moment of inertia
... be moving the fastest at the bottom of the incline? Would a sliding object beat both these objects? ...
... be moving the fastest at the bottom of the incline? Would a sliding object beat both these objects? ...
Electrostatics worksheet
... uniform electric field of strength 1.0 x 105 N/C. 20. A – 5.0 mC charge travels due south under the influence of a 10. N force when placed into a uniform electric field. What force would a 10. mC charge experience if placed in the same field and in which direction would it move? 21. What is the magn ...
... uniform electric field of strength 1.0 x 105 N/C. 20. A – 5.0 mC charge travels due south under the influence of a 10. N force when placed into a uniform electric field. What force would a 10. mC charge experience if placed in the same field and in which direction would it move? 21. What is the magn ...
Static Electricity
... Electricity and Magnetism • Each electron in an atom is identical to every other electron so they all have the same mass and the same negative charge • The nucleus is composed of positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons • All protons are identical and the charge of the proton is exactly th ...
... Electricity and Magnetism • Each electron in an atom is identical to every other electron so they all have the same mass and the same negative charge • The nucleus is composed of positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons • All protons are identical and the charge of the proton is exactly th ...
20) A charged particle moves across a constant magnetic field. The
... D) follow a circular path. Answer: D 22) A charged particle is observed traveling in a circular path in a uniform magnetic field. If the particle had been traveling twice as fast, the radius of the circular path would be A) twice the original radius. B) four times the original radius. C) one-half th ...
... D) follow a circular path. Answer: D 22) A charged particle is observed traveling in a circular path in a uniform magnetic field. If the particle had been traveling twice as fast, the radius of the circular path would be A) twice the original radius. B) four times the original radius. C) one-half th ...
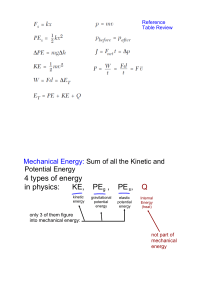
4 types of energy in physics: KE, PEg , PEs, Q
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
... What is its kinetic energy just as it reaches the ground? ...
PHYSICS 231 INTRODUCTORY PHYSICS I Lecture 12
... • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) • Units are Newton-meters Door Demo ...
... • F is the force • d is the lever arm (or moment arm) • Units are Newton-meters Door Demo ...
4.8 Integrals using grad, div, and curl
... curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equation) I x ...
... curlf~ = rotf~ = ∇ Note that the curl is applied to a vector and the result is a vector. One essential aspect of the curl is the solution of area integrals (Stokes integral equation) I x ...
Getting to Know: Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration
... The second law can be written using the following formula: F= m•a. We say this equation as, “Force equals mass times acceleration.” Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. We won’t use this law much in this concept, but it’s still a good id ...
... The second law can be written using the following formula: F= m•a. We say this equation as, “Force equals mass times acceleration.” Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. We won’t use this law much in this concept, but it’s still a good id ...