These mountains are formed by compression Fault structures is a
... •Vesuvian-very explosive after a dormant period with ash/gas clouds and gas-filled lava. ...
... •Vesuvian-very explosive after a dormant period with ash/gas clouds and gas-filled lava. ...
Volcanoes
... Vents: holes in the crust where magma and gas are released. Plug: mass of solid lava that blocks a volcano’s vent. Geothermal energy: power made from heat within the Earth. Geyser: fountain of hot water and steam erupting from the ground in a volcanic area. ...
... Vents: holes in the crust where magma and gas are released. Plug: mass of solid lava that blocks a volcano’s vent. Geothermal energy: power made from heat within the Earth. Geyser: fountain of hot water and steam erupting from the ground in a volcanic area. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... • A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called aa flow. • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced i ...
... • A lava flow with a surface of rough, jagged blocks and sharp, angular projections is called aa flow. • As the temperature of lava increases, the viscocity decreases. • Highly explosive volcanoes tend to have magma with high silica, high viscosity, and higher gas content. • The particles produced i ...
Earthquake, Volcano and Mountain Review Sheet
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
Our Dynamic Earth
... • Volcanoes are mountains with openings in Earth’s crust through which magma, gases, and ash reach Earth’s surface. • Volcanoes can change Earth’s surface. • When the magma erupts from the volcano the top of the mountain can be changed, either built up or exploded off. ...
... • Volcanoes are mountains with openings in Earth’s crust through which magma, gases, and ash reach Earth’s surface. • Volcanoes can change Earth’s surface. • When the magma erupts from the volcano the top of the mountain can be changed, either built up or exploded off. ...
Buchite type glasses in the West Eifel Volcanic Field (Germany
... represent both local and regional electric fields. The most widespread SP anomalies associated with hydrothermal and subsurface water flow (steaming potential) [2]. Under the influence of electric energy electrochemical processes are inevitable. These processes include: the extraction of elements fr ...
... represent both local and regional electric fields. The most widespread SP anomalies associated with hydrothermal and subsurface water flow (steaming potential) [2]. Under the influence of electric energy electrochemical processes are inevitable. These processes include: the extraction of elements fr ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Student Sheet 24.1c (continued) 13. This map shows where geologists discovered deep layers of ash in the soil around Mt. Hekia, an active volcano in Iceland. The numbers represent different thicknesses (in meters) of ash deposited around the volcano. Geologists believe the ash deposits formed when M ...
... Student Sheet 24.1c (continued) 13. This map shows where geologists discovered deep layers of ash in the soil around Mt. Hekia, an active volcano in Iceland. The numbers represent different thicknesses (in meters) of ash deposited around the volcano. Geologists believe the ash deposits formed when M ...
2_2013_papervolcanoactivity
... relationship between the internal structure of the volcano and its exterior shape and features. This exercise may give the student an insight as to how a stratovolcano is formed. ...
... relationship between the internal structure of the volcano and its exterior shape and features. This exercise may give the student an insight as to how a stratovolcano is formed. ...
Section 1 - kjpederson
... 5. magma chamber: the pocket beneath a volcano where magma collects 6. pipe: a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 7. pyroclastic flow: the expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption 8. vent: the opening through which m ...
... 5. magma chamber: the pocket beneath a volcano where magma collects 6. pipe: a long tube through which magma moves from the magma chamber to Earth’s surface 7. pyroclastic flow: the expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption 8. vent: the opening through which m ...
Directed Reading
... gently sloping sides b. structure that is formed from lava and pyroclastic material ejected during a volcanic eruption c. volcano that is rarely more than a few hundred meters high and has steep slope angles that can be close to 40° d. volcano that is made from alternating layers of hardened lava fl ...
... gently sloping sides b. structure that is formed from lava and pyroclastic material ejected during a volcanic eruption c. volcano that is rarely more than a few hundred meters high and has steep slope angles that can be close to 40° d. volcano that is made from alternating layers of hardened lava fl ...
Challenge and Extension - Effingham County Schools
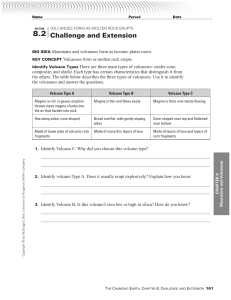
... 8.2 Challenge and Extension BIG IDEA Mountains and volcanoes form as tectonic plates move. KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it f ...
... 8.2 Challenge and Extension BIG IDEA Mountains and volcanoes form as tectonic plates move. KEY CONCEPT Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts. Identify Volcano Types There are three main types of volcanoes: cinder cone, composite, and shield. Each type has certain characteristics that distinguish it f ...
What IS A VOLCANO?
... Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks erupt through a volcano and come out as lava. The temperature of magma is extremely high while that of lava are lower as it cools down when it comes out under the ...
... Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks erupt through a volcano and come out as lava. The temperature of magma is extremely high while that of lava are lower as it cools down when it comes out under the ...
Ch 6 power point
... • More explosive than Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km • Produce pyroclastic flows – Hot volcanic fragments (tephra) that, buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow very rapidly ...
... • More explosive than Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km • Produce pyroclastic flows – Hot volcanic fragments (tephra) that, buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow very rapidly ...
Учитель: Размахнина О
... superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and form giant bubbles of liquid 4______________ called magma 5_______________. This magma is lighter than the surrounding rock, so it rises up, finding cracks and weakness in the Ea ...
... superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and form giant bubbles of liquid 4______________ called magma 5_______________. This magma is lighter than the surrounding rock, so it rises up, finding cracks and weakness in the Ea ...
Directed Reading
... b. the distance from the top of the volcano to its base. c. the viscosity of magma. d. the geologic age of the volcano. ...
... b. the distance from the top of the volcano to its base. c. the viscosity of magma. d. the geologic age of the volcano. ...
Volcano Glossary III
... An explosive eruption that ejects new lava fragments that do not become rounded while in the air. This is possible because the lava is too viscous or already solidified. Vulcanian eruptions generally eject a large proportion of volcanic ash. Andesitic and dacitic magmas are most common because their ...
... An explosive eruption that ejects new lava fragments that do not become rounded while in the air. This is possible because the lava is too viscous or already solidified. Vulcanian eruptions generally eject a large proportion of volcanic ash. Andesitic and dacitic magmas are most common because their ...
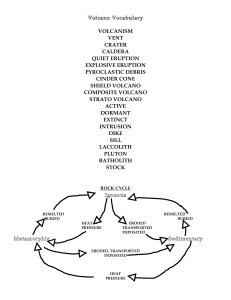
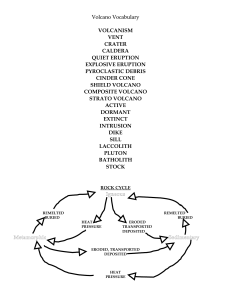
volcanism vent crater caldera quiet eruption explosive
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
Volcanoes - leavingcertgeography
... Pyroclastic flows (also called ash-flows) are high speed avalanches of hot ash, rock fragments, and gas which move down the sides of a volcano during explosive eruptions. These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at hi ...
... Pyroclastic flows (also called ash-flows) are high speed avalanches of hot ash, rock fragments, and gas which move down the sides of a volcano during explosive eruptions. These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at hi ...
Tectonic Activity
... Pyroclastic flows (also called ash-flows) are high speed avalanches of hot ash, rock fragments, and gas which move down the sides of a volcano during explosive eruptions. These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at hi ...
... Pyroclastic flows (also called ash-flows) are high speed avalanches of hot ash, rock fragments, and gas which move down the sides of a volcano during explosive eruptions. These flows occur when the vent area or ash column collapses. Because pyroclastic flows can reach 1500 degrees F and travel at hi ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... blast from the fissure or vent. • Shield Volcano- covers a wide area and generally result from lava eruptions. • Cinder Cone- formed from explosive eruption. • Composite Volcano- results from altering layers of pyroclastic material and lava. ...
... blast from the fissure or vent. • Shield Volcano- covers a wide area and generally result from lava eruptions. • Cinder Cone- formed from explosive eruption. • Composite Volcano- results from altering layers of pyroclastic material and lava. ...
Volcano - Greenwich Central School
... An area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it. ...
... An area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust above it. ...
Volcano Vocabulary - watertown.k12.wi.us
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
... The height is usually less than 600 feet (200 meters). The Cinder Cone tends to erode quickly and may bleed from the bottom or sides- called a "flank eruption". These volcanoes do not often cause damage in that they are small, intermittent explosions of Felsic lava. Examples are Wizard Island (Crate ...
Document
... DIKES AND SILLS Magma can force its way across or between rock layers Magma that forces itself across rock layers hardens into a dike When magma squeezes between horizontal layers of rock, it forms a sill Dikes and sills are examples of igneous intrusions An intrusion is always younger th ...
... DIKES AND SILLS Magma can force its way across or between rock layers Magma that forces itself across rock layers hardens into a dike When magma squeezes between horizontal layers of rock, it forms a sill Dikes and sills are examples of igneous intrusions An intrusion is always younger th ...
What mainly controls eruptive style? Viscosity in magma 2. Eruptive
... ex: Battleground Lake, Ubehebe (CA) ...
... ex: Battleground Lake, Ubehebe (CA) ...
Potrillo volcanic field

The Potrillo volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field located on the Rio Grande Rift, in a portion of its rift valley, in southern New Mexico, United States and northern Chihuahua, Mexico. The volcanic field lies 22 miles (35 km) southwest of Las Cruces, New Mexico.