5th set - Nathan Dawson
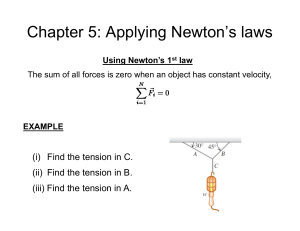
... the car to not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding? ...
... the car to not have to rely on friction to round the curve without skidding? ...
Coulomb’s Law
... Conduction (animation to show friction and conduction charging) And Polarization (applet to show how electrons move) ...
... Conduction (animation to show friction and conduction charging) And Polarization (applet to show how electrons move) ...
Answer on Question 51719, Physics, Electromagnetism 2. What are
... A scalar is a quantity that is completely specified by its magnitude and has no direction, while a vector is a quantity that specifies both the magnitude and a ...
... A scalar is a quantity that is completely specified by its magnitude and has no direction, while a vector is a quantity that specifies both the magnitude and a ...
Electricity and magnetism
... stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. • Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller generators may be powered by gasoline. ...
... stationary, and rotating magnets are rotated by turbines. Turbines are huge wheels that rotate when pushed by water, wind, or steam. • Thus mechanical energy is changed to electrical energy by a generator. Smaller generators may be powered by gasoline. ...
Title: Apr 25ана8:19 AM (1 of 9)
... True/Correct it. [10 points total] For each of the statements below, write TRUE or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. An electric current is generated in a wire when the wire is moved so that it cuts across magnetic field lines. _____________________________________________ ...
... True/Correct it. [10 points total] For each of the statements below, write TRUE or rewrite the italicized part to make the statement true. An electric current is generated in a wire when the wire is moved so that it cuts across magnetic field lines. _____________________________________________ ...
SPH 4U REVIEW
... Electric Potential 2.1 x 10-5 J of work are done in moving a point charge, q = 1.3 x 10-6 C, against an electric field. Determine the potential difference between the initial and final positions. ...
... Electric Potential 2.1 x 10-5 J of work are done in moving a point charge, q = 1.3 x 10-6 C, against an electric field. Determine the potential difference between the initial and final positions. ...
3 Maxwell`s equations and material equations
... above equations are called macroscopic Maxwell’s equations. The first and the third equations are independently known as Gauss’ law for electrostatics and magnetostatics respectively. When we write them in Maxwell’s equation the status of these are raised from statics to dynamics. In other words the ...
... above equations are called macroscopic Maxwell’s equations. The first and the third equations are independently known as Gauss’ law for electrostatics and magnetostatics respectively. When we write them in Maxwell’s equation the status of these are raised from statics to dynamics. In other words the ...
Name Date_____________________ Per. ______ HW Physics
... accelerator and emerges horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B field would cancel out the force of gravity and keep the beam of protons moving in a straight line? (Hint: Gravitational force must equal Magnetic force) ...
... accelerator and emerges horizontally from the accelerator into a uniform magnetic field. What B field would cancel out the force of gravity and keep the beam of protons moving in a straight line? (Hint: Gravitational force must equal Magnetic force) ...
Worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 500 Gauss, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b ...
... 1. An electron is traveling to the right with a speed of 8.5 x 106 m/s when a magnetic field is turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 500 Gauss, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b ...
Activities, including background information and student sheets
... Faraday develops a concept of lines of force to explain the action of a magnetic field. It was the scientist Michael Faraday who first studied in detail the phenomena involving the interaction between electricity and magnetism. At the time of Faraday’s experiments, the popular view of physicists was ...
... Faraday develops a concept of lines of force to explain the action of a magnetic field. It was the scientist Michael Faraday who first studied in detail the phenomena involving the interaction between electricity and magnetism. At the time of Faraday’s experiments, the popular view of physicists was ...
1. Electric field lines indicate A. Both direction and relative strength B
... 8. Electric field lines show the strength and _____ of an electric field. A. Polarization B. Direction ...
... 8. Electric field lines show the strength and _____ of an electric field. A. Polarization B. Direction ...
Electric Field - Sites at Penn State
... It was in 1864 when the interrelationship between electric field and magnetic field was presented by James Clerk Maxwell to the Royal Society of London. Before his publication, electric field and magnetic field were considered as two distinctive entities. It was Maxwell himself who combined Ampere’s ...
... It was in 1864 when the interrelationship between electric field and magnetic field was presented by James Clerk Maxwell to the Royal Society of London. Before his publication, electric field and magnetic field were considered as two distinctive entities. It was Maxwell himself who combined Ampere’s ...
Maxwell`s equations
... changing the magnetic field strength, moving a magnet toward or away from the coil, moving the coil into or out of the magnetic field, rotating the coil relative to the magnet, etc. ...
... changing the magnetic field strength, moving a magnet toward or away from the coil, moving the coil into or out of the magnetic field, rotating the coil relative to the magnet, etc. ...
PPT
... Fig. 32-5 (a) A circular parallel-plate capacitor, shown in side view, is being charged by a constant current i. (b) A view from within the capacitor, looking toward the plate at the right in (a).The electric field is uniform, is directed into the page (toward the plate), and grows in magnitude as t ...
... Fig. 32-5 (a) A circular parallel-plate capacitor, shown in side view, is being charged by a constant current i. (b) A view from within the capacitor, looking toward the plate at the right in (a).The electric field is uniform, is directed into the page (toward the plate), and grows in magnitude as t ...
Correlation Of The Imbalance Of Electric Charges To Universal
... what actually exists. As seen in the scale model diagram above, the speed of light is primarily based on the visible light spectrum, which is only a tiny bit of the electromagnetic spectrum. As a result, there are things that exist outside this realm, and are Multi-dimensional in movement. This caus ...
... what actually exists. As seen in the scale model diagram above, the speed of light is primarily based on the visible light spectrum, which is only a tiny bit of the electromagnetic spectrum. As a result, there are things that exist outside this realm, and are Multi-dimensional in movement. This caus ...
Electromagnetism

Electromagnetism is a branch of physics which involves the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force usually shows electromagnetic fields, such as electric fields, magnetic fields, and light. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three fundamental interactions are the strong interaction, the weak interaction, and gravitation.The word electromagnetism is a compound form of two Greek terms, ἤλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"", and μαγνῆτις λίθος magnētis lithos, which means ""magnesian stone"", a type of iron ore. The science of electromagnetic phenomena is defined in terms of the electromagnetic force, sometimes called the Lorentz force, which includes both electricity and magnetism as elements of one phenomenon.The electromagnetic force plays a major role in determining the internal properties of most objects encountered in daily life. Ordinary matter takes its form as a result of intermolecular forces between individual molecules in matter. Electrons are bound by electromagnetic wave mechanics into orbitals around atomic nuclei to form atoms, which are the building blocks of molecules. This governs the processes involved in chemistry, which arise from interactions between the electrons of neighboring atoms, which are in turn determined by the interaction between electromagnetic force and the momentum of the electrons.There are numerous mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field. In classical electrodynamics, electric fields are described as electric potential and electric current in Ohm's law, magnetic fields are associated with electromagnetic induction and magnetism, and Maxwell's equations describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated and altered by each other and by charges and currents.The theoretical implications of electromagnetism, in particular the establishment of the speed of light based on properties of the ""medium"" of propagation (permeability and permittivity), led to the development of special relativity by Albert Einstein in 1905.Although electromagnetism is considered one of the four fundamental forces, at high energy the weak force and electromagnetism are unified. In the history of the universe, during the quark epoch, the electroweak force split into the electromagnetic and weak forces.