* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - BigEngine
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
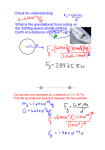
Name:____________________ Date:____________________ Chapter 5 Review - Forces ( / ) Please solve the following problems showing the formula, your number substitution, and your circled final answer to the correct number of significant figures and with the proper units! 1. A force acts on a 2.0 kg mass and gives it an acceleration of 3.0 m / s 2 . (a) How large is the force? (b) What acceleration is produced by the same force when acting on a mass of: (i) 1.0 kg (ii) 4.0 kg 2. An 800.0 N person stands on a scale on the floor in an elevator. What is the scale reading if the elevator has an acceleration of: (a) 1.8 m / s 2 up (b) 2.2 m / s 2 down (c) 9.8 m / s 2 down 3. A cord passing over a frictionless pulley has a 4.0 kg ( m1 ) object tied to one end and a 12.0 kg ( m2 ) object tied to the other. Find the acceleration of the two masses and the tension in the cord. m1 m2 4. If a force of 270 N is required to start a 40.0 kg box moving across a concrete floor with constant velocity, what is the coefficient of friction between the floor and the box? 5. A 52 N sled is pulled across a cement sidewalk at a constant speed. A horizontal force of 36 N is exerted. What is the coefficient of friction? 6. A 4500 kg helicopter accelerates upwards at 2.0 m / s 2 . What lift force is exerted by the air on the propellers? 7. Two objects, a certain distance apart, have a mutual force of gravity of 60N. a. What would the force of gravity be if the distance between the objects was doubled? [Hint: Use algebra.] b. What would the force of gravity be if the distance between the objects was halved? c. What would the force of gravity be if the mass of one of the objects was tripled? 8. Suppose that the applied force has a magnitude of 420 N. If m1 = 12 kg, and the acceleration of m1 is 5.2 m/s2 to the right, a) What is the magnitude of the friction force? b) What is the value of the coefficient of kinetic friction? 9. A 1400 kg vehicle is accelerated from rest to 16 m/s over a distance of 92 m. What is the net force during this acceleration? 10. A motorbike and rider having a mass of 160 kg, coast to a stop in 51 meters. Their original velocity was 15 m/s. What was the stopping force exerted by the road on the motorbike and rider? 11. A 3.2 x 103 kg satellite is 2.4 x 106 m from the centre of the moon. What is the magnitude of the moon’s gravitational force on the satellite? (1 mark) 12. Two objects, each with a mass of 8.0 x 102 kg produce a gravitational force between them of 3.7 x 10-6 N. What is the distance between them? (2 marks) 13. Object A, with mass m1, is a distance d away from object B, of mass m2. This results in a gravitational force of F. Suppose the mass of m1 is tripled, and moved three times further away from m2 than it was originally. What is the gravitational force between the objects now? A. F/9 B. F/3 C. 3F D. 9F 14. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Mars is 3.8 m/s2. How much would a 6.3 kg watermelon weigh on Mars? 15. The mass of Mars is 6.421 x 1023 kg. Use your answer from the above question and Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation to calculate the radius of Mars. 16. Consider the following diagram. m1=3.0 kg m2=6.0 kg a) Draw a free body diagram showing the forces acting on m1. b) Find the acceleration of the system. Key Formulae: F ma Fg Gm1m2 r2 Data Values: Mass of Earth Radius of Earth Gravitational Constant Acceleration of gravity on Earth’s Surface Mass of Moon Radius of Moon Mass of Sun Fg = mg 5.98 x 1024 kg 6.38 x 106 m G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 g = 9.8 m/s2 7.35 x 1022 kg 1.74 x 106 m 1.98 x 1030 kg