* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer Key Physics Study Guide A
Quantum vacuum thruster wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic mass wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Woodward effect wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
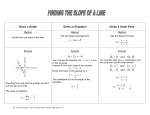
Physics Final Exam Study Guide (2012) SP1. Students will analyze the relationships between force, mass, gravity, and the motion of objects. a. Calculate average velocity, instantaneous velocity, and acceleration in a given frame of reference. Key words: instantaneous speed What are some examples of when you can measure your instantaneous speed? speedometer Compare and contrast scalar and vector quantities. Key words: direction and magnitude. What quantities are scalars? Time, speed, mass What are vectors? Velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, impulse b. Compare graphically and algebraically the relationships among position, velocity, acceleration, and time. Key terms: velocity, acceleration, speed Key equations: v = d/t (A sprinter runs 100 meter in 10.5 s; Calculate his speed) 100/10.5 = 9.5 a = (vf – vi) /t (A car slows down from 50 m/s to 35 m/s in 2 s; Calculate the car’s acceleration) (35 – 50) / 2 = -7.5 Identify and interpret position v. time and velocity v. time graph, identify the slope of each What quantity can be determined from the slope of What quantity can be determined from the slope of this graph? velocity this graph? acceleration Identify the slope at each interval as +, -, 0 Identify the slope at each interval as +, -, 0 Calculate the slope at each interval (slope =rise/run) Calculate the slope at each interval (slope =rise/run) Intervals: Intervals: (6s to 12s) (2s to 5s) (5s to 7s) (6s to 12s) 7s) 0 to 2 seconds zero slope = 0 2 to 5 second (-3 – 0) / (5 – 2) = -3/3 = -1 slope = -1 5 to 7 seconds (2 - -3) / (7 – 5) = 5/2 = 2.5 slope = 2.5 7 to 12 seconds zero slope slope = 0 12 to 14 seconds ( -6 – 2) / (14 – 12) = -8/2 = -4 slope = -4 14 to 16 seconds ( -2 - -6) / (16 – 14) = 4/2 = 2 slope = 2 16 to 18 seconds zero slope slope = 0 18 to 19 seconds ( 0 - -2) / ( 19 – 18) = 2/1 = 2 slope = 2 (2s to 5s) (5s to Falling objects in a vacuum. g=10m/s2. Be able to calculate velocity after a certain time in free-fall (v=gt) An object falls from rest. What is its speed after 5 seconds? gt = v 10x5 = 50 m/s …after 8 seconds? gt = v 10x8 = 80 m/s All projectiles (thrown objects) on earth accelerate DOWN (due to gravity) What does constant velocity mean in term of acceleration and force? Constant velocity means there is zero acceleration. Zero acceleration means zero net force. c. Measure and calculate the magnitude of frictional forces and Newton’s three Laws of Motion. Key terms: inertia How do you find weight on Earth given mass? W = mg (What is the weight of a 40 kg man on earth?) mg = W 40x10 = 400 N What are Newton’s 3 laws and what do they mean? 1st Law: inertia; If an object is sitting still it will remain still unless it is acted upon by an outside force. If an object is moving, it will keep on moving, unless it is acted upon by an outside force. 2nd Law: F = ma 3rd Law: action-reaction When two objects collide, the force is the same on each, regardless of which one has a greater mass. What effect does friction have on motion? Friction opposed motion. It will slow it down. Is air resistance a frictional force? Yes Be able to calculate Force (F=ma). (A force of 40N is applied to a 10kg box, how fast does the box accelerate?) F = ma 40 = 10a a = 40/10 a = 4m/s2 How are accelerations produced? By forces How is net force calculated? (When do you add the force/ when do you subtract the forces) Add when the forces are acting in the same direction. Subtract when the forces are acting in the opposite direction. ****A small car and a large truck collide head-on. Which one experiences the greater force? The force is the same for both ...the greater acceleration? The acceleration is greater for the small mass … the greater impulse? Same impulse … the greater change in momentum? Same change in momentum **** d. Measure and calculate the magnitude of gravitational forces. As things get further away from each other, gravitational forces __decrease by the square of the distance______ As things get closer, gravitational forces __increase______________ As things get more mass, gravitational forces ____increase___________ As things get less mass, gravitational forces __decrease________ SITUATION (A) SITUATION (B) g. Measure and calculate centripetal force. Calculate centripetal force: F=mv2/r (What is the centripetal force of a 2kg ball being spun in a circle with a radius of 3m at 5 m/s?) mv2/r = 2(52)/3 = 50/3 = 16.7 N Which direction does centripetal force always act? Toward the center h. Determine the conditions required to maintain a body in a state of static equilibrium. Balanced forces exist when? Be able to locate center of gravity - The point at which an object is balanced on both ends. Where is the center of gravity of the seesaw below? Is the center of gravity of the hammer in the same place? Why? Which arrow shows the Center of Gravity? Center of gravityof the men: in the center Center of gravity of the hammer: toward the heavier end (the 1st arrow) SP2. Students will evaluate the significance of energy in understanding the structure of matter and the universe. b. Explain how the instability of radioactive isotopes results in spontaneous nuclear reactions. Define the types of radiation below based on strength, danger, and ability to penetrate material o Alpha Rays o Beta Rays o Gamma Rays Understand half-life and be able to calculate Define the types of radiation below based on strength, danger, and ability to penetrate material o Alpha Rays least dangerous; will penetrate the least o Beta Rays o Gamma Rays most dangerous; will penetrate the most A substance has a half-life of 100 years. If there was 24 grams of the substance at time 0, how much would remain after 100 years (1 half-life)? … after 200 years (2 half-lifes)? … after 300 years? Start: 24 grams 1 half life later : 12 grams 2 half-lifes later: 6 grams 3 half-lifes later: 3 grams SP3. Students will evaluate the forms and transformations of energy. a. Analyze, evaluate, and apply the principle of conservation of energy and measure the components of work-energy theorem by • describing total energy in a closed system. • identifying different types of potential energy. • calculating kinetic energy given mass and velocity. • relating transformations between potential and kinetic energy. Understand work. W=Fd Compare and contrast kinetic and potential energy Calculate Kinetic Energy, KE = ½mv2 Calculate Potential energy. PE=mgh Understand the Law of Conservation of Energy. (Total Energy = ?) Identify the 7 different types of energy: Sound, Chemical, Radiant, Electrical, Atomic, Mechanical, & Thermal and energy transformations between each. b. Explain the relationship between matter and energy. c. Measure and calculate the vector nature of momentum. Be able to calculate momentum: p=mv Relate Newton’s 3rd law to momentum (i.e. Explosions, Gun shooting a bullet) e. Demonstrate the factors required to produce a change in momentum. Momentum = mass x velocity What happens to momentum as Mass increases? Momentum increases …velocity increases? Momentum increases e. Analyze the relationship between temperature, internal energy, and work done in a physical system. Identify examples of thermal expansion. Does water follow this rule? No. Water expands as it cools. Define the relationship between temperature change and the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of a substance. Key terms: radiation, conduction, convection Know how color affects heat absorption Dark colors absorb more heat than light colors g. Analyze and measure power. P=W/t; the faster something does work, the more powerful it is. SP4. Students will analyze the properties and applications of waves. a. Explain the processes that results in the production and energy transfer of electromagnetic waves. Know the electromagnetic spectrum, and how it is arranged in terms of wavelength, energy, and frequency. Be able to identify high vs. low frequency from a diagram How does frequency relate to energy? What is the relationship between frequency and period? f=1/p, p=1/f b. Experimentally determine the behavior of waves in various media in terms of reflection, refraction, and diffraction of waves. What is the Doppler Effect? Key terms: reflection, refraction, diffraction d. Demonstrate the transfer of energy through different mediums by mechanical waves. How does frequency relate to pitch of a sound wave? Frequency is the same as pitch How does traveling through different mediums affect the speed and how well the sound is transmitted? Sound travels fastest through a solid and sound travels slowest through a gas. Sound does not travel at all through a vacuum like empty space. What does the amplitude of a sound wave relate to loudness? The louder it is the greater the amplitude Compare and contrast electromagnetic v. mechanical waves. e. Determine the location and nature of images formed by the reflection or refraction of light. What do converging lenses do to parallel rays of light? SP5. Students will evaluate relationships between electrical and magnetic forces. a. Describe the transformation of mechanical energy into electrical energy and the transmission of electrical energy. o What is an electromagnet? Electromagnets produce a strong magnetic field that can be turned on and off with electricity. o What is the strength of an electric field inside of a charge sphere? zero c. Determine equivalent resistances in series and parallel circuits. o Compare and contrast parallel and series circuits o Be able to calculate the Total Resistance in a series and parallel circuit. Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Three resistors are in series. What is the total resistance? 12 Ω + 4 Ω + 8 Ω = Ω Add the resistors. The total resistance is a series circuit is greater than the largest resistor. So the total resistance must be larger than 12 Ω Three resistors are in parallel. What is the total resistance? 1/12 Ω + 1/4 Ω + 1/8 Ω = Ω In parallel circuits, the total resistance is less than the smallest resistor. So the total resistance must be less than 4 Ω