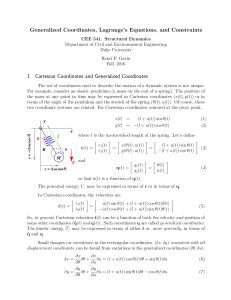
Electric Potential
... Electric potential energy (U) is the work required to bring a positive unit charge from infinity to a point in an electric field. Electric potential (V) is the change in energy per unit charge as the charge is brought from one point to another. The electric field between two charged plates is consta ...
... Electric potential energy (U) is the work required to bring a positive unit charge from infinity to a point in an electric field. Electric potential (V) is the change in energy per unit charge as the charge is brought from one point to another. The electric field between two charged plates is consta ...
Ch. 16 Electrical Energy and Capacitance
... Capacitors in series share 1 common point. For capacitors in series, the magnitude of the charges must be the same on all plates. see figure 16.19 After the series capacitors are fully charged, an equivalent capacitor must have a charge of –Q on the plate nearest the + terminal of the battery and a ...
... Capacitors in series share 1 common point. For capacitors in series, the magnitude of the charges must be the same on all plates. see figure 16.19 After the series capacitors are fully charged, an equivalent capacitor must have a charge of –Q on the plate nearest the + terminal of the battery and a ...
(8) Force, motion, and energy. The student knows force and motion
... 13. The equation for kinetic energy is written as follows. kinetic energy = [(mass)(velocity)2] / 2 What can you conclude from this equation? A. The greater the mass of a moving object is, the less kinetic energy it has. B. The slower an object is moving, the more kinetic energy it has. C. Both mass ...
... 13. The equation for kinetic energy is written as follows. kinetic energy = [(mass)(velocity)2] / 2 What can you conclude from this equation? A. The greater the mass of a moving object is, the less kinetic energy it has. B. The slower an object is moving, the more kinetic energy it has. C. Both mass ...
PDF (English
... objects, systems, and processes. Hi, my name is Sanjay Sarma, and I am a professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT. Today we are going to demystify the origins of the forces that appear to act on objects in rotating frames. Before watching this video, you should be familiar with how to define basis ...
... objects, systems, and processes. Hi, my name is Sanjay Sarma, and I am a professor of Mechanical Engineering at MIT. Today we are going to demystify the origins of the forces that appear to act on objects in rotating frames. Before watching this video, you should be familiar with how to define basis ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... Subtract one-half of this value from the length previously measured to get the value of L and record this in Data Table 3 on the worksheet. 17 Using the accepted value of 9.81 m/s2 for g, predict and record the period of the pendulum for this value of L. 18 Pull the pendulum bob to one side and rele ...
... Subtract one-half of this value from the length previously measured to get the value of L and record this in Data Table 3 on the worksheet. 17 Using the accepted value of 9.81 m/s2 for g, predict and record the period of the pendulum for this value of L. 18 Pull the pendulum bob to one side and rele ...
Exam I, vers. 0001 - University of Colorado Boulder
... Is the magnitude of the electric force on +q due to the two +Q charges in case A greater than, less than, or equal to, the magnitude of the electric force on +q due to the single +2Q charge in case B? (a) (1 point) Write greater than, less than, or equal to: ________LESS THAN__________________ (b) ( ...
... Is the magnitude of the electric force on +q due to the two +Q charges in case A greater than, less than, or equal to, the magnitude of the electric force on +q due to the single +2Q charge in case B? (a) (1 point) Write greater than, less than, or equal to: ________LESS THAN__________________ (b) ( ...
Lecture 6.1
... • From Newton’s 2nd law, a = W/m is independent of m -- means W = mg • The weight (i.e., the force that makes objects in free fall accelerate downward) is proportional to ...
... • From Newton’s 2nd law, a = W/m is independent of m -- means W = mg • The weight (i.e., the force that makes objects in free fall accelerate downward) is proportional to ...
Gravity and Motion
... • Acceleration = change in velocity over time • Review: velocity = change in speed and/or direction weight = gravitational force (unbalanced) ...
... • Acceleration = change in velocity over time • Review: velocity = change in speed and/or direction weight = gravitational force (unbalanced) ...