen Occupational Health and Bloodborne Pathogens Patient placement Disease prevention considerations Disposable items Skin conditions Open wounds Pregnancy HBV prevention – immunization PPE Indirect and Direct Contract Droplet infection – 20 feet or more Cough, sneeze, whistle Indirect – touching something that has the microorganism on it Direct – contact with patient or their body fluids What are possibilities for direct contact? Disease Transmission Communicable diseases Acute Chronic Disease description Means of transmission Incubation period S&S TX Prevention Disease Transmission Susceptible Vulnerable Resistance Infection cycle p. 543 How to break the cycle! Diseases to know AIDS Varicella URI – common cold Conjunctivitis Pediculosis HIB HAV HBV HCV HSV Impetigo Influenza Meningitis Pinworms Pneumonia Scabies Strep throat Scarlet fever Immunity Immune system – cellular resistance Health – homeostais Nutrition Rest Emotional health Exercise Specialized defense mechanisms Respiratory cilia Coughing Sneezing Secretions pH Requirements of microorganisms O2 pH Warm temp – 98.6 F Nutrients Water host 5 types of microorganisms Bacteria Virus Fungi Parasite Protozoa Bacteria Varied morphology Single-celled No nucleus No organelles Cell division q20min Pathogenic/Nonpathogenic Viruses Smallest microorganisms Electron microscope needed Only reproduce in a host Herpes Virus HCV SARS Protozoa Complex single-celled microorganisms Attach to other organisms Dysentery Malaria Trichomonas vaginalis Parasitic Fungi Simple parasitic plants (molds) Budding Depend on another source for food 100 different kinds in humans – only 10 cause problems Athlete’s foot Ringworm Parasites Obligate – depends entirely on host Facultative – can live independently for a while Internal and external Worms Scabies Microorganisms Flora Heterotrophic Autotrophic Organic Inorganic Aerobes Anaerobes Infection Control Sanitization Disinfection Sterilization Sanitization Wash and scrub to remove materials Handwashing Gloves should be worn Rinse in cool water Soak in warm detergent – 20 minutes Wash and scrub with brush Rinse hot Dry Disinfection Chemical or physical Kill pathogens Germicide Bactericide Objects not people Where can we find these products? Sterilization Destroy all living organisms and spores Autoclave Shelf life – 30 days, dry Expiration date Check for integrity Sterilizing instruments Autoclave Chemicals – 10 hours Sharp instruments Rubber Vinyl Sterilization Autoclaving Incineration Dry heat oven Autoclave