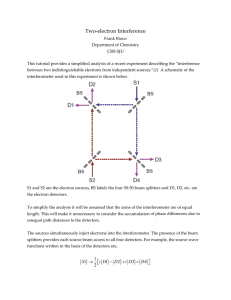
Decoherence of matter waves by thermal emission of radiation
... spatial and velocity-dependent distribution of the internal molecular energy by accounting for the stochastic absorption process, the laser beam characteristics, and the rapid radiative cooling between the beams as determined by equation (1) below. It reproduces the detected number of ions in the he ...
... spatial and velocity-dependent distribution of the internal molecular energy by accounting for the stochastic absorption process, the laser beam characteristics, and the rapid radiative cooling between the beams as determined by equation (1) below. It reproduces the detected number of ions in the he ...
Course Syllabus - Honors Chemistry
... c. Trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and sizes of ions and atoms. d. The number of electrons available for bonding. e. The nucleus of the atom contains most of its mass. f.* The lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and that the transuranium elements were synthesized and ide ...
... c. Trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and sizes of ions and atoms. d. The number of electrons available for bonding. e. The nucleus of the atom contains most of its mass. f.* The lanthanide, actinide, and transactinide elements and that the transuranium elements were synthesized and ide ...
1. Which of the following statements best describes the
... Gas particles are packed closely together, but have some ability to move. ...
... Gas particles are packed closely together, but have some ability to move. ...
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Wave Function, ψ The Heisenberg
... Question: The bright-line spectrum produced by the excited atoms of an element contains wavelength that (a) are the same for all elements (b) are characteristic of the particular element (c) are evenly distributed throughout the entire visible spectrum (d) are different from the wavelength in its da ...
... Question: The bright-line spectrum produced by the excited atoms of an element contains wavelength that (a) are the same for all elements (b) are characteristic of the particular element (c) are evenly distributed throughout the entire visible spectrum (d) are different from the wavelength in its da ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... _____________________ to be emitted (leave the atoms entirely – like in a solar panel); called the _____________________ effect. If light was a wave, then all amounts of light energy should cause this to happen, but this was not the case. It always took some _____________________ amount of energy to ...
... _____________________ to be emitted (leave the atoms entirely – like in a solar panel); called the _____________________ effect. If light was a wave, then all amounts of light energy should cause this to happen, but this was not the case. It always took some _____________________ amount of energy to ...
Theoretical work in the CUA. Strongly correlated many
... structure] → SU(N) Kondo lattice model [for N=2, colossal magnetoresistance in manganese oxides and heavy fermion materials] ...
... structure] → SU(N) Kondo lattice model [for N=2, colossal magnetoresistance in manganese oxides and heavy fermion materials] ...
PPT
... The electrons in a large group of hydrogen atoms are excited to the n=3 level. How many spectral lines will ...
... The electrons in a large group of hydrogen atoms are excited to the n=3 level. How many spectral lines will ...
Atoms1 - Cbsephysicstutorials
... integral multiple of h/2 π , h being Planck’s constant. nh L = mvr = , n = 1, 2, 3.... 2π where n is called principal quantum number. c) Stationary orbits: While revolving in the permissible orbits, an electron does not radiate energy. These non-radiating orbits are called stationary orbits. d) Freq ...
... integral multiple of h/2 π , h being Planck’s constant. nh L = mvr = , n = 1, 2, 3.... 2π where n is called principal quantum number. c) Stationary orbits: While revolving in the permissible orbits, an electron does not radiate energy. These non-radiating orbits are called stationary orbits. d) Freq ...
Does Quantum Mechanics Make Sense?
... State of definite momentum – p – for a free particle. A free particle, a photon, an electron, a rock, is the simplest system. A free particle is a particle moving without any forces acting on it, no electric or magnetic fields, no gravity, etc. Photon with perfectly defined momentum p, (momentum ei ...
... State of definite momentum – p – for a free particle. A free particle, a photon, an electron, a rock, is the simplest system. A free particle is a particle moving without any forces acting on it, no electric or magnetic fields, no gravity, etc. Photon with perfectly defined momentum p, (momentum ei ...
Review Sheet for Final Exam
... -absorption and emission Electrons absorb energy to jump up to a higher energy level because it is harder to keep an electron farther away from the nucleus so more energy is needed. This causes certain energies of light to be absorbed. When the electron wants to go back to a lower energy level, it ...
... -absorption and emission Electrons absorb energy to jump up to a higher energy level because it is harder to keep an electron farther away from the nucleus so more energy is needed. This causes certain energies of light to be absorbed. When the electron wants to go back to a lower energy level, it ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Travis D. Fridgen\My Documents
... figure, how penetration affects the energy splitting of the 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals for a manyelectron atom. From the diagrams above it can be seen that the 3s electrons penetrate very close to the nucleus (the smallest and second smallest maxima), closer than the 3p electrons, which penetrate closer ...
... figure, how penetration affects the energy splitting of the 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals for a manyelectron atom. From the diagrams above it can be seen that the 3s electrons penetrate very close to the nucleus (the smallest and second smallest maxima), closer than the 3p electrons, which penetrate closer ...
Chapter 4 - SchoolRack
... exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space) EM radiation includes X rays, UV and IR light, microwaves, radiowaves ...
... exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space) EM radiation includes X rays, UV and IR light, microwaves, radiowaves ...
“Pixel” team
... with 2 slots for 1 inch filters each equipped with compensation plates if not in use. The three fibre coupled modules should be adjustable independently such as to ensure that all three beams image the identical (within 5µm) sample area throughout the wavelength range 250-750 nm (i.e. no chromatic ...
... with 2 slots for 1 inch filters each equipped with compensation plates if not in use. The three fibre coupled modules should be adjustable independently such as to ensure that all three beams image the identical (within 5µm) sample area throughout the wavelength range 250-750 nm (i.e. no chromatic ...
Scientific Poster Example/Template
... What is a Phase Slip? A phase slip occurs when the magnitude of the superconducting order parameter fluctuates to zero at a point, allowing the phase of the order parameter to slip by 2π before the magnitude returns to its original value ...
... What is a Phase Slip? A phase slip occurs when the magnitude of the superconducting order parameter fluctuates to zero at a point, allowing the phase of the order parameter to slip by 2π before the magnitude returns to its original value ...
Non-classical light and photon statistics
... • Area of active research, highly wavelength dependent • Photon number resolved detection: up to some maximum n • Can obtain g(k) directly up to k=n • Area of active research, true PNR detection still rare ...
... • Area of active research, highly wavelength dependent • Photon number resolved detection: up to some maximum n • Can obtain g(k) directly up to k=n • Area of active research, true PNR detection still rare ...
Atomic Spectroscopy
... According to that rule, only transitions between two “adjacent” series are possible: for example p → s or d → p are allowed, while s → s or s → d are forbidden. The strongest allowed optical transitions are shown in Fig. 3. Note that each level for given n and l is split into two because of the fine ...
... According to that rule, only transitions between two “adjacent” series are possible: for example p → s or d → p are allowed, while s → s or s → d are forbidden. The strongest allowed optical transitions are shown in Fig. 3. Note that each level for given n and l is split into two because of the fine ...
Glowing Tubes for Signs, Television Sets, and Computers
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
... passes between the electrodes. The fast-moving particles excite the gas in the tube, causing a glow between the plates. ...
The Quantum-Mechanical Model of the Atom
... The Bohr Atomic Model The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. It also failed to explain the fine splitting of the lines of the emission spectrum. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any att ...
... The Bohr Atomic Model The Bohr model didn’t work for atoms other than hydrogen. It also failed to explain the fine splitting of the lines of the emission spectrum. Though limited, Bohr’s approach did attempt to explain the quantized energy levels of electrons. Later developments showed that any att ...
Phonons II
... atoms that are treated as an assembly of 3N one-dimensional oscillators approximated all atoms vibrating at the same frequency (unrealistic, but makes things easier) ...
... atoms that are treated as an assembly of 3N one-dimensional oscillators approximated all atoms vibrating at the same frequency (unrealistic, but makes things easier) ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.