Q1. A small mass is situated at a point on a line joining two large
... Coulomb’s law, where both the charges and separation of two point charges are altered. The 30% who chose distractor C are likely to have misunderstood the law of force by using inverse proportion instead of inverse square proportion. ...
... Coulomb’s law, where both the charges and separation of two point charges are altered. The 30% who chose distractor C are likely to have misunderstood the law of force by using inverse proportion instead of inverse square proportion. ...
Physics 1010: The Physics of Everyday Life
... Kind of like “conservation of energy” for non-moving water: Pressure + gravitational potential energy = constant Pressure is energy density (energy per unit volume) ...
... Kind of like “conservation of energy” for non-moving water: Pressure + gravitational potential energy = constant Pressure is energy density (energy per unit volume) ...
Independence of Path and Conservative Vector Fields
... where: r(a) = A is the initial point of C. r(b) = B is the terminal point of C. ...
... where: r(a) = A is the initial point of C. r(b) = B is the terminal point of C. ...
AP Physics This and Samples
... 16) Two equal forces are applied to a door at the doorknob. The first force is applied perpendicular to the door; the second force is applied at 30° to the plane of the door. Which force exerts the greater torque? A) both exert equal non-zero torques B) the second applied at an angle C) both exert z ...
... 16) Two equal forces are applied to a door at the doorknob. The first force is applied perpendicular to the door; the second force is applied at 30° to the plane of the door. Which force exerts the greater torque? A) both exert equal non-zero torques B) the second applied at an angle C) both exert z ...
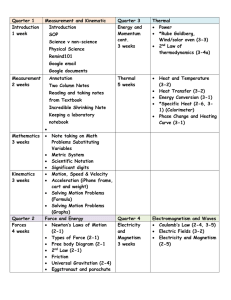
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
... A3. Determine the resultant vector A4, Determine the components of vectors. A5. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving horizontally A6. Calculate the velocity and location of objects moving as projectiles. B1. Explain the difference between mass and weight. B2. Explain the law of iner ...
Physics 51
... 23.29.(a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, the ring exerts an attractive force directed toward the ...
... 23.29.(a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, the ring exerts an attractive force directed toward the ...
Regents Physics Review
... zeros you have to deal with, so scientists instead would write this number as 1×10-9 m. See how much simpler life can be with scientific notation? Scientific notation follows these simple rules. Start by showing all the significant figures in the number you’re describing, with the decimal point aft ...
... zeros you have to deal with, so scientists instead would write this number as 1×10-9 m. See how much simpler life can be with scientific notation? Scientific notation follows these simple rules. Start by showing all the significant figures in the number you’re describing, with the decimal point aft ...
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS BY COMPUTER SIMULATION (*)
... sample. Time averages are then calculated over those trajectories. MC methods 13-4 1 generate statistical ensembles by giving random displacements to the molecules and accepting, or rejecting, the resulting configurations with a probability proportional to appropriate Boltzmann factors. Ensemble ave ...
... sample. Time averages are then calculated over those trajectories. MC methods 13-4 1 generate statistical ensembles by giving random displacements to the molecules and accepting, or rejecting, the resulting configurations with a probability proportional to appropriate Boltzmann factors. Ensemble ave ...
General Principles and Electrostatics
... where Qm is the charge of mth point charge and Vm is the potential at point ‘m’. 18. What is a parallel plate capacitor? A parallel plate capacitor is a capacitor with two parallel conducting plates separated by a distance ‘d’. The region between the plates contains a dielectric. When a potential V ...
... where Qm is the charge of mth point charge and Vm is the potential at point ‘m’. 18. What is a parallel plate capacitor? A parallel plate capacitor is a capacitor with two parallel conducting plates separated by a distance ‘d’. The region between the plates contains a dielectric. When a potential V ...
simple machines.
... Example of a lever A lever can be made by balancing a board on a log. Pushing down on one end of the board lifts a load on the other end of the board. The downward force you apply is the input force. The upward force the board exerts on the load is the output force. Parts of the lever All levers inc ...
... Example of a lever A lever can be made by balancing a board on a log. Pushing down on one end of the board lifts a load on the other end of the board. The downward force you apply is the input force. The upward force the board exerts on the load is the output force. Parts of the lever All levers inc ...