The Coulomb-interaction-induced breaking of the Aufbau principle
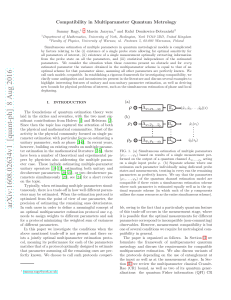
... We considered Jz values from the range {− 29 , ..., 92 }. The k and n quantum numbers numerate the basis functions in ρ and z directions, respectively. The set of values that was used in calculation is k ∈ {1, 8} and z ∈ {1, 6}. At this stage {aHH , aLHSO , bR } constitutes the set of the variationa ...
... We considered Jz values from the range {− 29 , ..., 92 }. The k and n quantum numbers numerate the basis functions in ρ and z directions, respectively. The set of values that was used in calculation is k ∈ {1, 8} and z ∈ {1, 6}. At this stage {aHH , aLHSO , bR } constitutes the set of the variationa ...
MODULE MAPS OVER LOCALLY COMPACT QUANTUM GROUPS
... Let G = (L∞ (G), Γ, ϕ, ψ) be a von Neumann algebraic locally compact quantum group and let L1 (G) be the convolution quantum group algebra of G. If we let C0 (G) be the reduced C ∗ -algebra associated with G, then its operator dual M (G) is a faithful completely contractive Banach algebra containing ...
... Let G = (L∞ (G), Γ, ϕ, ψ) be a von Neumann algebraic locally compact quantum group and let L1 (G) be the convolution quantum group algebra of G. If we let C0 (G) be the reduced C ∗ -algebra associated with G, then its operator dual M (G) is a faithful completely contractive Banach algebra containing ...
Quantum Renormalization of the Spin Hall Effect
... effect (AHE) and the spin Hall effect (SHE). A charge current perpendicular to the applied electric field is produced in ferromagnetic metals (AHE), while a spin current rather than a charge current is induced in semiconductors and metals without magnetism (SHE). An extrinsic mechanism of these two ...
... effect (AHE) and the spin Hall effect (SHE). A charge current perpendicular to the applied electric field is produced in ferromagnetic metals (AHE), while a spin current rather than a charge current is induced in semiconductors and metals without magnetism (SHE). An extrinsic mechanism of these two ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT (Abstract)
... UNIT I : The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics (9 h) Historical background of quantum mechanics. Detailed discussion of postulates of quantum mechanics – State function or wave function postulate, Born interpretation of the wave function, well behaved functions, orthonormality of wave functions; Oper ...
... UNIT I : The Foundations of Quantum Mechanics (9 h) Historical background of quantum mechanics. Detailed discussion of postulates of quantum mechanics – State function or wave function postulate, Born interpretation of the wave function, well behaved functions, orthonormality of wave functions; Oper ...
March 2002 Vol - Basarab Nicolescu
... macrophysical world. This means that two levels of Reality are different if, passing from one to another, there is a break of the laws and break of the fundamental concepts (as causality, for example). The discontinuity present in the quantum world is also present in the structure of the Levels of R ...
... macrophysical world. This means that two levels of Reality are different if, passing from one to another, there is a break of the laws and break of the fundamental concepts (as causality, for example). The discontinuity present in the quantum world is also present in the structure of the Levels of R ...
Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics
... governed by an ordinary differential equation of first order (i.e. Newton’s second law), so that the whole dynamics of a given system can be described by stating the position and the velocity of its constituents at some time t0 , it is evident that through each point of Λ there runs exactly one traj ...
... governed by an ordinary differential equation of first order (i.e. Newton’s second law), so that the whole dynamics of a given system can be described by stating the position and the velocity of its constituents at some time t0 , it is evident that through each point of Λ there runs exactly one traj ...
THE DEMYSTIFICATION OF EMERGENT
... intuitively understand. One defines a set of rules for the interaction of a class of objects with each other and with the environment, and within the constraints set by the rules, the resulting observed behavior is often very complex, transcending the simplicity of the rules themselves. A concrete a ...
... intuitively understand. One defines a set of rules for the interaction of a class of objects with each other and with the environment, and within the constraints set by the rules, the resulting observed behavior is often very complex, transcending the simplicity of the rules themselves. A concrete a ...
arXiv:1412.5987v1 [hep-ex] 18 Dec 2014
... kinematic distributions of gluons producing the J/ψ or the ψ(2S) are rather similar and since the coherent energy loss does not depend on the final quantum numbers of the resonances, the same theoretical calculations hold for both J/ψ and ψ(2S). Theoretical models predict y dependence which are in r ...
... kinematic distributions of gluons producing the J/ψ or the ψ(2S) are rather similar and since the coherent energy loss does not depend on the final quantum numbers of the resonances, the same theoretical calculations hold for both J/ψ and ψ(2S). Theoretical models predict y dependence which are in r ...
Quantum critical phenomena and stability of atomic and molecular
... pioneering work of Herschbach et al. [ 6] , they found wide use in the ® eld of atomic and molecular physics [ 7] . In this method one takes the dimension D of space, as a variable, solves the problem at some dimension D =/ 3 where the physics becomes much simpler and then uses perturbation theory o ...
... pioneering work of Herschbach et al. [ 6] , they found wide use in the ® eld of atomic and molecular physics [ 7] . In this method one takes the dimension D of space, as a variable, solves the problem at some dimension D =/ 3 where the physics becomes much simpler and then uses perturbation theory o ...
Linde - Stanford University
... This stage of self-sustained exponentially rapid expansion of the universe was not very long. In a realistic version of our model its duration could be as short as 10-35 seconds. When the energy density of the field becomes sufficiently small, viscosity becomes small, inflation ends, and the scala ...
... This stage of self-sustained exponentially rapid expansion of the universe was not very long. In a realistic version of our model its duration could be as short as 10-35 seconds. When the energy density of the field becomes sufficiently small, viscosity becomes small, inflation ends, and the scala ...
Eikonal Approximation K. V. Shajesh
... 2m . With this correspondence we ask the question, can we not have a corresponding eikonal approximation in quantum mechanics? Yes we can. The eikonal approximation in quantum mechanics works for processes involving the scattering of particles with large incoming momentum and when the scattering ang ...
... 2m . With this correspondence we ask the question, can we not have a corresponding eikonal approximation in quantum mechanics? Yes we can. The eikonal approximation in quantum mechanics works for processes involving the scattering of particles with large incoming momentum and when the scattering ang ...
Die Naturwissenschaften 1935
... B. When, at a given moment in time, not all variables are fully determined by a subset, then of course they cannot be determined either at a later moment in time from accessible data at an earlier time. This might be called a breach of causality, but it is basically nothing new compared to A. When ...
... B. When, at a given moment in time, not all variables are fully determined by a subset, then of course they cannot be determined either at a later moment in time from accessible data at an earlier time. This might be called a breach of causality, but it is basically nothing new compared to A. When ...
Compatibility in Multiparameter Quantum Metrology
... prioritise the uncertainty cost of different parameters. As in the single parameter case, the bound is saturable in the limit of an infinite number of repetitions of an experiment using the maximum likelihood estimator [25]. The first substantial difference of multiparameter metrology from the single pa ...
... prioritise the uncertainty cost of different parameters. As in the single parameter case, the bound is saturable in the limit of an infinite number of repetitions of an experiment using the maximum likelihood estimator [25]. The first substantial difference of multiparameter metrology from the single pa ...
The Physics of Quantum Mechanics
... The place of quantum mechanics in nature Quantum mechanics is the framework for describing and analyzing small things, like atoms and nuclei. Quantum mechanics also applies to big things, like baseballs and galaxies, but when applied to big things, certain approximations become legitimate: taken tog ...
... The place of quantum mechanics in nature Quantum mechanics is the framework for describing and analyzing small things, like atoms and nuclei. Quantum mechanics also applies to big things, like baseballs and galaxies, but when applied to big things, certain approximations become legitimate: taken tog ...
Duality Theory of Weak Interaction
... are prohibited. The reason is that Aaµ is an SU (N1 )-tensor with tensor index a, and Gkµ is an SU (N2 )-tensor with tensor index k. The above combination violates PRI. This point of view clearly shows that the classical electroweak theory violates PRI. Hence the classical electroweak theory is only ...
... are prohibited. The reason is that Aaµ is an SU (N1 )-tensor with tensor index a, and Gkµ is an SU (N2 )-tensor with tensor index k. The above combination violates PRI. This point of view clearly shows that the classical electroweak theory violates PRI. Hence the classical electroweak theory is only ...
IMPRECISE MEASUREMENTS IN QUANTUM MECHANICS
... large part the progress of physics has been connected to the development of measurement techniques. Quantum theory has shown that measurements need also theoretical examination. Soon after the birth of quantum theory the deep nature of the theoretical issues related to measurements were generally re ...
... large part the progress of physics has been connected to the development of measurement techniques. Quantum theory has shown that measurements need also theoretical examination. Soon after the birth of quantum theory the deep nature of the theoretical issues related to measurements were generally re ...
Observation of oscillatory energy exchange in a coupled-atom
... the normal modes ofpthe composite system split by the exchange frequency g N . Here g is the effective coupling coefficient for any one of the N atoms to the cavity field. Several early experimental investigations of such phenomena used Rydberg atoms in microwave cavities.5 – 10 In particular, the e ...
... the normal modes ofpthe composite system split by the exchange frequency g N . Here g is the effective coupling coefficient for any one of the N atoms to the cavity field. Several early experimental investigations of such phenomena used Rydberg atoms in microwave cavities.5 – 10 In particular, the e ...








![arXiv:1412.5987v1 [hep-ex] 18 Dec 2014](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057205_1-733500b8b6bd2637f9a7ffd625392271-300x300.png)