Circular Motion Review
... g. If the mass of the Earth were doubled (without an alteration in its radius), then the acceleration of gravity on its surface would be approximately 20 m/s2. h. If the mass of the Earth were doubled and the radius of the earth were doubled, then the two changes would offset each other and the acce ...
... g. If the mass of the Earth were doubled (without an alteration in its radius), then the acceleration of gravity on its surface would be approximately 20 m/s2. h. If the mass of the Earth were doubled and the radius of the earth were doubled, then the two changes would offset each other and the acce ...
1.35 Gravitation AP C
... energy of an object in a bit more detail when it is in orbit around a body. ...
... energy of an object in a bit more detail when it is in orbit around a body. ...
CircularMotion&Gravitation
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “in a weightless environment”. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “in a weightless environment”. ...
Mrs
... d. none of the above _____ 28. Gravitational forces are the weakest forces found in nature. Because of this a. gravitational effect between a pencil and the earth cannot be seen b. there is no gravitational force between two 1-kg masses c. gravitational effects occur only when a large mass is involv ...
... d. none of the above _____ 28. Gravitational forces are the weakest forces found in nature. Because of this a. gravitational effect between a pencil and the earth cannot be seen b. there is no gravitational force between two 1-kg masses c. gravitational effects occur only when a large mass is involv ...
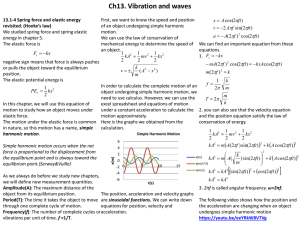
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... need to use calculus. However, we can use the T 2 k In this chapter, we will use this equation of excel spreadsheet and equations of motion motion to study how an object moves under under a constant acceleration to calculate the 2. you can also see that the velocity equation elastic force. motion ...
... need to use calculus. However, we can use the T 2 k In this chapter, we will use this equation of excel spreadsheet and equations of motion motion to study how an object moves under under a constant acceleration to calculate the 2. you can also see that the velocity equation elastic force. motion ...
Upgrade Your Physics 1
... the bricks together as a whole object, the two internal forces would not cancel out, and there would be some ‘left over’ force which could accelerate the whole object. 1 It makes sense that if the bricks are identical then they will accelerate together at the same rate. But what if they are not? Thi ...
... the bricks together as a whole object, the two internal forces would not cancel out, and there would be some ‘left over’ force which could accelerate the whole object. 1 It makes sense that if the bricks are identical then they will accelerate together at the same rate. But what if they are not? Thi ...
The total energy in a simple harmonic oscillator is the constant sum
... From this expression, we see that the velocity is a maximum (vmax) at x=0. Notice that the maximum velocity depends on three factors. It is directly proportional to amplitude. As you might guess, the greater the maximum displacement, the greater the maximum velocity. It is also greater for stiffer s ...
... From this expression, we see that the velocity is a maximum (vmax) at x=0. Notice that the maximum velocity depends on three factors. It is directly proportional to amplitude. As you might guess, the greater the maximum displacement, the greater the maximum velocity. It is also greater for stiffer s ...
Topic 6 Problem Set 2016
... Two masses of 4.501022 kg each are located along the x-axis. The first mass is at the origin, and the second mass is at x = +1.25106 m. 44. Find the gravitational field strength at the point on the x-axis directly between the two masses. 45. Find the gravitational field strength at x = +2.50106 m ...
... Two masses of 4.501022 kg each are located along the x-axis. The first mass is at the origin, and the second mass is at x = +1.25106 m. 44. Find the gravitational field strength at the point on the x-axis directly between the two masses. 45. Find the gravitational field strength at x = +2.50106 m ...
Circular Motion - strikerphysics11
... magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of a red blood cell at a radial distance of 8.0 cm from the centrifuge’s axis of rotation? Compare this with g. A ball attached to a string is swung with uniform motion in a horizontal circle over a person’s head. If the string breaks, what will be the traje ...
... magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of a red blood cell at a radial distance of 8.0 cm from the centrifuge’s axis of rotation? Compare this with g. A ball attached to a string is swung with uniform motion in a horizontal circle over a person’s head. If the string breaks, what will be the traje ...
FRAME-Newtons Laws
... Essential Details An object in motion stays in motion until acted upon by an outside, unbalanced force. ...
... Essential Details An object in motion stays in motion until acted upon by an outside, unbalanced force. ...
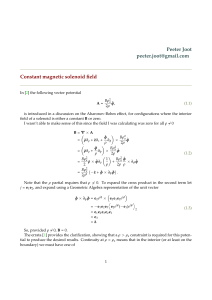
Exam No. 01 (Fall 2013) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... 2. (Schwinger et al., problem 7, chapter 1.) A charge q moves in the vacuum under the influence of uniform fields E and B. Assume that E · B = 0 and v · B = 0. (a) At what velocity does the charge move without acceleration? (b) What is the speed when ε0 E 2 = µ0 H 2 ? 3. A plane wave is incident, in ...
... 2. (Schwinger et al., problem 7, chapter 1.) A charge q moves in the vacuum under the influence of uniform fields E and B. Assume that E · B = 0 and v · B = 0. (a) At what velocity does the charge move without acceleration? (b) What is the speed when ε0 E 2 = µ0 H 2 ? 3. A plane wave is incident, in ...
H1/H2 Physics Definition Booklet 1. Measurement No. Term
... Elastic collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Inelastic collision in which momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. Completely inelastic collision in which momentum is conserved and the particles stick together after collision so that their final velocities are t ...
... Elastic collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. Inelastic collision in which momentum is conserved but kinetic energy is not. Completely inelastic collision in which momentum is conserved and the particles stick together after collision so that their final velocities are t ...