* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 2: Solve for Unknown Angles—Transversals
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
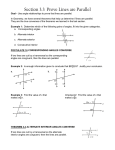
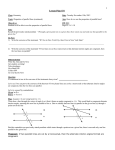
Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ U2 GEOMETRY Lesson 2: Solve for Unknown Angles—Transversals Learning Targets: I can identify all types of angles formed by parallel lines cut by transversal and apply the knowledge of relationships between angles formed by parallel lines cut by a transversal to find the missing angle. Opening Activity: Solve the following equations 1. 4(𝑥 − 2) = 8(𝑥 − 3) − 12 2. (𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 + 5) = 𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 − 2 New Vocabulary A transversal is a line that intersects two or more lines (in the same plane). Remember that: - the word INTERIOR means BETWEEN the lines. - the word EXTERIOR means OUTSIDE the lines. - the word ALTERNATE means "opposite sides" of the transversal and “on different” lines When the lines are NOT parallel When the lines are parallel... "Names" given to pairs of angles formed by two parallel lines cut by a transversal: alternate interior angles alternate exterior angles corresponding angles interior angles on the same side of the transversal Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ U2 GEOMETRY Alternate interior angles are "interior" (between the parallel lines), and on "alternate" sides of the transversal Identify the pairs of alternate interior angles ___________ ___________ If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the alternate interior angles are congruent. Converse If two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate interior angles are congruent, the lines are parallel. Alternate exterior angles are "exterior" (outside the parallel lines), and on "alternate" sides of the transversal Identify the pairs of alternate interior angles ___________ ___________ If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, the alternate exterior angles are congruent. Converse If two lines are cut by a transversal and the alternate exterior angles are congruent, the lines are parallel. If you copy one of the corresponding angles and you translate (“slide”) it along the transversal, it will coincide with the other corresponding angle. Identify all the pairs of coresponding angles ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, corresponding angles are congruent. Converse If two lines are cut by a transversal and corresponding angles are congruent, the lines are parallel.. Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ U2 GEOMETRY The "interior" angles (between the parallel lines) on the same side of the transversal, are called “same-side interior angles”. Identify all pairs of same-side interior angles ___________ ___________ If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, same-side interior angles are supplementary. Converse If two lines are cut by a transversal and the same-side interior angles are supplementary, the lines are parallel. Using the theorems above, what equations can you create from the diagram at the right? Congruent: ______ = _____ Type: _______________ Supplementary: ____ + ____ = ____ Type: _______________ Example 1 In the diagram below, find the unknown (labeled) angles. Give reasons for your solutions. 𝑚∠𝑎 = _______ Reason:________________________ 𝑚∠𝑏 = _______ Reason:________________________ 𝑚∠𝑐 = _______ Reason:________________________ Example 2 Given the diagram at the right with straight lines m, n and t. Which statement could always be used to prove m || n ? Choose: ∠2 and ∠6 are supplementary m∠2 = m∠3 ∠3 and ∠5 are supplementary m∠5 = m∠7 Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ U2 GEOMETRY Lesson 2: Solve for Unknown Angles—Transversals Classwork Two lines 𝐴𝐵 and 𝐶𝐷 are parallel if and only if any one of the following conditions are true: Corresponding Angles are equal in measure. or Alternate Interior Angles are equal in measure. or Same Side Interior Angles are supplementary: 1. Transversal intersects and , as shown in the diagram below. Which statement could always be used to prove a) b) c) and are supplementary d) and are supplementary ? 2. A transversal intersects two lines. Which condition would always make the two lines parallel? a) Vertical angles are congruent. b) Alternate interior angles are congruent. c) Corresponding angles are supplementary. d) Same-side interior angles are complementary. 3. Find m∠ 1 and then m∠ 2. Justify each answer. m 1 __________because __________________________________ ____________________________________________________ m 2 _________because ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________ Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ In Problems 4 and 5, use the diagram at the right. 4. Given ∠2 ≅ ∠6, what justifies 𝑘 ∥ 𝑚. a. Converse Alternate Interior Angles Theorem b. Converse Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem c. Converse Corresponding Angles Theorem d. There is not enough info to state parallel 5. Given 𝑛 ∥ 𝑝 , what justifies ∠1 ≅ ∠12 a. Alternate Interior Angles Theorem b. Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem c. Corresponding Angles Theorem d. There is not enough info to make this statement 6. Determine the relationship between ∠1 & ∠10. a. Alternate Interior b. Same-side Interior c. Corresponding Angles d. None of these 7. Determine the relationship between ∠5 & ∠15. a. Alternate Exterior b. Alternate Interior c. Same-side Interior d. None of these 8. If 𝑚∠9 = 62°, then find the measure the following angles: a. 𝑚∠1 = ________ b. 𝑚∠2 = ________ c. 𝑚∠4 = ________ d. 𝑚∠5 = ________ e. 𝑚∠15 = _______ U2 GEOMETRY Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ 9. Period:________ Date:__________ Given straight lines p, q, t, and s and angles as marked. Which value of x will make lines p and q parallel? Choose: 73º 87º 107º 113º 10. Given the diagram shown at the right. Assume all lines are straight. Find the measures of all of the numbered angles 1 through 12. m∠1 ________________ m∠2 ________________ m∠3 _________________ m∠4 _________________ m∠5 ________________ m∠6 _________________ m∠7 _________________ m∠8 _________________ m∠9 _________________ m∠10 _________________ m∠11 _________________ m∠12 _________________ 11. U2 GEOMETRY Lesson 2 RCSD Geometry Local MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM Name:___________________________________ Period:________ Date:__________ GEOMETRY Lesson 2: Solve for Unknown Angles—Transversals Homework 1. Find the measure of the unknown angle, and give the name of the theorem used. A. B. ma = ________ mb = ________ Theorem: ____________________ Theorem: ________________________ __________________________________ ________________________________ C. D. mc = ________ md = ________ Theorem: ____________________ Theorem: _______________________ __________________________________ ________________________________ 2. Given that 𝑝 ∥ 𝑞 and 𝑙 ∥ 𝑚 , find the measures of all the numbered angles in the diagram at right, giving reasons for each measurement. The first one is done for you. a. 𝑚∠1 = 42 by _corresponding angle theorem__ to __Given Angle___. b. 𝑚∠2 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. c. 𝑚∠3 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. d. 𝑚∠4 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. e. 𝑚∠5 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. f. 𝑚∠6 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. g. 𝑚∠7 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. h. 𝑚∠8 = _____ by ______________________________ to ________________. U2