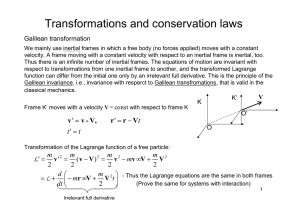
Phys 202A Homework 7 Solutions 7. Since point P lies directly
... Their sum is zero. Note that the +3.0q charge and the –12q charge produce electric fields at P in opposite directions. The –12q charge has a magnitude four times that of the +3.0q charge but is twice as far away. Since E q r 2 , the forces due to these two charges also sum to zero. So the net field ...
... Their sum is zero. Note that the +3.0q charge and the –12q charge produce electric fields at P in opposite directions. The –12q charge has a magnitude four times that of the +3.0q charge but is twice as far away. Since E q r 2 , the forces due to these two charges also sum to zero. So the net field ...
hp1f2013_class04_3d
... Choosing coordinates well is important A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angle ...
... Choosing coordinates well is important A tennis ball is hit at 50 mps at an angle of 5 degrees above the horizontal. The initial height is 2 m. Neglecting air drag, how far does the ball go before hitting the ground? Choose +x to be in the direction the ball starts at. Choose +y to be at right angle ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... • Zoo keepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the upward acceleration of the lion and stretcher is 0.657 m/s2. What force is needed to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? • Known: m = 175 kg Equation: F=ma a = 0 ...
... • Zoo keepers lift a stretcher that holds a sedated lion. The total mass of the lion and stretcher is 175 kg, and the upward acceleration of the lion and stretcher is 0.657 m/s2. What force is needed to produce this acceleration of the lion and the stretcher? • Known: m = 175 kg Equation: F=ma a = 0 ...
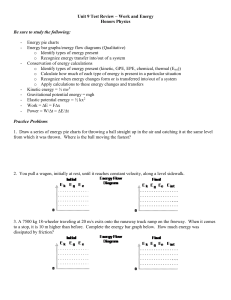
Unit 9 Test Review – Work and Energy
... o Recognize when energy changes form or is transferred into/out of a system o Apply calculations to these energy changes and transfers Kinetic energy = ½ mv2 Gravitational potential energy = mgh Elastic potential energy = ½ kx2 Work = E = Fx Power = W/t = E/t ...
... o Recognize when energy changes form or is transferred into/out of a system o Apply calculations to these energy changes and transfers Kinetic energy = ½ mv2 Gravitational potential energy = mgh Elastic potential energy = ½ kx2 Work = E = Fx Power = W/t = E/t ...
fiitjee aieee class room program
... The physical quantities not having same dimensions are (A) torque and work (B) momentum and Planck’s constant (C) stress and Young’s modulus (D) speed and (00)1/2 ...
... The physical quantities not having same dimensions are (A) torque and work (B) momentum and Planck’s constant (C) stress and Young’s modulus (D) speed and (00)1/2 ...
File
... 1. Use Newton’s first law to explain why packages in the back of a truck move forward if it comes to a quick stop. Explanations should use Newton’s first law. For example, packages in the back of a truck move forward if the truck comes to a quick stop because an object in motion continues its motion ...
... 1. Use Newton’s first law to explain why packages in the back of a truck move forward if it comes to a quick stop. Explanations should use Newton’s first law. For example, packages in the back of a truck move forward if the truck comes to a quick stop because an object in motion continues its motion ...