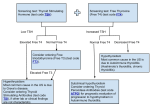
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Too many cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Condition Pituitary Carcinoma adenoma of pituita ry Prolactinoma Morphology Clinical Course Additional Notes Diff Dx Well-circumscribed lesion Often compress optic chiasm If Invasive: foci of hemorrhage & necrosis Relatively uniform, polygonal cells arrayed in sheets or cords. Sparse reticulin (CT) F(x)al status CANNOT be predicted by histologic appearance Weakly acidophilic or chromophobic cells PRL w/in secretory granules Endocrine abnormalities & mass FX Radiographic abnormalities of sella turcica Visual field abnormalities— bitemporal hemianopsia Elev’d intracranial pressure—w/ HA, N/V Peak incidence 30s-50s Assoc’d w/ MEN 1 Micro < 1 cm in diameter Macro >1cm in diameter Acute hemorrhage into an adenoma=pituitary apoplexy Hyperplasia of pituitary Hyperprolactinemia—amenorrhea, galactorrhea, loss of libido, and infertility Most frequent hyperf(x)ing pit. Adenoma (lactotrophs) Serum [PRL] proportional to size of adenoma Ages 20-40, more freq Dx in women HyperPRL: Pregnancy Lactating ♀ Lactotroph hyperplasia Stalk effect from other masses Drugs: DA receptor antagonists (phenothiazines, haldol), reserpine, estrogens Renal failure Hypothyroidism Tx: bromocriptine—causes lesions to diminish in size Growth Hormone Adenoma Corticotroph Cell Adenomas Granulated cells, acidophilic or chromophobic Immunohistochemical stains demo GH w/in cyto of neoplastic cells Small microadenomas Basophilic or chromophobic Stain w/ PAS Produce XS ACTH If in kids b4 epiphysis close: gigantism—gen’d increase in body size, disprop. Long arms and legs If inc’d levels of GH after closure: Acromegaly—most conspicuous in skin & soft tissues, hyperostosis ini spine & hips, prognathism XS ACTH—hypercortisolism (Cushing syndrome) Hyperpigmentation due to inc’d ACTH Mutant GTPase? GH excess correlated w/: gonadal dysf(x), DM, gen’d muscle weakness, HTN, arthritis, CHF, & inc’d risk of GI cancers. Tx: surgical removal thru transphenoidal approach, radiation therapy, or drug therapy Nelson syndrome: when large destructive adenomas develop after surgical removal of the adrenal glands for Tx of Cushing syndrome Condition Morphology Clinical Course Diabetes Insipidus ADH deficiency Polyuria, polydipsia Excretion of large volumes of dilute urine w/ low specific gravity Inc’d serum Na Inc’d serum osmolality Head trauma Tumors Inflamm d/o of hypothalamus & pituitary Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH) XS ADH Hyponatremia Cerebral edema Neurologic dysf(x) Normal blood volume, but total body water is increased Secretion of ectopic ADH by SCLC, nonneoplastic dz of lung, & local injury to hypothalamus or posterior pituitary 1. Diffuse hyperplasia of thyroid gland assoc’d w/ Graves dz 2. Ingestion of exogenous TH 3. Hyperf(x)al multinodular goiter 4. Hyperf(x)al adenoma of the thyroid 5. Thyroiditis 6. Ovarian teratoma Radiation injury, Surgical ablation, Hashimoto Thyroiditis, Iodine deficiency Drugs (Li, P-ASA), Pituitary lesions reducing TSH secretion, Hypothalamic lesions, Hemochromatosis, Amyloidosis, Sarcoidosis Hyperthyroidism Elevated levels of free T3 & T4 Low TSH in primary Hypothyroidism Nervousness Palpitations Rapid pulse, cardiomegaly Fatigability Muscular weakness (prox) Wt loss w/ good appetite Diarrhea Heat intolerance Warm skin XSive perspiration Emotional lability Menstrual changes Fine tremor of the hand Inability to concentrate Insomnia, osteoporosis Cretinism myxedema Additional Notes Cardiac manifestations are the earliest & most consistent features Thyrotoxic cardiomyopathy A normal rise in TSH after admin’d of TRH excludes secondary Diff Dx Condition Morphology Clinical Course Cretinism Hypothyroidism in infancy or early childhood Myxedema Hypothyroidism in older kids and adults Imprd devmnt skeletal system & CNS—severe MR, short stature, coarse facial features, a protruding tongue, & umbilical hernia Vary with age of onset Slowing of physical & mental activity Gen’d fatigue, Apathy Mental sluggishness Slowed speech & mental f(x)s Listless, cold intolerance SOB, dec’d exercise capacity Constipation Decreased sweating Edema Broadening & coarsening of facial features Enlargement of the tongue Deepening of the voice Additional Notes Diff Dx Dietary iodine deficiency Maternal thyroid deficiency Dec’d serum [T3] & [T4] Condition Hashimoto Thyroiditis Subacute (granulomatous) Thyroiditis Pathogenesis Morphology Clinical Course Diffusely enlarged gland Capsule is intact Well-demarcated margins Pale, gray-tan, firm, & somewhat nodular Mononuclear infiltrate—small lymphs, PCs Well-dev’d germinal ctrs Hurthle cells Inc’d interstital CT Fibrosis does NOT extend beyond capsule Painless enlargement of the gland Hypothyroidism May be preceded by transient thyrotoxicosis Involved areas are frim & yellow-white and stand out from more rubbery, normal brown thyroid substance Changes are patchy PMNs forming microabscesses Multinucleate giant cells Hx of URI b4 onset? Sudden or gradual Pain in the neck, which may radiate to the upper neck, jaw, throat or ears, particularly when swallowing. Fever, fatige, malaise, anorexia, and myalgia Elev’d free T4 & T3 levels Low TSH Decreased radioactive uptake Abs to thyroglobulin & thyroid Peroxidase, TSH receptor, possible iodine transporter High serum T3 & T4 Low serum TSH Low radioactive uptake Additional Notes Inc’d risk for dev’ing B-cell lymphomas Most common cause of hypothyroidism Gradual thyroid failure Autoimmune destruxn of gland Ages: 45-65 More common in women HLA-DR5, HLA-DR3 Primarily a defect in T cells Apoptosis med’d by FasFasL system (induced by IL1β) Ages:30-50 More common in women Caused by a viral infexn or postviral inflamm process Peaks in summer HLA-B35 Condition Pathogenesis Subacute Lymphocytic Thryoiditis Graves Dz Diffuse Nontoxic (simple) goiter Multinodular goiter Morphology Clinical Course Thyroid normal on gross inspexn Multifocal inflamm infiltrate—small lymphs, patchy disruption, & collapse of thyroid follicles Painless Mild hyperthyroidism OR goitrous enlargement High serum T3 & T4 Low serum TSH Low radioactive uptake Elev’d levels of Abs to thyroglobulin & thyroid Peroxidase Autoimmune disorder by Symmetrically enlarged Thyroid enlargement AutoAbs to the TSH receptor Diffuse hypertrophy & hyperplasia Audible bruit over thyroid or to thyroid-stimulating Igs of follicle epithelial cells Characteristic wide, staring gaze and lid lag Too many cells Colloid w/in lumen is pale w/ scalloped Exophthalmos margins Proptosis Pretibial myxedema—scaly thickening & Tissues of orbit are edematous induration of skin Involves entire gland w/o producing nodularity Iodine deficiency Irregular enlargment of thyroid Produce the most extreme thyroid nodules Hyperplastic stage Colloid involution Multilobulated, asymmetrically enlarged gland Intrathoracic or plunging goiter Irregular nodules containing variable amts of brown, gelatinous colloid Colloid rich follicles lined by flattened, inactive epithelium and areas of follicular epithelial hypertrophy and hyperplasia Additional Notes Middle-aged women, esp postpartum HLA-DR3 & DR5 Most common cause of endogenous hyperthyroidism Ages: 20-40 Women 7X more common HLA-B8 & DR3 High serum T3 & T4 Low serum TSH Increased radioactive uptake Elev’d TSH Sx caused by mass FX—may cause airway obstruxn, dysphagia, and compression of large vessels in the neck and upper thorax Plummer syndrome— hyperthyroidism w/ toxic multinodular goiter Condition Pathogenesis Morphology Clinical Course Additional Notes