Evolution Unit Review
... 33. The dark frogs had to have greater __________________ to survive and reproduce. A. Adaptation B. Fitness C. Coloration 34. The change in the frog population is a result of a darkening of the pond water they live in. The process that caused this to happen is called? A. Genetic drift B. Gene flow ...
... 33. The dark frogs had to have greater __________________ to survive and reproduce. A. Adaptation B. Fitness C. Coloration 34. The change in the frog population is a result of a darkening of the pond water they live in. The process that caused this to happen is called? A. Genetic drift B. Gene flow ...
Process of Evolution
... Theory—in everyday speech, an untested hypothesis or a guess Evolutionary theory is not a single hypothesis It refers to our understanding of the processes that result in genetic changes in populations over time and to our use of that understanding to interpret changes we observe in natural ...
... Theory—in everyday speech, an untested hypothesis or a guess Evolutionary theory is not a single hypothesis It refers to our understanding of the processes that result in genetic changes in populations over time and to our use of that understanding to interpret changes we observe in natural ...
Natural Selection and Evolution
... mechanism for evolution: Some variation in heritable characteristics exists within every species, some of these characteristics give individuals an advantage over others in surviving and reproducing, and the advantaged offspring, in turn, are more likely than others to survive and reproduce. The pro ...
... mechanism for evolution: Some variation in heritable characteristics exists within every species, some of these characteristics give individuals an advantage over others in surviving and reproducing, and the advantaged offspring, in turn, are more likely than others to survive and reproduce. The pro ...
A. Darwinian
... __B__ The orange and black pattern of a Monarch butterfly serves as a warning to sharp-eyed birds that the Monarch is poisonous to eat and tastes bad. Individuals with the brightest color pattern were more likely to warn off birds and survive to reproduce than those with a dull or medium color patte ...
... __B__ The orange and black pattern of a Monarch butterfly serves as a warning to sharp-eyed birds that the Monarch is poisonous to eat and tastes bad. Individuals with the brightest color pattern were more likely to warn off birds and survive to reproduce than those with a dull or medium color patte ...
Evolution Summary
... Darwin did not know was how heritable traits were passed down through each generation. The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance and evolution. Genetics supports Darwin’s ideas. Scientists know that genes control traits and that many genes have at least t ...
... Darwin did not know was how heritable traits were passed down through each generation. The study of genetics helps scientists understand the relationship between inheritance and evolution. Genetics supports Darwin’s ideas. Scientists know that genes control traits and that many genes have at least t ...
Evolution - Marric.us
... These gaps do not indicate weakness in the theory of evolution itself. Rather, they point out uncertainties in our understanding of exactly ...
... These gaps do not indicate weakness in the theory of evolution itself. Rather, they point out uncertainties in our understanding of exactly ...
Ideas that shaped Darwin`s thinking
... These gaps do not indicate weakness in the theory of evolution itself. Rather, they point out uncertainties in our understanding of exactly ...
... These gaps do not indicate weakness in the theory of evolution itself. Rather, they point out uncertainties in our understanding of exactly ...
Theory of Evolution
... The first part of the name—Ursus—is the genus to which the organism belongs. A genus is a group of similar species. The genus Ursus contains five other species of bears, The second part of a scientific name— maritimus for polar bears—is the species and is often a description of the organism’s habita ...
... The first part of the name—Ursus—is the genus to which the organism belongs. A genus is a group of similar species. The genus Ursus contains five other species of bears, The second part of a scientific name— maritimus for polar bears—is the species and is often a description of the organism’s habita ...
To return to the chapter summary click escape or close this document.
... Lamarck’ Theory of Evolution • Organisms had need/desire to improve • Use and disuse • Inheritance of acquired characteristics ...
... Lamarck’ Theory of Evolution • Organisms had need/desire to improve • Use and disuse • Inheritance of acquired characteristics ...
study guide3 Sp11
... What are the characteristics of the phylum Chordata? the subphylum vertebrata? What is the evolutionary advantage of the notochord? Describe the key adaptations of the different classes of vertebrates studied. What is the evidence that humans evolved from primates? ...
... What are the characteristics of the phylum Chordata? the subphylum vertebrata? What is the evolutionary advantage of the notochord? Describe the key adaptations of the different classes of vertebrates studied. What is the evidence that humans evolved from primates? ...
Name: Gr.12 Biology Unit 3: Evolution (Ch.27) Section A: Multiple
... a. Compare and contrast classic Linnean taxonomy and phylogenetic systems of naming and classifying organisms. b. What are the four main requirements for natural selection to occur? List and explain each. Who is credited for coming up with idea of natural selection? (5) c. What is meant by “prezygot ...
... a. Compare and contrast classic Linnean taxonomy and phylogenetic systems of naming and classifying organisms. b. What are the four main requirements for natural selection to occur? List and explain each. Who is credited for coming up with idea of natural selection? (5) c. What is meant by “prezygot ...
1) UNIT 5 MechanismsOfEvolution
... When individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle Example: Beaks of finches. If a beak is very small, the bird can easily pick up small seeds. If a beak is very large, the bird can easily crack large seeds. If a beak is medium size, ...
... When individuals at the upper and lower ends of the curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle Example: Beaks of finches. If a beak is very small, the bird can easily pick up small seeds. If a beak is very large, the bird can easily crack large seeds. If a beak is medium size, ...
BLY 303 Lecture Notes, Guest Lecture 10/27/11 (O`Brien) Patterns in
... How can one tell if a character is uniquely derived or homoplasious? Occasionally the fossil record helps The best estimate of the true phylogeny is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes The best phylogenic hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest homoplasious changes ...
... How can one tell if a character is uniquely derived or homoplasious? Occasionally the fossil record helps The best estimate of the true phylogeny is the one that requires the fewest evolutionary changes The best phylogenic hypothesis is the one that requires the fewest homoplasious changes ...
Biology 5 Final Review
... a. Gene – segment(piece) of DNA –holds instructions for assembling proteins b. Codon – 3 nitrogen bases coding for a single amino acid c. Genetic code – sequence of codons that code for specific amino acids (DNA) d. Mutation – permanent change in a cells’ DNA 24. What does the lac operon control? Br ...
... a. Gene – segment(piece) of DNA –holds instructions for assembling proteins b. Codon – 3 nitrogen bases coding for a single amino acid c. Genetic code – sequence of codons that code for specific amino acids (DNA) d. Mutation – permanent change in a cells’ DNA 24. What does the lac operon control? Br ...
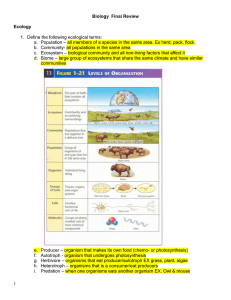
Ecology Unit Outline
... 2. Explain what a binomial nomenclature is and how it is correctly written. Evolution (Chapter 15 & 16) 3. Define the Theory of Evolution. ...
... 2. Explain what a binomial nomenclature is and how it is correctly written. Evolution (Chapter 15 & 16) 3. Define the Theory of Evolution. ...
evolution - kendricknovak
... • Back in England he looked at his findings – Tortoises and Finches ...
... • Back in England he looked at his findings – Tortoises and Finches ...
Notes on Evolution
... The Origins of Life (Modern) a. Biogenesis i. The idea that life can only arise from preexisting life b. Heterotroph hypothesis i. Conditions on early Earth were very different ii. NO OXYGEN OR CARBON DIOXIDE iii. Random chemical reactions gave rise to anaerobes which increased carbon dioxide in the ...
... The Origins of Life (Modern) a. Biogenesis i. The idea that life can only arise from preexisting life b. Heterotroph hypothesis i. Conditions on early Earth were very different ii. NO OXYGEN OR CARBON DIOXIDE iii. Random chemical reactions gave rise to anaerobes which increased carbon dioxide in the ...
PBS: What Darwin Never Knew Name: Biology Date: Period: 1
... 32. A study of human and chimp DNA sequences show that the differences weren’t in the actual genes, but in the ______________ that direct the genes. More than half of these switches are near a gene that involves the __________. That gene was different in 2 letters between the chimp and the chicken, ...
... 32. A study of human and chimp DNA sequences show that the differences weren’t in the actual genes, but in the ______________ that direct the genes. More than half of these switches are near a gene that involves the __________. That gene was different in 2 letters between the chimp and the chicken, ...
Overproduction
... Genetics and Natural Selection • Traits are controlled by genes, which are inherited during reproduction. • A population can be thought of as a gene pool. • Evolution through Natural Selection acts on an organism’s phenotype (traits or characteristics) not its genotype. As a result, it influences th ...
... Genetics and Natural Selection • Traits are controlled by genes, which are inherited during reproduction. • A population can be thought of as a gene pool. • Evolution through Natural Selection acts on an organism’s phenotype (traits or characteristics) not its genotype. As a result, it influences th ...
Evolution Directed Reading
... 3. What separates the Kaibab and Abert squirrel species? Grand Canyon Page 182-183 4. What are the 2 patterns that scientists have developed to describe the pace of evolution? ...
... 3. What separates the Kaibab and Abert squirrel species? Grand Canyon Page 182-183 4. What are the 2 patterns that scientists have developed to describe the pace of evolution? ...
Aim #75: How does evolution occur by natural
... • Struggle For Survival • Best Adapted To Survive • Darwin did NOT have knowledge of the genetic basis of inheritance ...
... • Struggle For Survival • Best Adapted To Survive • Darwin did NOT have knowledge of the genetic basis of inheritance ...
CPE 2nd semester exam Review
... Compare/contrast divergent and convergent evolution and the structures they lead to Give examples of divergent evolution, convergent evolution, coevolution, adaptive radiation and artificial selection Give examples of anatomical structures that have changed through evolution Interpret diagra ...
... Compare/contrast divergent and convergent evolution and the structures they lead to Give examples of divergent evolution, convergent evolution, coevolution, adaptive radiation and artificial selection Give examples of anatomical structures that have changed through evolution Interpret diagra ...
The Theory of Evolution
... – V = Variation: All life forms vary genetically within a population. It is this genetic variation upon which selection works. – I = Inheritance: Genetic traits are inherited from parents and are passed on to offspring. – S = Selection: Organisms with traits that are favorable to their survival get ...
... – V = Variation: All life forms vary genetically within a population. It is this genetic variation upon which selection works. – I = Inheritance: Genetic traits are inherited from parents and are passed on to offspring. – S = Selection: Organisms with traits that are favorable to their survival get ...
Introduction to evolution

Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. Biological populations evolve through genetic changes that correspond to changes in the organisms' observable traits. Genetic changes include mutations, which are caused by damage or replication errors in an organism's DNA. As the genetic variation of a population drifts randomly over generations, natural selection gradually leads traits to become more or less common based on the relative reproductive success of organisms with those traits.The age of the Earth is about 4.54 billion years old. The earliest undisputed evidence of life on Earth dates at least from 3.5 billion years ago, during the Eoarchean Era after a geological crust started to solidify following the earlier molten Hadean Eon. There are microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. Other early physical evidence of a biogenic substance is graphite in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland. More than 99 percent of all species, amounting to over five billion species, that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 10 million to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented and over 86 percent have not yet been described.Evolution does not attempt to explain the origin of life (covered instead by abiogenesis), but it does explain how the extremely simple early lifeforms evolved into the complex ecosystem that we see today. Based on the similarities between all present-day organisms, all life on Earth originated through common descent from a last universal ancestor from which all known species have diverged through the process of evolution. All individuals have hereditary material in the form of genes that are received from their parents, then passed on to any offspring. Among offspring there are variations of genes due to the introduction of new genes via random changes called mutations or via reshuffling of existing genes during sexual reproduction. The offspring differs from the parent in minor random ways. If those differences are helpful, the offspring is more likely to survive and reproduce. This means that more offspring in the next generation will have that helpful difference and individuals will not have equal chances of reproductive success. In this way, traits that result in organisms being better adapted to their living conditions become more common in descendant populations. These differences accumulate resulting in changes within the population. This process is responsible for the many diverse life forms in the world.The forces of evolution are most evident when populations become isolated, either through geographic distance or by other mechanisms that prevent genetic exchange. Over time, isolated populations can branch off into new species.The majority of genetic mutations neither assist, change the appearance of, nor bring harm to individuals. Through the process of genetic drift, these mutated genes are neutrally sorted among populations and survive across generations by chance alone. In contrast to genetic drift, natural selection is not a random process because it acts on traits that are necessary for survival and reproduction. Natural selection and random genetic drift are constant and dynamic parts of life and over time this has shaped the branching structure in the tree of life.The modern understanding of evolution began with the 1859 publication of Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species. In addition, Gregor Mendel's work with plants helped to explain the hereditary patterns of genetics. Fossil discoveries in paleontology, advances in population genetics and a global network of scientific research have provided further details into the mechanisms of evolution. Scientists now have a good understanding of the origin of new species (speciation) and have observed the speciation process in the laboratory and in the wild. Evolution is the principal scientific theory that biologists use to understand life and is used in many disciplines, including medicine, psychology, conservation biology, anthropology, forensics, agriculture and other social-cultural applications.