Problem set 3
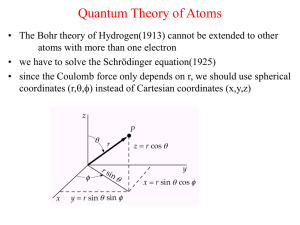
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
... 1. Recall that the angular momentum raising operator is L+ = ~eiφ (∂θ + i cot θ ∂φ ). Use this to find L− . 2. Use the above formulae for L± to find the coordinate representation of the angular momentum basis states Y11 , Y10 and Y1,−1 up to normalization. 3. Write out the 9 equations summarized in ...
phys_syllabi_411-511.pdf
... 3. Schrödinger’s Equation & the Wave-function, _. 4. Born’s Interpretation of _: probability density, expectation values, “states” as eigenfunctions, “observables” as eigenvalues. 5. Particle motion without forces: the free particle, a particle confined to a box, tunneling. 6. Particle motion in a f ...
... 3. Schrödinger’s Equation & the Wave-function, _. 4. Born’s Interpretation of _: probability density, expectation values, “states” as eigenfunctions, “observables” as eigenvalues. 5. Particle motion without forces: the free particle, a particle confined to a box, tunneling. 6. Particle motion in a f ...
Course Poster
... quantum field theories. Applications from: fluid mechanics, elasticity, electromagnetism, atomic and particle physics. ...
... quantum field theories. Applications from: fluid mechanics, elasticity, electromagnetism, atomic and particle physics. ...
Eighth International Conference on Geometry, Integrability and Quantization
... is a better conception. Rather than conceiving the particle as a bulk of fluid, we have supposed that it is composed of pointlike quantum modes. This enabled the construction of our Geometro-Differential Model (G-D-M) for extended particles and its quantization by a method of induced representation ...
... is a better conception. Rather than conceiving the particle as a bulk of fluid, we have supposed that it is composed of pointlike quantum modes. This enabled the construction of our Geometro-Differential Model (G-D-M) for extended particles and its quantization by a method of induced representation ...
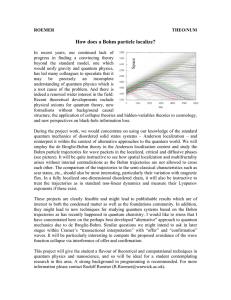
How does a Bohm particle localize?
... arises without internal contradictions as the Bohm trajectories are not allowed to cross each other. The comparison of the trajectories to the semi-classical characteristics such as scar states, etc., should also be most interesting, particularly their variation with magnetic flux. In a fully locali ...
... arises without internal contradictions as the Bohm trajectories are not allowed to cross each other. The comparison of the trajectories to the semi-classical characteristics such as scar states, etc., should also be most interesting, particularly their variation with magnetic flux. In a fully locali ...
Lecture notes, part 6
... Fundamental Postulate of Statistical Mechanics: Given an isolated system at equilibrium, it is found with equal probability in each of its accessible microstates (set of quantum numbers) consistent with what is known about the system at a macroscopic level (eg. its temperature) Example: consider the ...
... Fundamental Postulate of Statistical Mechanics: Given an isolated system at equilibrium, it is found with equal probability in each of its accessible microstates (set of quantum numbers) consistent with what is known about the system at a macroscopic level (eg. its temperature) Example: consider the ...
Student Presentation
... have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
... have been previously regarded as particles also show wave-like characteristics with wavelengths given by the equation: λ = h/p = h/mv – h (Planck’s constant) = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s ...
x 100 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND SYMBOLS
... number is 3. What are the possible value sets (l, ml, ms) for the other three quantum numbers? 2. Is it possible for an electron in an atom to have these quantum numbers: n=2, l =1, ml =3, ms =1/2? Why or why not? ...
... number is 3. What are the possible value sets (l, ml, ms) for the other three quantum numbers? 2. Is it possible for an electron in an atom to have these quantum numbers: n=2, l =1, ml =3, ms =1/2? Why or why not? ...
Atomic Structure and Quantum Theory
... the energy is not continuous but rather quantized… quantum mechanics was born ...
... the energy is not continuous but rather quantized… quantum mechanics was born ...
Topological Insulators
... been seen is a two-dimensional particle gas experiencing the fractional quantum Hall effect. That effect requires formidable extremes of low temperature and high magnetic field, as well as rare, specially fabricated materials, making experimental exploration of.TQC very difficult. But now a team sup ...
... been seen is a two-dimensional particle gas experiencing the fractional quantum Hall effect. That effect requires formidable extremes of low temperature and high magnetic field, as well as rare, specially fabricated materials, making experimental exploration of.TQC very difficult. But now a team sup ...
Quantum mechanics in electronics
... which occupies the value 0, 1 or both simultaneously • Concepts used : entanglement , superposition ...
... which occupies the value 0, 1 or both simultaneously • Concepts used : entanglement , superposition ...
ppt
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
... Finally, we can connect everything we know about commutators and the Dirac’s quantum condition and obtain the most fundamental property of the Quantum World For a state that is not an eigenstate of Aˆ , we get various possible results everytime we measure the observable Aˆ in identical systems. A me ...
Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons
... Quantum Mechanics and its Linear Algebra Influence By: Mandy Switzer Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, and photons. With quantum mechanics, one can more easily and more correctly see how and why particles behave a certain way, which was very difficu ...
... Quantum Mechanics and its Linear Algebra Influence By: Mandy Switzer Quantum mechanics is the physics of the small, such as electrons, protons, neutrons, and photons. With quantum mechanics, one can more easily and more correctly see how and why particles behave a certain way, which was very difficu ...