* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SNC1P - MsKhan
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
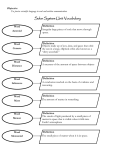
SNC1P Name: _______________ Date: ________________ Unit 4 - Space Exploration In this unit we will be studying... 1. ...celestial objects such as the Sun, moon, and planets [Chapter 8] 2. ...celestial objects beyond our Solar System [Chapter 9] 3. ...space research & exploration [Chapter 10] 8.1 - The Night Sky A celestial object is any object in space, such as: -the Sun = a medium-sized ________________ -a star is a massive collection of gases and is luminous (it gives off its own light) -the Sun is the closest star to the Earth, which is why it appears so LARGE -planets = large, round, celestial objects that orbit around ________________ -there are 8 planets orbiting around our Sun -planets are not ________________, but they appear bright like stars because they reflect the light of the Sun -we can see Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn from Earth with the unaided eye (with no binoculars or telescopes) -moons = smaller celestial objects orbiting around ________________ -moons are also visible because they reflect the light of the Sun -Earth has 1 moon, Jupiter and Saturn have more than 60 moons each -galaxies = huge, rotating collections of gas, dust, stars, planets, and other celestial objects -Earth is part of the ________________ Way galaxy, a spiral-shaped galaxy -the Solar System = the Sun and all the celestial objects that travel around it **Do questions #1-5 on page 296** 8.4 - Planets To be classified as a planet, a celestial object must: i. orbit a star ii. contain enough mass to be round in shape iii. be able to clear other celestial objects out of its orbit Pluto is considered a ________________planet because it doesn't meet iii. Pluto crosses the orbit of Neptune, but it can't clear it out of its orbit. Inner Planets (4 closest to the Sun): -called "terrestrial planets" because they have a solid ________________ surface -Mercury, Venus, Earth, ________________ -Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun (and the fastest) -Venus is almost the same size as Earth -Mars has a red surface Outer Planets (4 furthest away from the Sun): -called "gas giants" because they are made up mostly of ________________ -Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, ________________ -Jupiter is the largest planet -Uranus spins on almost a horizontal axis -Neptune is the furthest planet from the Sun -all have rings, but Saturn's rings are the most visible **Do questions #1,2,3 on page 307** Universe star Key Term: orbit luminous planet celestial object Solar System galaxies dwarf planet Definition: any object that exists in space a massive collection of gases in space that emits large amounts of energy producing and giving off light; shining a large, round celestial object that travels around a star the closed path that a celestial object takes around another object; elliptical or circular in shape huge, rotating collections of gas, dust, stars, planets, and other celestial objects everything that exists, including all matter, energy, and space the Sun and all the celestial bodies that travel around it a celestial object that orbits the Sun and has a spherical or round shape, but does not clear its own orbit 9.1 - Motion in the Solar System For more than 2000 years, people believed that our solar system was ________________ (the Earth is in the middle), but it was discovered in the 16th century that it is ________________ (the Sun is in the middle, and the planets revolve around it). The distance from the Earth to the Sun is 150 000 000 km, or 1 ________________ unit (AU). Smaller objects in our Solar System include: asteroids -smaller rocky objects with irregular shapes -mostly located in the asteroid belt between Mars and ________________ meteroids comets -smaller than asteroids -burn up when they enter Earth's atmosphere, causing streaks of light across the sky called meteors or "________________" stars -some are large enough to hit the surface of the Earth as meteorites -large chunks of ________________, dust, and rock that orbit the Sun -when they are close enough to the Sun, the frozen gases evaporate and a long ________________ is visible All planets ________________ around the Sun, and ________________ on their axis. -the revolution of the Earth takes about 365 days -the rotation of the Earth takes 24 hours, 1 Earth day -this is what causes the Sun (and Moon) to "rise" and "set" **Do questions #1-5 on page 335**