Key Homework 5.3.
... 1. a. A direct current I flows in a straight wire of length 2L situated along the z-axis (stretching from –L to L). Find the magnetic vector potential in a field point P that is situated in the bisecting plane (see figure below). ...
... 1. a. A direct current I flows in a straight wire of length 2L situated along the z-axis (stretching from –L to L). Find the magnetic vector potential in a field point P that is situated in the bisecting plane (see figure below). ...
Bill Nye: Magnetism
... 4. Magnetism comes from moving electrons. What do we call moving electrons? ...
... 4. Magnetism comes from moving electrons. What do we call moving electrons? ...
DEVICE TOPIC THEORETICAL Lenz’s Law Demonstration
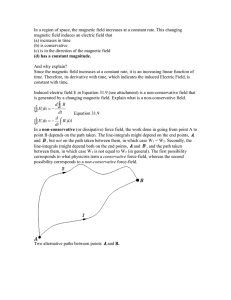
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
... Faraday’s Law of induction states that an electric current can be produced by a changing magnetic field. The direction of the induced emf and induced current is determined from Lenz’s Law which states that the polarity of the induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current that will create a ...
Induction AP/IB
... • In these examples, if the B field is increasing, the induced field acts in opposition to it. If it is decreasing, the induced field acts in the direction of the applied field to try to keep it ...
... • In these examples, if the B field is increasing, the induced field acts in opposition to it. If it is decreasing, the induced field acts in the direction of the applied field to try to keep it ...
Unit 6 Magnetism
... lines is a high voltage so as to reduce the amount of energy lost as heat • A transformer can either decrease the voltage (step down) or increase it (step up) • Step up transformers have more turns of wire in the secondary coil than in the primary coil ...
... lines is a high voltage so as to reduce the amount of energy lost as heat • A transformer can either decrease the voltage (step down) or increase it (step up) • Step up transformers have more turns of wire in the secondary coil than in the primary coil ...
Chapter 1 Test – Electricity
... Part II. Multiple Choice: read each question and choose the best answer. Circle the correct answer. 1) Know what is magnetic? 2) What will make an electromagnet stronger?? 3) A bar magnet is hanging from a string. What happens if you hold a compass near the magnet? 4) Maglev trains use the power of ...
... Part II. Multiple Choice: read each question and choose the best answer. Circle the correct answer. 1) Know what is magnetic? 2) What will make an electromagnet stronger?? 3) A bar magnet is hanging from a string. What happens if you hold a compass near the magnet? 4) Maglev trains use the power of ...
Magnets and Electricity
... Ten Facts about Magnets (from the book Driving Force) • 1. North poles point north, south poles point south. • 2. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. • 3. Magnetic forces attract only magnetic materials. • 4. Magnetic forces act at a distance. • 5. While magnetized, temporary magnets act like p ...
... Ten Facts about Magnets (from the book Driving Force) • 1. North poles point north, south poles point south. • 2. Like poles repel, unlike poles attract. • 3. Magnetic forces attract only magnetic materials. • 4. Magnetic forces act at a distance. • 5. While magnetized, temporary magnets act like p ...
Home Work Problem Set 11
... (HRW 32-60) 11-6 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or antiparallel to an externally applied magnetic field B (this will be the case ifμis due to the spin of a single electron). According to s ...
... (HRW 32-60) 11-6 Consider a solid containing N atoms per unit volume, each atom having a magnetic dipole momentμ. Suppose the direction ofμcan be only parallel or antiparallel to an externally applied magnetic field B (this will be the case ifμis due to the spin of a single electron). According to s ...
8Jsumm
... The two ends of a bar magnet are called the north seeking pole and the south seeking pole or north pole and south pole for short. A north pole and a south pole attract each other. Two north poles or two south poles will repel each other. The space around a magnet where it has an effect is called its ...
... The two ends of a bar magnet are called the north seeking pole and the south seeking pole or north pole and south pole for short. A north pole and a south pole attract each other. Two north poles or two south poles will repel each other. The space around a magnet where it has an effect is called its ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... it is the deflecting force due to the motion of the charge ...
... it is the deflecting force due to the motion of the charge ...
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is the magnetic effect of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude (or strength); as such it is a vector field. The term is used for two distinct but closely related fields denoted by the symbols B and H, where H is measured in units of amperes per meter (symbol: A·m−1 or A/m) in the SI. B is measured in teslas (symbol:T) and newtons per meter per ampere (symbol: N·m−1·A−1 or N/(m·A)) in the SI. B is most commonly defined in terms of the Lorentz force it exerts on moving electric charges.Magnetic fields can be produced by moving electric charges and the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. In special relativity, electric and magnetic fields are two interrelated aspects of a single object, called the electromagnetic tensor; the split of this tensor into electric and magnetic fields depends on the relative velocity of the observer and charge. In quantum physics, the electromagnetic field is quantized and electromagnetic interactions result from the exchange of photons.In everyday life, magnetic fields are most often encountered as a force created by permanent magnets, which pull on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, cobalt, or nickel, and attract or repel other magnets. Magnetic fields are widely used throughout modern technology, particularly in electrical engineering and electromechanics. The Earth produces its own magnetic field, which is important in navigation, and it shields the Earth's atmosphere from solar wind. Rotating magnetic fields are used in both electric motors and generators. Magnetic forces give information about the charge carriers in a material through the Hall effect. The interaction of magnetic fields in electric devices such as transformers is studied in the discipline of magnetic circuits.