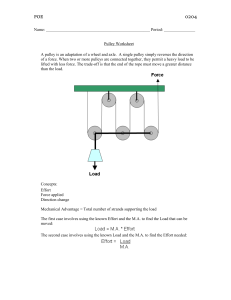
Pulley Worksheet
... that if you want to hold the weight suspended in the air, you only have to apply 50 pounds of force (the ceiling exerts the other 50 pounds of force on the other end of the rope). If you want to lift the weight 100 feet higher, then you have to reel in twice as much rope - 200 feet of rope must be p ...
... that if you want to hold the weight suspended in the air, you only have to apply 50 pounds of force (the ceiling exerts the other 50 pounds of force on the other end of the rope). If you want to lift the weight 100 feet higher, then you have to reel in twice as much rope - 200 feet of rope must be p ...
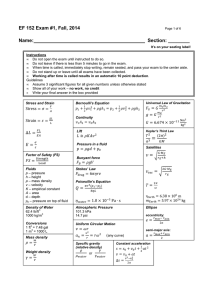
$doc.title
... I have an object a]ached to a spring, and now I’ve compressed it 5cm from it’s equilibrium point. Which way will the mass move if I let it go? ...
... I have an object a]ached to a spring, and now I’ve compressed it 5cm from it’s equilibrium point. Which way will the mass move if I let it go? ...
High School Introductory Physics MCAS Release Items Spring 2015
... a. Calculate the current generated in the blanket when the switch is connected to point X. Show your calculations and include units in your answer. b. Calculate the power generated in the blanket when the switch is connected to point X. Show your calculations and include units in your answer. c. ...
... a. Calculate the current generated in the blanket when the switch is connected to point X. Show your calculations and include units in your answer. b. Calculate the power generated in the blanket when the switch is connected to point X. Show your calculations and include units in your answer. c. ...
G-Force - Supercharged Science
... How does this all relate to “G‐Forces”? Well, like we learned before the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2. And the g‐force that you experience is just a multiple of this number. For example, if you experience an acceleration of 19.6 m/s2, you would divide this by 9.8 m/s2 to ...
... How does this all relate to “G‐Forces”? Well, like we learned before the acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2. And the g‐force that you experience is just a multiple of this number. For example, if you experience an acceleration of 19.6 m/s2, you would divide this by 9.8 m/s2 to ...
The Complete Group 1 Laboratory Manual
... are made at the start of class. 2. A work station and lab partners will be assigned to you in the first lab meeting. You will do experiments in a group but you are expected to bear your share of responsibility in doing the experiments. You must actively participate in obtaining the data and not mere ...
... are made at the start of class. 2. A work station and lab partners will be assigned to you in the first lab meeting. You will do experiments in a group but you are expected to bear your share of responsibility in doing the experiments. You must actively participate in obtaining the data and not mere ...
СОДЕРЖАНИЕ Введение
... any more detail just now. There is electrical energy, which has to do with pushing and pulling by electric charges. There is radiant energy, the energy of light, which we know is a form of electrical energy because light can be represented as wigglings of the electromagnetic field. There is chemical ...
... any more detail just now. There is electrical energy, which has to do with pushing and pulling by electric charges. There is radiant energy, the energy of light, which we know is a form of electrical energy because light can be represented as wigglings of the electromagnetic field. There is chemical ...
physics study guide chapter 12: electricity
... The force increases with the magnitude of the charges The force decreases with the separation between the charges. The direction of the electric force depends on the direction of the repulsion or the attraction; it does NOT depend on the sign of the charge. According to Newton’s third law of motion, ...
... The force increases with the magnitude of the charges The force decreases with the separation between the charges. The direction of the electric force depends on the direction of the repulsion or the attraction; it does NOT depend on the sign of the charge. According to Newton’s third law of motion, ...