Chapter 15 Transaction Management
... Transaction 2 reads and uses for calculation Transaction 1 updates and commits Transaction 2 updates and commits ...
... Transaction 2 reads and uses for calculation Transaction 1 updates and commits Transaction 2 updates and commits ...
MIS 301- Database
... Locate data with a distributed data dictionary Determine location from which to retrieve data and process query components DBMS translation between nodes with different local DBMSs (using middleware) Data management functions: security, concurrency, deadlock control, query optimization, failure reco ...
... Locate data with a distributed data dictionary Determine location from which to retrieve data and process query components DBMS translation between nodes with different local DBMSs (using middleware) Data management functions: security, concurrency, deadlock control, query optimization, failure reco ...
Efficient Deployment of Network Management Policy Using Distributed Database Abstraction
... a relational database, it contains records having attributes belonging to data flows, such as, switch port, header fields (i.e., Ethernet and IP source/destination) and actions. This flow table has same properties like any other database table and required CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) oper ...
... a relational database, it contains records having attributes belonging to data flows, such as, switch port, header fields (i.e., Ethernet and IP source/destination) and actions. This flow table has same properties like any other database table and required CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) oper ...
poster_db4o2d - HSR-Wiki
... This project aims to extend a pure object database with 2D geospatial types. The extension consists of the Java Topology Suite (JTS). db4o is an open source database written in Java and .NET. It is well suited for single user system scenarios and embedded systems running on mobile or desktop platfor ...
... This project aims to extend a pure object database with 2D geospatial types. The extension consists of the Java Topology Suite (JTS). db4o is an open source database written in Java and .NET. It is well suited for single user system scenarios and embedded systems running on mobile or desktop platfor ...
slides
... to introduce basic principles and implementation techniques of distributed databases including distributed database design and architecture, query processing and optimization, transaction management, recovery, and reliability protocols to expose active research issues in distributed database syste ...
... to introduce basic principles and implementation techniques of distributed databases including distributed database design and architecture, query processing and optimization, transaction management, recovery, and reliability protocols to expose active research issues in distributed database syste ...
DBMS functions
... Need for Recovery Control system crash transaction or system error local error or execution error concurrency control enforcement disk failure: read-write malfunction Physical problems and catastrophes: ...
... Need for Recovery Control system crash transaction or system error local error or execution error concurrency control enforcement disk failure: read-write malfunction Physical problems and catastrophes: ...
Distributed Database
... Local sites can operate the database when the network connection is lost Increasing confidence Local control of the data ...
... Local sites can operate the database when the network connection is lost Increasing confidence Local control of the data ...
Techniques Everyone Should Know
... between the commit protocol and the WAL, the paper here contains two variants of AC that improve its performance. The Presumed Abort variant allows processes to avoid forcing an abort decision to disk or acknowledge aborts, reducing disk utilization and network traffic. The Presumed Commit optimizat ...
... between the commit protocol and the WAL, the paper here contains two variants of AC that improve its performance. The Presumed Abort variant allows processes to avoid forcing an abort decision to disk or acknowledge aborts, reducing disk utilization and network traffic. The Presumed Commit optimizat ...
Digital Library Architecture
... Architectural considerations • Real-time service during scheduled hours + batch processing overnight • Combine information from several databases • Database consistency after any type of failure two-phase commit reload from checkpoint + log detailed audit trail • How will transaction errors be avoi ...
... Architectural considerations • Real-time service during scheduled hours + batch processing overnight • Combine information from several databases • Database consistency after any type of failure two-phase commit reload from checkpoint + log detailed audit trail • How will transaction errors be avoi ...
91.309/310 Database
... • A database management system (DBMS) is a software package designed to store and manage data efficiently, e.g., MS Access, MySQL, IBM DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server. ...
... • A database management system (DBMS) is a software package designed to store and manage data efficiently, e.g., MS Access, MySQL, IBM DB2, Oracle, MS SQL Server. ...
Big Data and the Database Community
... * Everyone is going in the direction of cost-based optimizers, traditional database operators, and push-based query execution ...
... * Everyone is going in the direction of cost-based optimizers, traditional database operators, and push-based query execution ...
6. Database Management Systems
... rdered Indices, B+ Trees and B tree Index Files • Static hashing, Dynamic hashing • Index Definition in SQL, multiple key access Transaction : • Transaction Concepts, Transaction states • Implementation of atomicity and Durability • Concurrent executions, Serializability, Recoverability • Implementa ...
... rdered Indices, B+ Trees and B tree Index Files • Static hashing, Dynamic hashing • Index Definition in SQL, multiple key access Transaction : • Transaction Concepts, Transaction states • Implementation of atomicity and Durability • Concurrent executions, Serializability, Recoverability • Implementa ...
Operating System Support for Virtual Machines
... • Concurrency control considerations – OLTP transactions are very short-lived – Single threaded execution avoids page latching – Not needed for some transaction classes (singlesited/one shot/sterile) ...
... • Concurrency control considerations – OLTP transactions are very short-lived – Single threaded execution avoids page latching – Not needed for some transaction classes (singlesited/one shot/sterile) ...
Lecture Slides DBTransactions
... • A transaction can have one of two outcomes • Committed : if it completes successfully and the database reaches a new consistent state • Aborted: if the transaction does not execute successfully. • Rolled back/undone : If a transaction is aborted the database must be restored to the consistent stat ...
... • A transaction can have one of two outcomes • Committed : if it completes successfully and the database reaches a new consistent state • Aborted: if the transaction does not execute successfully. • Rolled back/undone : If a transaction is aborted the database must be restored to the consistent stat ...
Power Point - Arizona State University
... Support the relational data model Use SQL as the primary mechanism for application interaction ACID support for transactions A non-locking concurrency control mechanism so real-time reads will not conflict with writes, and thereby cause them to stall 5. A scale-out, shared-nothing architecture, capa ...
... Support the relational data model Use SQL as the primary mechanism for application interaction ACID support for transactions A non-locking concurrency control mechanism so real-time reads will not conflict with writes, and thereby cause them to stall 5. A scale-out, shared-nothing architecture, capa ...
Concurrency and Transaction Management in an Object Oriented
... transaction fails; the updated item is access by another transaction before it is changed back to its original value ...
... transaction fails; the updated item is access by another transaction before it is changed back to its original value ...
Database Management System - The Institute of Finance
... Discuss the evolution of database system Basically identifying the entities, attributes and their relationships Creating the conceptual data models using the E_R model ...
... Discuss the evolution of database system Basically identifying the entities, attributes and their relationships Creating the conceptual data models using the E_R model ...
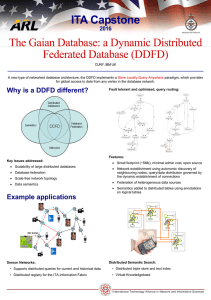
The Gaian Database: a Dynamic Distributed Federated Database
... • Distributed registry for the ITA Information Fabric ...
... • Distributed registry for the ITA Information Fabric ...
Syllabus
... 1. Question No. 1 should be compulsory and cover the entire syllabus. This question should have objective or short answer type questions. It should be of 25 marks. 2. Apart from Question No. 1, rest of the paper shall consist of four units as per the syllabus. Every unit should have two questions. H ...
... 1. Question No. 1 should be compulsory and cover the entire syllabus. This question should have objective or short answer type questions. It should be of 25 marks. 2. Apart from Question No. 1, rest of the paper shall consist of four units as per the syllabus. Every unit should have two questions. H ...