PDF
... Definition 1.1. Let us recall that a quantum automaton is defined as a quantum algebraic topology object– the quantum triple QA = (G, H −
... Definition 1.1. Let us recall that a quantum automaton is defined as a quantum algebraic topology object– the quantum triple QA = (G, H −
Quantum Mechanics and General Relativity
... of quantum mechanics is that which deals with the smallest structures in the universe, for example electrons, quarks, muons and other elementary particles. From this spring such applications as nuclear physics and solid state electronics. General Relativity on the other hand describes particularly t ...
... of quantum mechanics is that which deals with the smallest structures in the universe, for example electrons, quarks, muons and other elementary particles. From this spring such applications as nuclear physics and solid state electronics. General Relativity on the other hand describes particularly t ...
class (Recovered)
... Homework is mandatory, Exam (mandatory for undergrad) and/or paper presentation/ project Topics in Quantum Information, by Ashwin Nayak. Lecture notes, by John Preskill. More lecture notes on his ...
... Homework is mandatory, Exam (mandatory for undergrad) and/or paper presentation/ project Topics in Quantum Information, by Ashwin Nayak. Lecture notes, by John Preskill. More lecture notes on his ...
3.4oquantum.4u
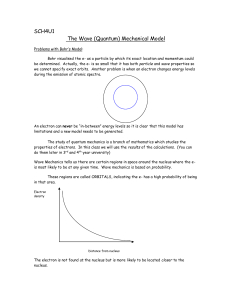
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
Wave-Particle Duality - the Principle of Complementarity The
... The Wave Function and Its Interpretation Question: An electromagnetic wave has oscillating electric and magnetic fields. What is oscillating in a matter wave? Answer: This role is played by the wave function, Ψ. The square of the absolute value of the wave function at any point is proportional to t ...
... The Wave Function and Its Interpretation Question: An electromagnetic wave has oscillating electric and magnetic fields. What is oscillating in a matter wave? Answer: This role is played by the wave function, Ψ. The square of the absolute value of the wave function at any point is proportional to t ...
Searching for the Field-Induced Non-Magnetic Phase - ICAM
... compound for the study is the cubic caged compound PrV2Al20, which has a strong hybridization between conduction electrons and the 4f- non-magnetic ground doublet having only orbital moments [1]. In fact, anomalous metallic state emerges owing to the putative “two-channel” Kondo effect using the orb ...
... compound for the study is the cubic caged compound PrV2Al20, which has a strong hybridization between conduction electrons and the 4f- non-magnetic ground doublet having only orbital moments [1]. In fact, anomalous metallic state emerges owing to the putative “two-channel” Kondo effect using the orb ...
Quantum Computing at the Speed of Light
... Harnessing quantum states for information storage and manipulation (in so called “qubits”) is the objective of quantum computing, with the potential to revolutionize technology in areas of great importance to society (e.g. cryptography, data base searching, quantum simulation of advance materials, s ...
... Harnessing quantum states for information storage and manipulation (in so called “qubits”) is the objective of quantum computing, with the potential to revolutionize technology in areas of great importance to society (e.g. cryptography, data base searching, quantum simulation of advance materials, s ...
Quantum Mechanics
... • It didn’t do a very good job of explaining how ions formed. • Bohr was able to improve on his 1913 model, but he needed Wolfgang Pauli to really make sense of it. ...
... • It didn’t do a very good job of explaining how ions formed. • Bohr was able to improve on his 1913 model, but he needed Wolfgang Pauli to really make sense of it. ...
Mott insulators, Noise correlations and Coherent Spin Dynamics in Optical Lattices
... Similar to Richard Feynman’s original proposal for a quantum computer as a simulator for the quantum dynamics of other physical systems, neutral atoms in optical lattices already today offer powerful possibilities for simulating fundamental Hamiltonians of condensed matter physics. In fact, many nov ...
... Similar to Richard Feynman’s original proposal for a quantum computer as a simulator for the quantum dynamics of other physical systems, neutral atoms in optical lattices already today offer powerful possibilities for simulating fundamental Hamiltonians of condensed matter physics. In fact, many nov ...
The Parable of the Three Umpires
... If that's not confusing, the nuclear dance Of electrons and suchlike is governed by chance! No sweat, though--my theory permits us to judge Where some of 'em is and the rest of 'em was." Not everyone bought this. It threatened to wreck The comforting linkage of cause and effect. ...
... If that's not confusing, the nuclear dance Of electrons and suchlike is governed by chance! No sweat, though--my theory permits us to judge Where some of 'em is and the rest of 'em was." Not everyone bought this. It threatened to wreck The comforting linkage of cause and effect. ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester Matthew Jones
... + cos • The solutions are periodic with frequency ...
... + cos • The solutions are periodic with frequency ...
Hogan: An Alternative Version of Quantum Mechanics
... faster than the speed of light The quantum potential exerts an influence on the particle that is not within the constraints of the speed of light In Bohm’s theory relativity applies only to “observational content” of the theory ...
... faster than the speed of light The quantum potential exerts an influence on the particle that is not within the constraints of the speed of light In Bohm’s theory relativity applies only to “observational content” of the theory ...
The Weird World of Quantum Information
... experiments could not be explained by classical mechanics. First, let's discuss why would atom poses a magnetic moment. Even in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, an electron, which is a charged particle, occupies a circular orbit, rotating with orbital angular momentum L. A moving charge is equival ...
... experiments could not be explained by classical mechanics. First, let's discuss why would atom poses a magnetic moment. Even in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, an electron, which is a charged particle, occupies a circular orbit, rotating with orbital angular momentum L. A moving charge is equival ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... He put forward this postulate in order to explain the phenomena of blackbody radiation. He postulated that an electromagnetic wave can only interact with matter in integer multiples of h, where is the frequency of the wave, and h is a quantity known as Planck’s constant. Planck’s constant has a v ...
... He put forward this postulate in order to explain the phenomena of blackbody radiation. He postulated that an electromagnetic wave can only interact with matter in integer multiples of h, where is the frequency of the wave, and h is a quantity known as Planck’s constant. Planck’s constant has a v ...
Particle-like Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation
... Another important discovery which helped create the underlying principles about the atomic structure was the phenomenon called Blackbody Radiation - the visible glow that all solids give off when heated; (Max Planck (1900)). He found that as the object was heat at a higher temperature, the colour (o ...
... Another important discovery which helped create the underlying principles about the atomic structure was the phenomenon called Blackbody Radiation - the visible glow that all solids give off when heated; (Max Planck (1900)). He found that as the object was heat at a higher temperature, the colour (o ...