Chapter 3 - Houston ISD
... Units for the One newton is the amount of force that causes an acceleration of 1 meter/sec2 for second law a body of 1-kilogram mass. To use Newton’s second law in calculations, you must be sure to have units of meters/sec2 for acceleration, newtons for force, and kilograms for mass. In these calcul ...
... Units for the One newton is the amount of force that causes an acceleration of 1 meter/sec2 for second law a body of 1-kilogram mass. To use Newton’s second law in calculations, you must be sure to have units of meters/sec2 for acceleration, newtons for force, and kilograms for mass. In these calcul ...
SOH CAH TOA too[1].
... • If an object is NOT accelerating (at rest or a constant velocity) the net force must be zero. • This means that all the forces must balance out and cancel. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface (not always up if surface is at an angle). ...
... • If an object is NOT accelerating (at rest or a constant velocity) the net force must be zero. • This means that all the forces must balance out and cancel. • The normal force is always perpendicular to the surface (not always up if surface is at an angle). ...
electric potential
... A positive charge is released from rest and moves in the direction of the electric field The change in potential is negative The change in potential energy is negative The force and acceleration are in the direction of the field Conservation of Energy can be used to find its speed ΔE ΔU ...
... A positive charge is released from rest and moves in the direction of the electric field The change in potential is negative The change in potential energy is negative The force and acceleration are in the direction of the field Conservation of Energy can be used to find its speed ΔE ΔU ...
Physics - Pakchoicez.com
... 32. A vector in any given direction, whose magnitude is one is called __________. 33. The product of mass and velocity is called __________. 34. At maximum height the vertical velocity of a projectile is __________. 35. The physical quantity, which tends to rotate a body is called __________. 36. Ei ...
... 32. A vector in any given direction, whose magnitude is one is called __________. 33. The product of mass and velocity is called __________. 34. At maximum height the vertical velocity of a projectile is __________. 35. The physical quantity, which tends to rotate a body is called __________. 36. Ei ...
PHYS 110B - HW #4
... ~ ∗ is the induced field as the magnetic where E is the field given in the problem and E field turns off. This is the expression for the force on one of the plates. One could simply multiply this value by 2 to account for the total force on the capacitor (intuitively one expects that the electric fi ...
... ~ ∗ is the induced field as the magnetic where E is the field given in the problem and E field turns off. This is the expression for the force on one of the plates. One could simply multiply this value by 2 to account for the total force on the capacitor (intuitively one expects that the electric fi ...
Electric Potential
... Work done by the force given by: • W = F d cos(q) • Positive: Force is in direction moved • Negative: Force is opposite direction moved • Zero: Force is perpendicular to direction moved ...
... Work done by the force given by: • W = F d cos(q) • Positive: Force is in direction moved • Negative: Force is opposite direction moved • Zero: Force is perpendicular to direction moved ...
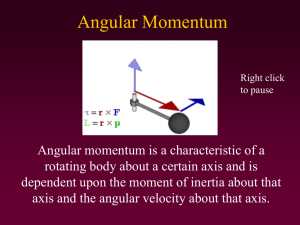
Angular Momentum
... that has a high moment of inertia. • This is partly due to the force-velocity properties of human muscle. • An example would be spinning a person on a turn table with the arms outstretched as opposed to tucked in. ...
... that has a high moment of inertia. • This is partly due to the force-velocity properties of human muscle. • An example would be spinning a person on a turn table with the arms outstretched as opposed to tucked in. ...
Electric Potential
... Electric Potential • Electric potential is a concept we use to be able to predict and calculate energies to move charges • The energy needed to move a charge from one potential V1 to another, V2, is simply • ΔU = q(V2 – V1) • It is the same physical quantity on batteries ...
... Electric Potential • Electric potential is a concept we use to be able to predict and calculate energies to move charges • The energy needed to move a charge from one potential V1 to another, V2, is simply • ΔU = q(V2 – V1) • It is the same physical quantity on batteries ...
Document
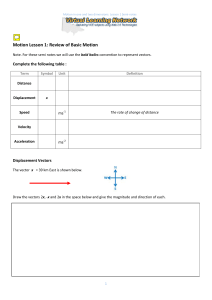
... 2.4 Uniform circular motion Draw a vector diagram to illustrate that the acceleration of a particle moving with constant speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. A particle is said to be in uniform circular motion if it travels in a circle (or arc) with constant speed v. v re ...
... 2.4 Uniform circular motion Draw a vector diagram to illustrate that the acceleration of a particle moving with constant speed in a circle is directed towards the center of the circle. A particle is said to be in uniform circular motion if it travels in a circle (or arc) with constant speed v. v re ...
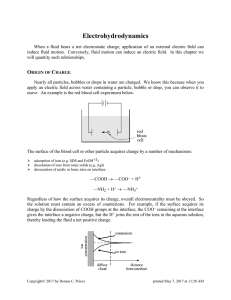
Ch. 16 Electrical Energy and Capacitance
... Work done on a force to move an object is the product of the component of the force parallel to the displacement and the displacement. W = F d cos in figure 16.1 Wab = F x = qEx(xf – xi) ...
... Work done on a force to move an object is the product of the component of the force parallel to the displacement and the displacement. W = F d cos in figure 16.1 Wab = F x = qEx(xf – xi) ...


![SOH CAH TOA too[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013805902_1-f7f5cc4c91f8996f11dbf6b53fe17c1a-300x300.png)