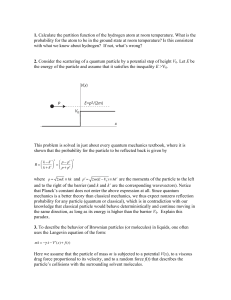
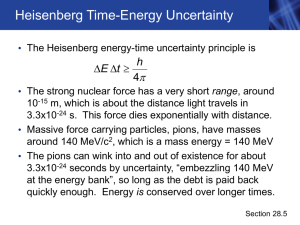
1. Calculate the partition function of the hydrogen atom at room
... and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than classical mechanics, we thus expect nonzero reflection probability for any particle (quantum or ...
... and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than classical mechanics, we thus expect nonzero reflection probability for any particle (quantum or ...
ppt
... • Key difference between NS and NSIT: - NS cannot be violated due to causality BI necessary - NSIT can be violated according to quantum mechanics no need for LGI ...
... • Key difference between NS and NSIT: - NS cannot be violated due to causality BI necessary - NSIT can be violated according to quantum mechanics no need for LGI ...
Spring 2007 Colloquium Series Physics Department University of Oregon 4:00pm Thursdays, 100 Willamette
... coherence are one of the two major ingredients (the other being the control of matter) for this scientific adventure. Lasers with state-of-the-art frequency control can now maintain phase coherence over one second, that is, 10^15 optical waves can pass by without losing track of a particular cycle. ...
... coherence are one of the two major ingredients (the other being the control of matter) for this scientific adventure. Lasers with state-of-the-art frequency control can now maintain phase coherence over one second, that is, 10^15 optical waves can pass by without losing track of a particular cycle. ...
mjcrescimanno.people.ysu.edu
... Now that we have solved the QHO and studied aspects of the solution and displayed evidence that it actually corresponds with the classical HO, we now rederive the QHO in from a more abstract, algebraic (and more useful!) point of view. This is not just repackaging; it will be key to undertstanding m ...
... Now that we have solved the QHO and studied aspects of the solution and displayed evidence that it actually corresponds with the classical HO, we now rederive the QHO in from a more abstract, algebraic (and more useful!) point of view. This is not just repackaging; it will be key to undertstanding m ...
... a. Find the partition function of an ideal gas of N diatomic molecules in which the two atoms don't interact with each other b. What is the energy of the gas? What is the heat capacity? c. How would the above change if the two atoms of each molecule interact with each other? Consider the interaction ...
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... theory): a cat, a flask of poison, and a radioactive source are placed in a sealed box. If an internal monitor detects radioactivity (i.e. a single atom decaying), the flask is shattered, releasing the poison that kills the cat. The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics implies that after a ...
... theory): a cat, a flask of poison, and a radioactive source are placed in a sealed box. If an internal monitor detects radioactivity (i.e. a single atom decaying), the flask is shattered, releasing the poison that kills the cat. The Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics implies that after a ...
Series 5 - Problems
... we learned for time-independent quantum mechanics - the particle in a box. Take V (x) = 0 for 0 < x < L and V (x) = ∞ everwhere else. a) What are the energy eigenstates, the energy eigenvalues (in terms of the quantum number n) and the spacing between energy levels for this physical situation? b) Le ...
... we learned for time-independent quantum mechanics - the particle in a box. Take V (x) = 0 for 0 < x < L and V (x) = ∞ everwhere else. a) What are the energy eigenstates, the energy eigenvalues (in terms of the quantum number n) and the spacing between energy levels for this physical situation? b) Le ...
Electronic structure and spectroscopy
... with: • Ĥ being the Hamilton operator of the system; • Ψ is the state function of the system; • E is the energy of the system. This is an eigenvalue equation, Ψ being the eigenfunction of Ĥ, E is the eigenvalue. This has to be solved in order to obtain the states of, e.g. molecules. According to D ...
... with: • Ĥ being the Hamilton operator of the system; • Ψ is the state function of the system; • E is the energy of the system. This is an eigenvalue equation, Ψ being the eigenfunction of Ĥ, E is the eigenvalue. This has to be solved in order to obtain the states of, e.g. molecules. According to D ...
The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac`s famous Equation D(N)
... The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac’s famous Equation D(N) ...
... The Nilpotent generalization of Dirac’s famous Equation D(N) ...
Questions for learning Quantum Mechanics of FYSA21
... you measure the observable represented by the operator  with an eigenvalue a and the corresponding normalised eigenfunction Ψa (x), what is the probability of obtaining the value a? (1p) 10. If you have just measured the obeservable  of a Quantum Mechanical system and obtained the value a and th ...
... you measure the observable represented by the operator  with an eigenvalue a and the corresponding normalised eigenfunction Ψa (x), what is the probability of obtaining the value a? (1p) 10. If you have just measured the obeservable  of a Quantum Mechanical system and obtained the value a and th ...
ppt - Max-Planck
... forcing superpositions to decay; altering quantum physics Alternative answer: - Coarse-grained measurements measurement resolution is limited; within quantum physics A. Peres, Quantum Theory: Concepts and Methods, Kluver (2002) ...
... forcing superpositions to decay; altering quantum physics Alternative answer: - Coarse-grained measurements measurement resolution is limited; within quantum physics A. Peres, Quantum Theory: Concepts and Methods, Kluver (2002) ...