- Philsci
... having the Fock Space Hamiltonian Operator H in (11), because in this case the total number operator commutes with the Hamiltonian, i.e., [N,H] = 0. But not all Hamiltonians commute ...
... having the Fock Space Hamiltonian Operator H in (11), because in this case the total number operator commutes with the Hamiltonian, i.e., [N,H] = 0. But not all Hamiltonians commute ...
Multiparticle Quantum: Exchange
... Identical bosons can have the same wavefunction (and thus the same quantum numbers) Fermions never have the same (one-particle) wave function (state is identically zero if a=b) ...
... Identical bosons can have the same wavefunction (and thus the same quantum numbers) Fermions never have the same (one-particle) wave function (state is identically zero if a=b) ...
Effective Topological Field Theories in Condensed Matter Physics
... In condensed matter physics, we ask what are the fundamental states of matter? In the classical world we have solid, liquid and gas. The same H2O molecules can ...
... In condensed matter physics, we ask what are the fundamental states of matter? In the classical world we have solid, liquid and gas. The same H2O molecules can ...
A Brief Introduction into Quantum Gravity and Quantum Cosmology
... very small dimensions of the path and for very great curvatures. Perhaps this failure is in strict analogy with the failure of geometrical optics . . . that becomes evident as soon as the obstacles or apertures are no longer great compared with the real, finite, wavelength. . . . Then it becomes a q ...
... very small dimensions of the path and for very great curvatures. Perhaps this failure is in strict analogy with the failure of geometrical optics . . . that becomes evident as soon as the obstacles or apertures are no longer great compared with the real, finite, wavelength. . . . Then it becomes a q ...
Banks
... stable dS space (see later) with entropy k ln dim P, which gives same time avg density matrix. Entropy of this system the same as that of dS space with “final” c.c. (determines N, which is a cosmological initial condition)*. This quantum theory gives a universe that resembles N horizon volumes of dS ...
... stable dS space (see later) with entropy k ln dim P, which gives same time avg density matrix. Entropy of this system the same as that of dS space with “final” c.c. (determines N, which is a cosmological initial condition)*. This quantum theory gives a universe that resembles N horizon volumes of dS ...
CHAPTER 1. SPECIAL RELATIVITY AND QUANTUM MECHANICS 1.1 PARTICLES AND FIELDS §
... volume with periodic boundary conditions so that their wave-vectors are integer multiples of 2π over the volume’s linear dimension in each direction). Then the states of this system can be described as having zero photons, one single photon, two photons, and so on. According to the postulates of qua ...
... volume with periodic boundary conditions so that their wave-vectors are integer multiples of 2π over the volume’s linear dimension in each direction). Then the states of this system can be described as having zero photons, one single photon, two photons, and so on. According to the postulates of qua ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
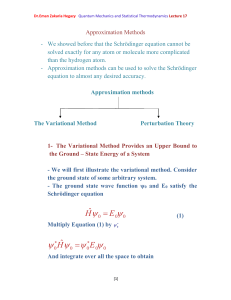
... the Ground – State Energy of a System - We will first illustrate the variational method. Consider the ground state of some arbitrary system. - The ground state wave function ψ0 and E0 satisfy the Schrödinger equation ...
... the Ground – State Energy of a System - We will first illustrate the variational method. Consider the ground state of some arbitrary system. - The ground state wave function ψ0 and E0 satisfy the Schrödinger equation ...
Set #5 - comsics
... excited states? What would be the wavelengths of the standing de Broglie waves? Sketch the behavior of the lowest two wave functions. (Krane, Q6, pg. 168) 9. A particle in an infinite well is in the ground state with an energy of 1.26 eV. How much energy must be added to the particle to reach the se ...
... excited states? What would be the wavelengths of the standing de Broglie waves? Sketch the behavior of the lowest two wave functions. (Krane, Q6, pg. 168) 9. A particle in an infinite well is in the ground state with an energy of 1.26 eV. How much energy must be added to the particle to reach the se ...
What Is Quantum Physics? by Joan Parisi Wilcox
... As you move down the scale of matter, you move from cells to molecules to atoms. At this realm, the science of chemistry dominates biology. But if you keep going, you eventually see that chemistry, as the famed physicist Richard Feynman reminded us, is dependent on physics, as atoms are made of suba ...
... As you move down the scale of matter, you move from cells to molecules to atoms. At this realm, the science of chemistry dominates biology. But if you keep going, you eventually see that chemistry, as the famed physicist Richard Feynman reminded us, is dependent on physics, as atoms are made of suba ...
The Atom
... neutrons in the outermost shell protons in central shells electrons in the innermost shell electrons in the outermost shell ...
... neutrons in the outermost shell protons in central shells electrons in the innermost shell electrons in the outermost shell ...
Department of Chemistry - The City College of New York
... mechanical wave equation, and also be able to apply selection rules, which specify allowed transitions between quantum mechanical states. Use quantum mechanical energies as energy states in statistical thermodynamic expressions dealing with the distribution of particles over available energy states. ...
... mechanical wave equation, and also be able to apply selection rules, which specify allowed transitions between quantum mechanical states. Use quantum mechanical energies as energy states in statistical thermodynamic expressions dealing with the distribution of particles over available energy states. ...
Quantum review
... Equation for probability of a single electron being found along a single axis (x-axis) Erwin Schrodinger ...
... Equation for probability of a single electron being found along a single axis (x-axis) Erwin Schrodinger ...
Quantum Theory. A Mathematical Approach
... physical theories, in particular relativity and quantum theory, one needs to know such topics as functional analysis, Lie groups and algebra, differential geometry. That makes it easy for mathematicians to acquire a basic understanding of these theories. Physicist are not familiar with this kind of ...
... physical theories, in particular relativity and quantum theory, one needs to know such topics as functional analysis, Lie groups and algebra, differential geometry. That makes it easy for mathematicians to acquire a basic understanding of these theories. Physicist are not familiar with this kind of ...
Quantum Chemistry - Winona State University
... denoted and called the wavefunction or state function) that contains all the information that can be known about the system. • Every physical observable is represented by a linear operator called the “Hermitian” operator. • Measurement of a physical observable will give a result that is one of the ...
... denoted and called the wavefunction or state function) that contains all the information that can be known about the system. • Every physical observable is represented by a linear operator called the “Hermitian” operator. • Measurement of a physical observable will give a result that is one of the ...
May 2001
... A spring has spring constant K, unstretched length L, and mass per unit length ρ. The spring is suspended vertically from one end in a constant gravitational field g, and stretches under tis own weight. ...
... A spring has spring constant K, unstretched length L, and mass per unit length ρ. The spring is suspended vertically from one end in a constant gravitational field g, and stretches under tis own weight. ...
AtomsFirst2e_day6_sec3.7
... values for each of the 4 quantum numbers •Be able to describe an experiment that could be used to show that half of the electrons in an atom have a spin = ½ and the other half have a spin = -½. •Be able to draw a figure that shows the shape and location of nodes in any orbital in the 1st, 2nd, or 3r ...
... values for each of the 4 quantum numbers •Be able to describe an experiment that could be used to show that half of the electrons in an atom have a spin = ½ and the other half have a spin = -½. •Be able to draw a figure that shows the shape and location of nodes in any orbital in the 1st, 2nd, or 3r ...
Lieb-Robinson Bounds and the Speed of Light from
... establishes that all the observables that are outside of the effective light cone centered on P with speed of light vLR will have an exponentially small commutator with the observables in P. This result sets a limit to the speed of interactions in the spin system. It proves that any signal outside o ...
... establishes that all the observables that are outside of the effective light cone centered on P with speed of light vLR will have an exponentially small commutator with the observables in P. This result sets a limit to the speed of interactions in the spin system. It proves that any signal outside o ...