Midterm 1 - University of California, Berkeley
... a) (8pts) If the width of the NMOS transistor in the second stage is Wn = 1, find the size of the PMOS transistor, such that the second inverter exhibits the same LH and HL ...
... a) (8pts) If the width of the NMOS transistor in the second stage is Wn = 1, find the size of the PMOS transistor, such that the second inverter exhibits the same LH and HL ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 15. With a neat circuit explain the working of a decade counter. How does the counter returns to normal state when preset to one of the illegal states? ...
... 15. With a neat circuit explain the working of a decade counter. How does the counter returns to normal state when preset to one of the illegal states? ...
Final Exam W0809
... You MUST attempt Q.1 (soft skill component) . For Q.2-Q.7, answer any FOUR questions. Fill in the Table below indicating the answers that the instructor need to mark. If you do not fill in the Table, the instructor will mark your answers according to his discretions Show all steps clearly in neat an ...
... You MUST attempt Q.1 (soft skill component) . For Q.2-Q.7, answer any FOUR questions. Fill in the Table below indicating the answers that the instructor need to mark. If you do not fill in the Table, the instructor will mark your answers according to his discretions Show all steps clearly in neat an ...
Signal Resistance of the Current Mirror
... The output voltage of the long-tailed pair circuits above will not be zero when both the inputs are zero. As the circuits stand, the quiescent VO will be 12 - (4.7 2.43/2) = 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output ...
... The output voltage of the long-tailed pair circuits above will not be zero when both the inputs are zero. As the circuits stand, the quiescent VO will be 12 - (4.7 2.43/2) = 6.3 V; it would be much better if it were zero! Several methods exist of making the quiescent value zero. 1. Take the output ...
Basic Electronics
... of the conduction-electron density and the hole density is ALWAYS equal to the square of ni: ...
... of the conduction-electron density and the hole density is ALWAYS equal to the square of ni: ...
1 CMOS Logic Gates
... The CMOS inverter is formed by connecting an n-type transistor and a p-type transistor in series, with the p-type inverted to operate from a single-voltage supply, as shown in Fig.1.3. The transfer characteristic of the inverter is also shown. The critical logic voltages, defined at the points on th ...
... The CMOS inverter is formed by connecting an n-type transistor and a p-type transistor in series, with the p-type inverted to operate from a single-voltage supply, as shown in Fig.1.3. The transfer characteristic of the inverter is also shown. The critical logic voltages, defined at the points on th ...
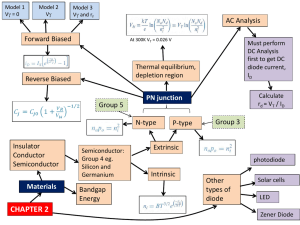
Chapter 3 Special-Purpose Diodes
... Transistor Characteristics and Parameters Analysis of this transistor circuit to predict the dc voltages and currents requires use of Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s voltage law and the beta for the transistor. Application of these laws begins with the base circuit to determine the amount of base current. U ...
... Transistor Characteristics and Parameters Analysis of this transistor circuit to predict the dc voltages and currents requires use of Ohm’s law, Kirchhoff’s voltage law and the beta for the transistor. Application of these laws begins with the base circuit to determine the amount of base current. U ...
Diodes
... electrical device that has a very high resistance to the flow of electrical current in t absence of light. • When light strikes the device, it lowers its resistance, allowing electrical current to flow through it and on to other devices or electrical circuits. ...
... electrical device that has a very high resistance to the flow of electrical current in t absence of light. • When light strikes the device, it lowers its resistance, allowing electrical current to flow through it and on to other devices or electrical circuits. ...
BFR740L3RH Maximum RF Input Power
... the transistor performance. The RF power translates into a voltage swing at the base of the bipolar transistor according to the input impedance of the device. If the RF voltage amplitude is high enough, the base emitter diode is driven into reverse operation for a certain part of each RF swing. Such ...
... the transistor performance. The RF power translates into a voltage swing at the base of the bipolar transistor according to the input impedance of the device. If the RF voltage amplitude is high enough, the base emitter diode is driven into reverse operation for a certain part of each RF swing. Such ...
Part 1 Some Basic Ideas and Components :
... the potential divider (in this experiment, the loads are resistors). Using the circuit shown above, adjust the rheostat so that the voltage across S and B is 2 volts. Connect a 10 kΩ resistor across S and B. Note the reading of the voltmeter when this resistor is connected. (Note that the maximum re ...
... the potential divider (in this experiment, the loads are resistors). Using the circuit shown above, adjust the rheostat so that the voltage across S and B is 2 volts. Connect a 10 kΩ resistor across S and B. Note the reading of the voltmeter when this resistor is connected. (Note that the maximum re ...
Exercise 2
... In order to visualize the output current when the simulation is over go to menu Results => Direct Plot and choose dc. In Schematic editor window select the drain transistor’s pin (fig. 2). The same result is if you set the output current before the simulation is started: Outputs To Be Plotted Se ...
... In order to visualize the output current when the simulation is over go to menu Results => Direct Plot and choose dc. In Schematic editor window select the drain transistor’s pin (fig. 2). The same result is if you set the output current before the simulation is started: Outputs To Be Plotted Se ...
The transistor amplifier
... input voltages (from a microphone or other amplifier stage etc.) to change Vb up and down, but only around the steady bias voltage already determined by R1 and R2. Note that these changes will typically be measured in a small number of millivolts, they are not large changes. At most, the signal volt ...
... input voltages (from a microphone or other amplifier stage etc.) to change Vb up and down, but only around the steady bias voltage already determined by R1 and R2. Note that these changes will typically be measured in a small number of millivolts, they are not large changes. At most, the signal volt ...
Lab 6 - PSU MNE
... pickup, and their output voltage is also a non-linear function of temperature. Some of these problems are neatly solved by a single chip thermocouple amplifier produced by Analog Devices. The AD595 is directly compatible with K type thermocouples, produces a linear output of 10 mV/°C, and comes in a ...
... pickup, and their output voltage is also a non-linear function of temperature. Some of these problems are neatly solved by a single chip thermocouple amplifier produced by Analog Devices. The AD595 is directly compatible with K type thermocouples, produces a linear output of 10 mV/°C, and comes in a ...
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)
... General configuration and definitions The transistor is the main building block “element” of electronics. It is a semiconductor device and it comes in two general types: the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and the Field Effect Transistor (FET). Here we will describe the system characteristics of t ...
... General configuration and definitions The transistor is the main building block “element” of electronics. It is a semiconductor device and it comes in two general types: the Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) and the Field Effect Transistor (FET). Here we will describe the system characteristics of t ...
History of the transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device with at least three terminals for connection to an electric circuit. The vacuum-tube triode, also called a (thermionic) valve, was the transistor's precursor, introduced in 1907.