IGNEOUS ROCKS & VOLCANISM - Missouri State University
... • active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes and volcanic areas • active--eruption can occur in the near future--Mt. St. Helens and other Cascade mountains are examples • dormant--presently inactive but believed capable of future eruptions • extinct--expected not to erupt again • Origin and global distr ...
... • active, dormant, and extinct volcanoes and volcanic areas • active--eruption can occur in the near future--Mt. St. Helens and other Cascade mountains are examples • dormant--presently inactive but believed capable of future eruptions • extinct--expected not to erupt again • Origin and global distr ...
Review for Exam 2
... of eruptions make these landforms, and how are these different from traditional volcanic eruptions? 9. Discuss the various volcanic hazards in terms of their potential short- and long-term impacts on humans. 10. What is a supervolcano? Give an example of one. 11. Discuss what is learned from a geolo ...
... of eruptions make these landforms, and how are these different from traditional volcanic eruptions? 9. Discuss the various volcanic hazards in terms of their potential short- and long-term impacts on humans. 10. What is a supervolcano? Give an example of one. 11. Discuss what is learned from a geolo ...
Volcanoes
... A place where molten rock, hot gases, and solid rock erupt through an opening in the crust. It is also the mountain built up by these materials. ...
... A place where molten rock, hot gases, and solid rock erupt through an opening in the crust. It is also the mountain built up by these materials. ...
Chapter 2, Section 7
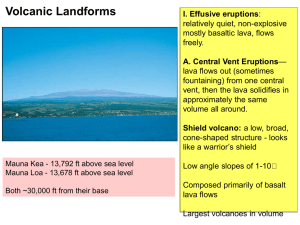
... broad, gently sloping volcanic cone with a flat-dome shape, usually several tens or hundreds of square miles in extent. ...
... broad, gently sloping volcanic cone with a flat-dome shape, usually several tens or hundreds of square miles in extent. ...
volcanoes
... HOT SPOT - Area where magma from deep in the mantle MELTS through crust above it. EXTINCT - A volcano that is UNLIKELY to erupt again. ISLAND ARC - String of ISLANDS formed by volcanoes along a deep ocean trench. (Has the word Island) CALDERA - Large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof ...
... HOT SPOT - Area where magma from deep in the mantle MELTS through crust above it. EXTINCT - A volcano that is UNLIKELY to erupt again. ISLAND ARC - String of ISLANDS formed by volcanoes along a deep ocean trench. (Has the word Island) CALDERA - Large hole at the top of a volcano formed when the roof ...
Course Learning Outcomes for Unit IV Reading Assignment Igneous
... collisions). The “Ring of Fire” describes the pattern of volcanoes found around the Pacific Basin. This activity is a result of oceanic subduction. Volcanoes refer to "the opening or vent through which the molten rock and associated gases are expelled” (USGS, 1999). Pressure can push magma to the su ...
... collisions). The “Ring of Fire” describes the pattern of volcanoes found around the Pacific Basin. This activity is a result of oceanic subduction. Volcanoes refer to "the opening or vent through which the molten rock and associated gases are expelled” (USGS, 1999). Pressure can push magma to the su ...
Volcanic Terms - Hamilton Field Naturalists Club
... Lava: A liquid flow of molten rock on the surface. The basaltic lava from the Western District volcanoes was hot (about 1100 degrees Celsius) and quite fluid and so could travel for long distances. On the sides of some craters we can find local 'lava flows' that were accumulations of spatter so hot ...
... Lava: A liquid flow of molten rock on the surface. The basaltic lava from the Western District volcanoes was hot (about 1100 degrees Celsius) and quite fluid and so could travel for long distances. On the sides of some craters we can find local 'lava flows' that were accumulations of spatter so hot ...
Slide 1
... 1. Why can’t the arcs* be more like the ridges? • Whenever I think of some possible new tectonicvolcanic/geochemical relationship for Central America, I check the RIDGE site and/or review the extensive literature on Mid-ocean ridges. The global set of convergent plate margins (CPMs) or arcs seems t ...
... 1. Why can’t the arcs* be more like the ridges? • Whenever I think of some possible new tectonicvolcanic/geochemical relationship for Central America, I check the RIDGE site and/or review the extensive literature on Mid-ocean ridges. The global set of convergent plate margins (CPMs) or arcs seems t ...
Volcanic Eruptions - Elliott County Schools
... • The lava and pyroclastic material that are ejected during volcanic eruptions build up around the vent and form volcanic cones. • The funnel-shaped pit at the top of a volcanic vent is known as a crater. • A crater usually becomes wider as weathering and erosion break down the walls of the crater a ...
... • The lava and pyroclastic material that are ejected during volcanic eruptions build up around the vent and form volcanic cones. • The funnel-shaped pit at the top of a volcanic vent is known as a crater. • A crater usually becomes wider as weathering and erosion break down the walls of the crater a ...
2 Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... explosive eruptions. As it piles up, it forms a mountain with steep slopes. Cinder cones are small. Most of them erupt for only a short time. For example, Paricutín is a cinder cone volcano in Mexico. In 1943, Paricutín appeared in a cornfield. It erupted for only nine years. Most cinder cone volcan ...
... explosive eruptions. As it piles up, it forms a mountain with steep slopes. Cinder cones are small. Most of them erupt for only a short time. For example, Paricutín is a cinder cone volcano in Mexico. In 1943, Paricutín appeared in a cornfield. It erupted for only nine years. Most cinder cone volcan ...
Volacano - OnCourse
... • Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes and lava plateaus. • Shield Volcanoes- Quiet eruptions gradually build up a gently sloping mountain. • Cinder Cone Volcanoes- Ash, cinders ...
... • Volcanic eruptions create landforms made of lava, ash and other materials. These landforms include shield volcanoes, cinder cone volcanoes, composite volcanoes and lava plateaus. • Shield Volcanoes- Quiet eruptions gradually build up a gently sloping mountain. • Cinder Cone Volcanoes- Ash, cinders ...
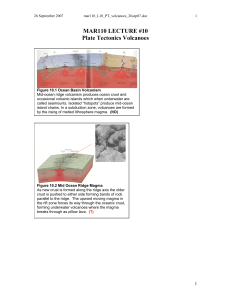
MAR110 LECTURE #10 Plate Tectonics Volcanoes
... Deep magma chambers - formed by the friction between the subducting Juan de Fuca plate and the North American plate – and feed the active volcanoes and spawn earthquakes in the Cascade Range. An active erupting volcano produces volcanic “bombs” (small to large pieces of solidified magma) and at time ...
... Deep magma chambers - formed by the friction between the subducting Juan de Fuca plate and the North American plate – and feed the active volcanoes and spawn earthquakes in the Cascade Range. An active erupting volcano produces volcanic “bombs” (small to large pieces of solidified magma) and at time ...
Quiz Three (2:00 to 2:05 PM) - University of South Alabama
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
... hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth quickly and is still hot (up to 1800 °C) and fluid (low viscosity). Lava erupted at convergent plate boundaries and continental hotspots has made it to the surface of the Earth very slowly. It is cooler (as low as 800 °C) and very contaminated by coun ...
38Beneath the Earth`s Surface
... On the Earth’s Surface A volcano is an opening in the earth from which magma and gas erupt. Gases within the magma build up enough pressure to force it upwards and eventually through gaps in the earth’s surface, causing an eruption. Once magma has erupted onto the earth’s surface, it is called lava ...
... On the Earth’s Surface A volcano is an opening in the earth from which magma and gas erupt. Gases within the magma build up enough pressure to force it upwards and eventually through gaps in the earth’s surface, causing an eruption. Once magma has erupted onto the earth’s surface, it is called lava ...
Teacher`s Guide - Discovery Education
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
... What important function do volcanoes perform for the Earth? (Volcanoes act like cooling vents by releasing heat from Earth's core.) ...
Volcanic Eruptions 2 - Earth Science > Home
... generally felsic lavas. Felsic lavas often contain a lot of trapped gases, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide. The gas in the lava creates pressure inside the volcano, like the bubbles in a can of soda. The pressure can make the volcano erupt explosively. In an explosive eruption, chunks of lava ...
... generally felsic lavas. Felsic lavas often contain a lot of trapped gases, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide. The gas in the lava creates pressure inside the volcano, like the bubbles in a can of soda. The pressure can make the volcano erupt explosively. In an explosive eruption, chunks of lava ...
Volcano Types (39)
... • Quiet eruptions form volcanoes over hot spots such as the Hawaiian volcanoes • Lavas that flow underwater form pillow lava formations • http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=gn_IW5V sxaw ...
... • Quiet eruptions form volcanoes over hot spots such as the Hawaiian volcanoes • Lavas that flow underwater form pillow lava formations • http://www.youtube.co m/watch?v=gn_IW5V sxaw ...
Volcanoes Part I: classification, deposits, and their distribution
... the region of subduction. ...
... the region of subduction. ...
Application of the Acronyms
... An igneous rock was lifted from the surface of a fresh volcanic lava flow of basalt. Before inspection you could logically determine that it has ________ crystals. ( no, large, small, huge) ...
... An igneous rock was lifted from the surface of a fresh volcanic lava flow of basalt. Before inspection you could logically determine that it has ________ crystals. ( no, large, small, huge) ...
Volcanoes
... A volcano is shaped like a mountain constructed from lava and/or pyroclastics. They erupt when “magma is generated by partial melting of the rock peridotite in the upper mantle to form magma with a basaltic composition”, ultimatly resulting in “buoyant molten rock will rise toward the surface” (Foun ...
... A volcano is shaped like a mountain constructed from lava and/or pyroclastics. They erupt when “magma is generated by partial melting of the rock peridotite in the upper mantle to form magma with a basaltic composition”, ultimatly resulting in “buoyant molten rock will rise toward the surface” (Foun ...
Test 4/Homework 4 (Chapter 9 Volcanoes)
... Most explosive volcanoes relation to plate boundaries Composite volcanoes (Definition, location w/ regard to plate boundary, type of lava) Temperature and chemical composition relation to volcanic eruption Correlate silica content (SiO2) with viscosity of a magma/lava Correlate magma/lava viscosity ...
... Most explosive volcanoes relation to plate boundaries Composite volcanoes (Definition, location w/ regard to plate boundary, type of lava) Temperature and chemical composition relation to volcanic eruption Correlate silica content (SiO2) with viscosity of a magma/lava Correlate magma/lava viscosity ...
Chapter 7 - Florida Gateway College
... Most explosive volcanoes relation to plate boundaries Composite volcanoes (Definition, location w/ regard to plate boundary, type of lava) Temperature and chemical composition relation to volcanic eruption Correlate silica content (SiO2) with viscosity of a magma/lava Correlate magma/lava viscosity ...
... Most explosive volcanoes relation to plate boundaries Composite volcanoes (Definition, location w/ regard to plate boundary, type of lava) Temperature and chemical composition relation to volcanic eruption Correlate silica content (SiO2) with viscosity of a magma/lava Correlate magma/lava viscosity ...
D38 Beneath Earth*s Surface
... small pieces of magma and ash into the air. • The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. • Often cinder cones form on the sides of larger volcanoes. ...
... small pieces of magma and ash into the air. • The magma then cools and hardens as it falls back to the Earth, forming a cinder cone. • Often cinder cones form on the sides of larger volcanoes. ...
Potrillo volcanic field

The Potrillo volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field located on the Rio Grande Rift, in a portion of its rift valley, in southern New Mexico, United States and northern Chihuahua, Mexico. The volcanic field lies 22 miles (35 km) southwest of Las Cruces, New Mexico.