* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson Title:Reading Graphs for Information
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Group (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Coxeter notation wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
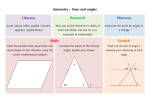
MCS Lesson of the Week Lesson Title: Oh My Polygon! Grade: 6 Strand: Geometry and Spatial Sense Learning Goal (Curriculum Expectations) Gr. 6 – classify and construct polygons and angles Reasoning and Proving – develop and apply reasoning skills to make and investigate conjectures and construct and defend arguments Representing – develop and apply reasoning skills to make and investigate conjectures and construct and defend arguments Key Ideas - Geometric objects have properties that allow them to be classified and described in a variety of different ways - Understanding relationships between geometric objects allow us to create any geometric object by composing and decomposing other geometric objects ICT Standards: Lesson Components Part 1: Minds On What do we know about: Right angles Acute angles Obtuse angles Straight angles Reflex angles? Students use the Notebook Angle Types Flash file to describe the different angles using attributes and geometric properties Anticipated Student Responses Opportunities for ICT Integration compare to benchmark angles o smaller than a right angle provide measurement ranges o between 0º and 89º compare to other types of angles o smaller than an obtuse angle describe the arms in comparison to other angles o the arms would be closer together than those of a 90º angle Use Notebook Flash file to investigate angles and record findings students could project their notes Part 2: Action Problem: Construct a polygon that has: o 3 different types of angles o at least 1 side with a length of 3 units Use PhotoBooth to share Geoboard or grid paper solutions Name and describe your polygon using geometric properties including lines of symmetry. Students work independently, in pairs, or small groups. Possible materials: Geoboards, grid paper, GSP, Smart Notebook IT Services: Teaching and Learning with Technology - Winter 2011 - http://community.elearningontario.ca MCS Lesson of the Week Part 3: Consolidation With the students, sort polygons according to the number of lines of symmetry. Generalize: When does a polygon have zero lines of symmetry? Only one line of symmetry? What types of polygons have more lines of symmetry? Consider the number of sides, lengths of sides, angles. Part 3: Highlights and Summary Polygons can be described and sorted according to: o number of sides o length of sides o types of angles o lines of symmetry There are different ways of finding lines of symmetry. The more sides a regular polygon has, the more lines of symmetry there will be. The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon is always equal to the number of vertices. Part 3: Practice How many lines of symmetry can a pentagon with 2 right angles have? Can a pentagon have more lines of symmetry? Explain and justify your solution. IT Services: Teaching and Learning with Technology - Winter 2011 - http://community.elearningontario.ca