* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download here - AdvaMedDX
Antimicrobial peptides wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
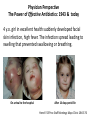
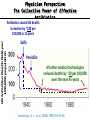
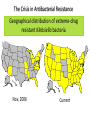
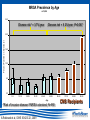
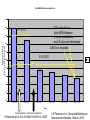
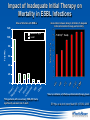
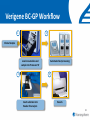
Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation June 3, 2013 Speakers Cynthia L. Sears, MD, Infectious Diseases Society of America and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Regina Davis Moss, PhD, MPH, MCHES, American Public Health Association Lance R. Peterson, MD, NorthShore Mike Musgnug, Alere Teresa Raich, PhD, Nanosphere AdvaMedDx.org 2 AdvaMedDx Founded in 2010 as a division of AdvaMed, the medical technology manufacturers association, to represent manufacturers of medical diagnostic tests AdvaMedDx functions as an “association within an association”, with over 70 member companies – from global industry leaders to early stage test developers Diagnostic tests provide critical insights at every stage of medical care The Diagnostic Innovation Testing and Knowledge Advancement Act of 2013, HR 2085, would reform the Medicare diagnostics payment system to reflect value of diagnostic tests to patient care and the health care system AdvaMedDx.org 3 AdvaMedDx.org Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation BAD BUGS, NEED DRUGS Why Antibiotics Deserve Congress’ Attention and Immediate Action Infectious Diseases Society of America Cynthia L. Sears, M.D. Professor of Medicine & Oncology Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine IDSA Treasurer Willard N. Sears Purple Heart, WWII Physician Perspective The Power of Effective Antibiotics: 1943 & today 4 y.o. girl in excellent health suddenly developed facial skin infection, high fever. The infection spread leading to swelling that prevented swallowing or breathing. On arrival to the hospital After 14 days penicillin Herrell ’43 Proc Staff Meetings Mayo Clinic 18:65-76 Physician Perspective The Collective Power of Effective Antibiotics US Infection Death Rate per 100,000 population Antibiotics caused US deaths to decline by ~220 per 100,000 in 15 years Sulfa 300 100 Penicillin All other medical technologies reduced deaths by ~20 per 100,000 over the next 45 years Armstrong, G. L. et al. JAMA 1999;281:61-66. Physician Perspective The Tragedy of Ineffective Antibiotics: The Crisis is Now Life-altering Disability Premature Death www.AntibioticsNow.org Rebecca Lohsen (17 yr)--Dead Carlos Don (12 yr)--Dead Mariana Bridi da Costa (22 yr)--Dead Ricky Lannetti (21 yr)--Dead Tom Dukes colostomy, lost 8” colon Addie Rerecich, 11yo Double lung transplant Stroke, nearly blind $6 million hospital bill The Crisis in Antibacterial Resistance Geographical distribution of extreme-drug resistant Klebsiella bacteria Nov, 2006 Nov, 2006 Current Extreme-drug resistant Acinetobacter Percent Extreme-drug Resistant Acinetobacter has risen dramatically 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Common Cause of Combat Wound Infections in US Soldiers 1999 2001 2003 2005 2007 2009 Hoffman et al ’10 ICHE 31:196-7; Higgins ’10 JAC 65:233-8; Lautenbach ’09 ICHE ’09 30:1186-92; Rosenthal ’10 Am J Infect Control 38:95-104; Hidron ‘ICHE ’08 29:996-1011; Dizbay ’10 Scand J Infect Dis; Kallen ’10 ICHE 31:528-31; NY Times Lives Devastated/Lost Due to Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria While precise numbers are unknown (& the CDC works to update the impact of antibiotic resistance): One resistant bacterium (MRSA) kills more Americans (~19,000) annually than emphysema, HIV/AIDS, Parkinson’s and homicide combined. CDC reports: 2 million HAIs/90,000 deaths Boucher HW, Bad Bugs, Noannually Drugs, No ESKAPE 2009; 48:1-12 inCIDU.S. Klevens RM et al, JAMA. 2007;298:1763-1771 The majority due to antibiotic-resistant bacteria Additional Costs/Length of Stay Associated with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria When antibiotic resistant bacterial infections are compared to antibiotic sensitive bacterial infections: Annual cost to the US healthcare system: $21-34 billion dollars RR Roberts, CID 2009:49, 1175-1184; Additional days: 8 million PD Maudlin, AAC 2010:54,hospital 109-115 additional days Antibiotic Development Total # New Antibacterial Agents IDSA’s Motivation/Perspective (systemic drugs) 16 14 12 Our patients need new antibiotics to stay healthy and alive! 1980 10 8 6 4 2 0 '83-'87 '88-'92 '93-'97 '98-'02 '03-'07 '08-'12 Primary Professional Activity IDSA Membership 10,000 strong Majority physicians providing clinical care, contributing to clinical care 4% 7% 2% 5% 8% 3% 14% 54% 3% 2012 Administration Basic Research Clinical Microbiology Clinical Research Hospital Epidemiology Patient Care Public Hlth Policy Initiatives 2004 BAD BUGS, NO DRUGS 2010 BAD BUGS, NEED DRUGS The 10 x ‘20 initiative 2011 IDSA PUBLIC POLICY CID 52 (Suppl 5):S397, 2011 recommends: CID 52 (Suppl 5):S397, 2011 1. Adoption of Economic Incentives and Collaborative Mechanisms to Address the Market Failure of Antibiotics 2. New Regulatory Approaches to Facilitate Antimicrobial Development & Approval 3. Greater Coordination of Relevant Federal Agencies’ Efforts 4. Enhancement of Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Systems 5. Strengthening Activities to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance 6. Significant Investments in Antimicrobial-Focused Research 7. Greater Investment in Rapid Diagnostics R&D and Integration into Clinical Practice 8. Eliminating Non-Judicious Antibiotic Use in Animals, Plants & Marine Environments Key Steps Congress can take to Address Antimicrobial Resistance STAAR Act Strategies to Address Antimicrobial Resistance Awaiting Introduction/Enactment Will strengthen federal coordination, accountability, leadership as well as support antimicrobial stewardship efforts in health care facilities Strengthen the antimicrobial pipeline 2012: Generating Antibiotics Incentives Now (GAIN, exclusivity) Enacted. 2013??: Still needed additional economic incentives (e.g., R&D tax credits) plus a new FDA regulatory pathway (limited population—LPAD) Increase funding for CDC & NIH Antimicrobial resistance surveillance, advanced detection methods, data collection and research Ban antibiotic use to fatten agricultural animals (cows, pigs, chickens) The Disheartening Current Status of the 10 x ‘20 Initiative Our Goal: Your Goal Protect This Global Treasure Prior generations gave us the gift of antibiotics. Today, we have a moral obligation to ensure this global treasure is available for our children and future generations. Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation: Congressional Briefing Washington, DC June 3, 2013 Lance R. Peterson, MD Recipient, Eisenberg Award for Local Innovation in Patient Safety and Quality, National Quality Forum, the Joint Commission Director of Microbiology and ID Research Epidemiologist, NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Professor University of Chicago, Chicago, IL USA Ten Wonders for Infection Control (How to Prevent Resistance and Lower Cost) Research Communication and Reporting Education Vaccination Hand Hygiene Screening and Isolation Antibioitc Stewardship Environmental Disinfection Outbreak Tracking Rapid Diagnosis FDA Cleared Amplification Tests for Surveillance (as of May 11, 2013) • MRSA (N = 6) • MRSA/MSSA (N = 3) • VRE (N = 1) Source: Association for Molecular Pathology Web Page <http://www.amp.org/FDATable/FDATable.pdf> MRSA Prevalence by Age n=18,898 25.0 Disease risk* = 3.7%/year Disease risk = 8.2%/year; P=0.067 Percent Positive on Admission 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 0-9 10-19 20-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 Age *Risk of invasive disease if MRSA colonized; N=993 A Robicsek et al, ICHE 30:623-32, 2009 60-69 70-79 80-89 90-99 CMS Recipients Medical and Economic Outcome • Excess expense of MRSA infection (compared to no infection) = $24,000 • During the 8 years of NorthShore MRSA containment program prevented 813 infections – Net direct benefit from medical expense reduction is over $16 million ($2M/Year) – ½ accrues to CMS – Number of deaths avoided = 144 (18/Year) LR Peterson. JCM 48:683-9, 2010 LR Peterson et al. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 33:732-8, 2007 RM Klevens et al. JAMA 298:1763-71, 2007 Total MRSA Healthcare Infections 10.0 9.0 70% reduction in total MRSA disease during hospitalization and 30 days post-discharge P = 0.15 8.0 Prevalence Density (Cases/10,000 patient-days) 7.0 2 BSI in 4 hospitals 6.0 P ≤ 0.001 Total 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 8/03 - 7/04 9/04 - 7/05 9/05 - 7/06 8/06 - 7/07 8/07 - 7/08 8/08 - 7/09 Years ICU surveillance Universal surveillance A Robicsek et al. Ann Int Med 148:409-18, 2008 LR Peterson et al. Decennial Meeting on Nosocomial Infections, Atlanta, 2010 Predictive Modeling for RiskBased Testing • Once a population is tested and sufficient data collected a prediction rule can be constructed that reduces need for testing • Derivation cohort – 23,314 (89.9% of patients) were tested on admission » 520 (2.2%) were MRSA colonized • Validation cohort – 26,650 (94.9% of patients) were tested on admission » 1,065 (4.0%) were MRSA colonized A Robicsek et al. ICHE 32:9-19, 2011 For a preventable infectious disease, testing cost declines with time Prospective validation, Sept-Nov 2011 What About Decolonizing Everyone? NEJM Results NS Results Comments Scope/Population 18 months/29 ICUs 38 months/5 ICUs Similar hospital 101,600 patient days 55,350 patient days types Outcome No screening and Decolonize all Screen all and only Isolate positives Rate of MRSA clinical isolates 2.1 per 1,000 patient days 0.3 per 1,000 patient days NS data based on 342,000 patients Rate of all cause bacteremia 3.6 per 1,000 patient days 1.0 per 1,000 patient days In ICU NS is >3-fold lower Rate of MRSA bacteremia 0.6 per 1,000* patient days 0.018 per 1,000 patient days In ICU NS is >30fold lower Cost $40 per patient $27-$37 per patient NS cost range based on test price (includes all MDROs) *Most reduction in Gram positive skin commensal organisms (Coagulase-negative staphylococci) S Huang et al. NEJM May 29, 2013 KE Peterson et al. ICHE 33:790-5, 2012 A Robicsek et al. ICHE 32:9-19, 2011 A Robicsek et al. Ann Int Med 148:409-18, 2008 LR Peterson et al. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 33:732-8, 2007 Impact of Inadequate Initial Therapy on Mortality in ESBL Infections Sites of infection with ESBLs 120 Klebsiella spp E. coli 100 Association between delay in initiation of adequate initial antimicrobial therapy and mortality P<.001 (Χ2, Trend) Total No. 80 60 40 20 bd nd om in al S ST O th er d A W ou lo o B to ry ira es p R U rin a ry * 0 *Only patients with non-urinary ESBL-E/K had a significantly elevated risk of death Time to institution of effective antimicrobial therapy, hours EP Hyle et al Arch Intern Med 165:1375-80, 2005 MRSA/MSSA from Blood Cultures • S. aureus bacteremia admitted from September 2008 through December 2008 (pre-qPCR) compared to March 2009 through June 2009 (postqPCR; GeneXpert) • Clinical and economic outcomes of 156 patients • Mean switch from vancomycin to cefazolin or nafcillin for methicillin-susceptible S. aureus bacteremia was 1.7 days shorter (P = .002) • Mean LOS was 6.2 days shorter (P = .07) and hospital costs were $21,387 less (P = .02) KA Bauer et al, CID 51:1074-80, 2010 Summary – Impact of Novel Testing • For control of critical pathogens the role of the clinical laboratory remains essential • Rapid technologies enable efficient detection of critical problems • The role of rapid diagnostics in microbiology partnering with infection control will revolutionize the prevention and treatment of challenging healthcare-associated infectious diseases and can reduce antibiotic resistance in this decade – Partnering between innovative industries and government will be critical to achieve the goal Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation Alere Inc. The role of rapid diagnostic tests in combating antibiotic resistance Michael Musgnug Vice President, Respiratory & Healthcare-Associated Infections June 3, 2013 34 Agenda 1. Who is Alere? 2. Alere’s infectious disease testing portfolio 3. The role of rapid diagnostics MRSA Pneumonia 4. TestTargetTreat campaign Alere’s Corporate Mission Alere empowers individuals to take greater control of their health under the supervision of their healthcare providers. We enable: » » » » » Earlier interventions More targeted treatment Fewer hospitalizations Reduced healthcare costs Better outcomes World-Class Diagnostics & Health Information Solutions World’s leading provider of near-patient diagnostic tests that, when combined with our novel health information solutions, enable the effective management of several chronic conditions. Major US sites: • • • • • • • • Total Employees Massachusetts 13,500 California (NorCal & SoCal) Maine Represented In Georgia 100+ countries New Jersey Washington Virginia Business Units Florida 6 Revolutionary Infectious Disease Tests We are the world’s leading provider of near-patient diagnostics for the most prevalent infectious diseases Diagnostics Leader » HIV Screening » Influenza » Malaria » C. difficile » Strep pneumo » Legionella » Strep A » Dengue Fever » RSV Transformational Testing Platforms The AlereTM CD4 Analyzer provides absolute CD4 results to initiate and help manage antiretroviral therapy The AlereTM Q enables molecular HIV viral load testing at the point of care; applications for TB and HCV in development The AlereTM i is a molecular platform for acute, near-patient testing; launch of flu application planned for 2014 The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis Antibiotic Resistance – a threat to mankind Test, Target, Treat versus… Test, Target, Treat… Alere’s Role in Antibiotic Stewardship How Does Alere Help Manage This Crisis? Does the patient need antibiotics? Flu RSV Strep A Which antibiotics are most appropriate? Strep pneumo Legionella Strep A Do they have an antibiotic resistant bacteria? MRSA Do they have an antibiotic-associated disease? C. difficile MRSA: Identifying antibiotic resistant bacteria for better outcomes MRSA – a big antibiotic resistance problem What is MRSA? How big is the problem? MRSA is methicillin-resistant Staph aureus, an antibiotic resistant version of a common bacterium MRSA rates have grown considerably with the overuse of antibiotics In 2005, there were 14 million cases of MRSA in the outpatient setting What is the economic impact? A case of healthcare-associated MRSA costs $94,707 The cost to isolate a patient with MRSA is $1250 per day Year % of S. aureus strains that are MRSA Shorr AF. JCM 2010 48:3258-62 1974 2% Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services website 1995 22% Gidengil CA. 48th annual meeting of the IDSA 2004 64% Alere’s MRSA Test Traditional microbiology methods take 24-48 hours to yield a result This simple test takes only 5 minutes Faster reporting of actionable results allows better patient management Patients with MRSA can continue on vancomycin and be put in isolation Patients without MRSA can be de-escalated and kept out of isolation Pneumonia: Rapid testing to support targeted therapy and improved outcomes Pneumonia – a major driver of healthcare costs 4.5 million cases of pneumonia annually, resulting in 2 million hospitalization1,2 Pneumonia, along with influenza, is the 9th leading cause of death in the United States3 #3 in the top 20 hospital discharge diagnosis groups for emergency department visits4 Total costs associated with pneumonia in US: $17 billion/year5 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Premature Deaths, Monthly Mortality and Monthly Physician Contacts: United States. MMWR 1997; 46:556. 2. Niederman MS, McCombs JS, Unger AN, et al. The Cost of Treating Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Clin. Ther. 1998; 20:820-837. 3. CDC Website: Deaths Final Data for 2010 4. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2010 Emergency Department Summary Tables 5. File TM Jr, Marrie TJ. Burden of community-acquired pneumonia in North American adults. Postgrad Med. 2010;122(2):130-141. Alere’s Pneumonia Test Standard of care diagnostic tools are lacking Take too long Not accurate enough The Alere test is a simple test that gives results in 15 minutes A positive result allows targeted antibiotic therapy, which helps prevent the growing resistance crisis Improved outcomes associated with Alere’s rapid pneumonia test The Alere test is recommended in the IDSA/ATS Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Guidelines Aids in reducing the overuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics, which leads to antibiotic resistance When its findings are positive, the Alere rapid test can help the doctor optimize antimicrobial therapy with favorable clinical outcomes • Potentially reduces the length of stay for hospitalized pneumonia patients with a savings of $2,300 per day Sordé, R., et al.; Arch Intern Med. Published online September 27, 2010. doi:10.1001/archinternmed.2010.347 Kozma, C.M., et al,; J Med Econ. 2010; 13(4):719-727. Alere’s TestTargetTreat™ Campaign What Doesn’t Kill Them Makes Them Stronger. The misuse of antibiotics has created a huge global health crisis. The Test Target Treat™ initiative from Alere empowers healthcare professionals to make targeted treatment decisions sooner with rapid diagnostics — reducing inappropriate antimicrobial use and the spread of resistance. TestTargetTreat.com Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation Rapid Diagnostics for Bloodstream Infections June 3rd, 2013 CONFIDENTIAL Opportunities to Combat BSIs Prevention Universal decolonization Clean practices (cleaning, germ soap washes, etc.) Screening Systematic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) Procalcitonin (PCT) Rapid Diagnostics FDA-Cleared Multiplexed Molecular Diagnostics Tests PNA-FISH MADLI-TOF 56 CONFIDENTIAL Why Rapid Diagnostics for BSIs Reduced Mortality Each hour that the administration of appropriate antimicrobial treatment is delayed a patient’s mortality rate increases 7.6%1 Reduce Costs Rapid identification of the bacteria and corresponding antimicrobial resistance reduces cost of antibiotics and patient length of stay2 Improved Antimicrobial Stewardship Initiatives Minimize patient exposure to unnecessary antibiotics Potentially “slow down” spread of antibiotic resistant bacteria 1Kumar 2Bauer et al. 2006. Crit Care Med, 34:1589-96. et al. 2010. Clin Infect Dis, 51:1074-80. 57 CONFIDENTIAL Rapid ID of Gram-Positive Bacteria and Resistance Reduced Mortality Up to 53% for S. aureus infections1 Up to 47% for Enterococci and Streptococci2 Clinical/Economic Outcomes Implementing rapid results reporting for S. aureus blood cultures can lead to an average 6.2-day reduction in length of stay and $21,387 reduction in cost per S. aureus-infected patient3 Rapid mecA reporting for patients with S. aureus bacteremia results in a 25.4hour reduction in the time to optimal antimicrobial therapy4 Patients with false-positive blood culture results triggered by contaminants such as S. epidermidis have hospitalization costs $8,750 higher than true negative blood culture patients5 1Ly et al. 2008. Ther Clin Risk Manag, 4:637-40., 2Gamage et al. 2011. 51st ICAAC, Poster D-1302b. et al. 2010. Clin Infect Dis, 51:1074-80, 4Carver et al. 2008. J Clin Microbiol, 46:2381-83 5Zwang and Albert 2006. J Hosp Med, 1:272-76. 3Bauer . 58 CONFIDENTIAL Current Laboratory Detection Methods of BSIs Blood Draw from Patient After 12-14 h incubation (24-48 h from time of draw), bacteria grow, lab begins ID Incubation on Blood Culture Monitoring System (6-18 h) Notify ordering physician of positive culture and plate for ID and susceptibility After 2-24 h (48 h total) ID is reported to physician via chart 48-72 h from time of draw, full ID and susceptibility reported to physician 59 Slide from Dr. Nate Ledeboer, MCW/DynaCare/Milwakee, WI CONFIDENTIAL Gram-Positive BSI Rapid Diagnostic Tests FDA Cleared Tests: AdvanDx (PNA FISH): S. aureus/CNS, E. faecalis/OE Nanosphere’s Gram-Positive Blood Culture Test (BC-GP) Tests in Development BioFire BCID Verigene Gram-Positive Blood Culture Nucleic Acid Test (BC-GP) Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus epidermidis Staphylococcus lugdunensis Staphylococcus spp. Genus Streptococcus spp. Listeria spp. mecA Resistance vanA vanB Species Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus anginosus Group Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) Streptococcus pyogenes (GAS) Enterococcus faecalis Enterococcus faecium 60 CONFIDENTIAL Verigene BC-GP Workflow 1 2 Clinical Sample Automated test processing Load consumables and sample into Processor SP 3 4 Insert substrate into Reader for analysis Results 61 CONFIDENTIAL BC-GP Outcome Study1: Banner Health Study: 6-months, 307 patients with positive blood cultures processed 67 (22%) MSSA, 49 (16%) MRSA, and 163 (53%) CoNS BC-GP results compared to traditional culture identification Results: Once MSSA alert received by Pharmacy Department, on average patient switched to nafcillin or cefazolin within 9 hours 1Koeneman BA, Silverberg JM, Khalsa A, Fisher H, McCabe KM, Saubolle MA, Mochon AB. Rapid Identification of MethicillinSensitive Staphylococcus aureus from Positive Blood Cultures using the Verigene System: A System-Wide Impact on Patient Treatment and Physician Compliance. Poster session presented at: American Society for Microbiology: 113th General Meeting; 2013 May 18-21; Denver, CO. 62 CONFIDENTIAL Rapid ID of Gram-Negative Bacteria and Resistance Treatment often complicated by antibiotic resistance MDR strains associated with prolonged hospital stays, higher health care costs, and increased mortality1 Resistance rates increasing among problematic gram-negative bacteria Acinetobacter spp., Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacteriaceae Extended Spectrum Beta-Lactamases (ESBLs) CTX-M becoming predominant type, replacing TEM-type and SHV-type Carbapenemases in U.S. Klebsiella pneumoniae Carbapenemase (KPC) predominant type Prevalence of NDM, OXA, VIM, IMP expected to grow 1Slama, T.G. (2008). Gram-negative antibiotic resistance: there is a price to pay. Critical Care 12(Suppl 4):S4. 63 CONFIDENTIAL 2010 2011 Trend in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella Pneumoniae from 2009 - 20111 It’s not a matter of if, but rather when this wave of carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae reaches the U.S. 1ECDC Surveillance Reports on Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe Report of the Chief Medical Officer, UK, 2011 2Annual 0 Reported Cases 2009 600 Spread of Carbapenem Resistance in GN Bacteria in Europe Trend in CRE cases in the United Kingdome from 2003-20112 64 CONFIDENTIAL Gram-Negative BSI Rapid Diagnostics Tests FDA Cleared Tests: AdvanDx (E. coli/P. aeruginosa, GNR Traffic Light) Tests in Development: Nanosphere Verigene BC-GN, BioFire BCID Verigene Gram-Negative Blood Culture Nucleic Acid Test (BC-GN)—In Development Acinetobacter spp. Escherichia coli Proteus spp. Klebsiella pneumoniae Genus Citrobacter spp. Enterobacter spp. KPC Species Klebsiella oxytoca Pseudomonas aeruginosa Serratia marcescens NDM CTX-M Resistance VIM IMP OXA 65 CONFIDENTIAL Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation Rapid Diagnostics are linked to: • Improved patient outcomes • Reduced healthcare costs • Decreased LOS • Decreased pharmacy costs • Decreased HAIs and readmissions • Improved antimicrobial stewardship 66 Fighting Antibiotic Resistance Through Innovation