Document
... --both lava flows & tephra --andesitic lava / found “near” coasts --medium amount of silica ...
... --both lava flows & tephra --andesitic lava / found “near” coasts --medium amount of silica ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... form where molten rock is vented at Earth’s surface. ...
... form where molten rock is vented at Earth’s surface. ...
11-Heimaey- Living with Natural Hazards.indd
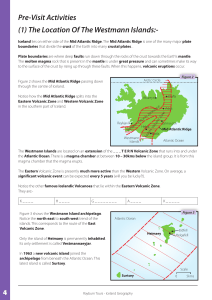
... (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through the rocks of the cru ...
... (1) The Location Of The Westmann Islands:Iceland lies on either side of the Mid Atlantic Ridge. The Mid Atlantic Ridge is one of the many major plate boundaries that divide the crust of the Earth into many crustal plates. . Plate boundaries are where deep faults run down through the rocks of the cru ...
Ch. 7.2 Volcanic Eruptions
... Pyroclastic material results from exploded felsic lava. The type of ...
... Pyroclastic material results from exploded felsic lava. The type of ...
Volcanoes
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
... The word Volcano is derived from the name of the ancient Roman island of Vulcano. The Romans believed that Vulcan, the god of Fire and the maker of weapons, used the volcano on that island to forge his weapons. ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
What do we expect in a volcanic eruption?
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
... • Solids lofted into atm • Lava flows from from others (called some pyroclastics. Better • Range from mafic than fireworks? (e.g. basalt) to • You bet!!! felsic, like all ign rx • Rocks may form from ...
Volcanic
... Magma solidified at great depth (so mineral sizes are large) Plutons (individual magma chambers) Batholiths (merged magma chambers) ...
... Magma solidified at great depth (so mineral sizes are large) Plutons (individual magma chambers) Batholiths (merged magma chambers) ...
Topic 8 Volcanoes
... from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. ...
... from lava fragments called cinders. The lava fragments are ejected from a single vent and accumulate around the vent when they fall back to earth. ...
GEOGRAPHY Chap – 7 VOLCANOES STD. 8 Q1. What is a volcano
... grow into large volcanic hills with alternating layers of lava and ash. They are called composite cones. Q4. How is a crater formed? ...
... grow into large volcanic hills with alternating layers of lava and ash. They are called composite cones. Q4. How is a crater formed? ...
VOLCANO NOTES
... Composite- tens of miles across and ten thousand or more feet in height. They have moderately steep sides and sometimes have small craters in their summits. Volcanologists call these "strato-" or composite volcanoes because they consist of alternating layers of solid lava flows mixed with layers of ...
... Composite- tens of miles across and ten thousand or more feet in height. They have moderately steep sides and sometimes have small craters in their summits. Volcanologists call these "strato-" or composite volcanoes because they consist of alternating layers of solid lava flows mixed with layers of ...
Document
... Match each volcano type listed on the right with the correct description listed on the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
... Match each volcano type listed on the right with the correct description listed on the left. Write the letter in the space provided. You may use the volcanoes listed on the right more than once. ...
Volcanic Eruptions - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
... - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is forced to the Earth’s surface - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano ...
Volcano by jose angel garcia gomez and alejandro cuthy gomez
... hardens into three types of mountains ...
... hardens into three types of mountains ...
Section 13
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Review Page 330
... Describe how calderas form. A caldera forms when the magma chamber of a volcano empties, causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
... Describe how calderas form. A caldera forms when the magma chamber of a volcano empties, causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
Section 13
... Describe how calderas form. A caldera forms when the magma chamber of a volcano empties, causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
... Describe how calderas form. A caldera forms when the magma chamber of a volcano empties, causing the volcanic cone to collapse in upon it, or when magma is ejected violently and the cone is destroyed. ...
Volcanoes I - Faculty Washington
... Define the following terms or phrases: Shield Volcano, Stratovolcano, Flood Basalts, Lahar, Pyroclastics, Lava. Distinguish between the volcanism found over hot spots, subduction zones, and spreading centers in terms of their rock composition, volcano type, magma viscosity, and danger. List an ...
... Define the following terms or phrases: Shield Volcano, Stratovolcano, Flood Basalts, Lahar, Pyroclastics, Lava. Distinguish between the volcanism found over hot spots, subduction zones, and spreading centers in terms of their rock composition, volcano type, magma viscosity, and danger. List an ...
Volcanic hazards in Dante`s Peak
... Evacuation issues (Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines is a good example) Vesuvius and Pompei Eruption prediction Tiltmeter — measures changes in size and shape of volcanoes (remember the bulge that formed on Mt. St. Helens in 1980) Crater vs. caldera Geothermal activity — hot springs, steam, etc. "Micr ...
... Evacuation issues (Mt. Pinatubo in the Philippines is a good example) Vesuvius and Pompei Eruption prediction Tiltmeter — measures changes in size and shape of volcanoes (remember the bulge that formed on Mt. St. Helens in 1980) Crater vs. caldera Geothermal activity — hot springs, steam, etc. "Micr ...
5volcano notes chapter
... Composite volcano-tall cone shaped with layers of lava then layers of ash. Cinder cone volcano-high silica, explosive, steep cone shaped hill Lava plateau-lava runs out of several small cracks, flows and forms a high area. 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcano ...
... Composite volcano-tall cone shaped with layers of lava then layers of ash. Cinder cone volcano-high silica, explosive, steep cone shaped hill Lava plateau-lava runs out of several small cracks, flows and forms a high area. 2. Landforms created by magma include: Volcanic neck-magma hardens in volcano ...
Chapter 6 Volcanoes
... ash and other gases reach upper atmosphere ash and gases spread around globe block sunlight enough to cause surface temp. drops ...
... ash and other gases reach upper atmosphere ash and gases spread around globe block sunlight enough to cause surface temp. drops ...
Potrillo volcanic field

The Potrillo volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field located on the Rio Grande Rift, in a portion of its rift valley, in southern New Mexico, United States and northern Chihuahua, Mexico. The volcanic field lies 22 miles (35 km) southwest of Las Cruces, New Mexico.