* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 1 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
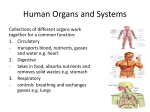
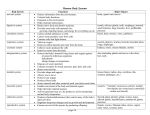
Day 1 Notes- 3 Green Anatomy- Structural components of an organism’s “body” and how it is built Physiology- The overall functioning of the body and all of its components (mostly chemical and electrical); PROCESSES 4 Themes for the Year: - “FFF”- Form Follows Function - Interdependence in Systems - Homeostasis - Disruption to homeostasisi.e. disease, injury, aging System Overview: 1. Integumentary- Provides protective covering to the body; maintaining body temp.; Absorption & secretion of nutrients & waste. (Skin, hair, nails) 2. Skeletal- Provides structural framework & protects inner organs; allows movement; Produces erthyrothrocytes & leukocytes. (Bones, bone marrow) 3. Muscular- Allows body to move and allows contraction of inner organs (heart, stomach, intestines); Helps protect inner organs; Helps in temp. regulation (biceps, triceps, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle) 4. Nervous (control system)Relaying impulses (electrical) to convey information to rest of body; Controls voluntary & involuntary reactions; Works w/ endocrine to manage all functioning of the body. (Brain, spinal chord & all associated nerves) 5. Endocrine (control system): works w/ nervous to control all body functions; Allows cellular communication through the use of hormones; production of hormones (Glands- Hypothalamus, pituitary, adrenal, thyroid, ovaries, testes) 6. Cardiovascular(Circulatory ): Transport O2, nutrients, waste, hormones via bloodstream; Helps to regulate body temp.; Maintenance of blood pressure. (Heart, vessels arteries, veins, capillaries) 7. Lymphatic (Immune): White blood cells, Lymphatic vessels & glands. Protection from disease and other pathogenic material; Maintain fluid balance of organs, tissues & blood; Aids in lipid absorption within the digestive tract. 8. Respiratory: Diffuses O2 into blood and CO2 out. Capillaries, lungs, trachea, nasal passageway. 9. Urinary: Passes metabolic waste out of body via the kidneys/bladder; regulates blood pH, blood volume & nutrient level; urethra (pee tube), ureters 10. Digestive: To allow nutrients (carbs, lipids, nucleic acids, proteins) into the body to be used for cellular respiration and alleviates solid waste material. Mouth Anus 11. Reproductive- Allows species survival by maintaining population numbers and maintenance of diversity within populations. Ovaries, Testes, Vas deferens, oviducts, gonads