Part 2: Quantum theory of light
... However, all attempts to predict the actual shape of the emission spectrum of a glowing object on the basis of classical physical theory proved futile. In 1900, the great German physicist Max Planck (who earlier in the same year had worked out an empirical formula giving the detailed shape of the b ...
... However, all attempts to predict the actual shape of the emission spectrum of a glowing object on the basis of classical physical theory proved futile. In 1900, the great German physicist Max Planck (who earlier in the same year had worked out an empirical formula giving the detailed shape of the b ...
Unit 4: Atoms and Nuclei
... • In this theory electrons are considered to be point objects in orbit around the nucleus • It gives a 1st order explanation of the spectral lines, & remains a useful treatment of electron behaviour • Next year you will gain enough QM knowledge to see how the true quantum description of such syst ...
... • In this theory electrons are considered to be point objects in orbit around the nucleus • It gives a 1st order explanation of the spectral lines, & remains a useful treatment of electron behaviour • Next year you will gain enough QM knowledge to see how the true quantum description of such syst ...
Atomic Theory Notes Packet
... 2.) Electrons farther from the nucleus contain (more, less) energy 3.) When electrons gain energy, they move from the _________ __________ to higher energy levels 4.) Electrons return to the ground state by releasing energy in specific amounts called ____________ ...
... 2.) Electrons farther from the nucleus contain (more, less) energy 3.) When electrons gain energy, they move from the _________ __________ to higher energy levels 4.) Electrons return to the ground state by releasing energy in specific amounts called ____________ ...
E ref (W)
... The initial structure: random cell consisting of 8000 W atoms, a density of 19.25 g/cm3, periodic boundary conditions applied along the three directions The system was first heated to 4000 K. Once molten, the sample was equilibrated at 4000 K for 200 ps. The liquid sample was then cooled to 300 K ...
... The initial structure: random cell consisting of 8000 W atoms, a density of 19.25 g/cm3, periodic boundary conditions applied along the three directions The system was first heated to 4000 K. Once molten, the sample was equilibrated at 4000 K for 200 ps. The liquid sample was then cooled to 300 K ...
- Catalyst
... Modern Reassessment of the Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms. Although atoms are composed of smaller particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons), the atom is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of a ...
... Modern Reassessment of the Atomic Theory 1. All matter is composed of atoms. Although atoms are composed of smaller particles (electrons, protons, and neutrons), the atom is the smallest body that retains the unique identity of the element. 2. Atoms of one element cannot be converted into atoms of a ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state? Page 2 ...
... The electron in hydrogen atom is initially in the third excited state. What is the maximum number of spectral lines which can be emitted when it finally moves to the ground state? Page 2 ...
Chapter 28
... • When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electrons accelerate and gain energy • In quantum terms, electron energies increase if there are a high number of unoccupied energy levels for the electron to jump to • For example, it takes very little energy for electrons to jump from the partially f ...
... • When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electrons accelerate and gain energy • In quantum terms, electron energies increase if there are a high number of unoccupied energy levels for the electron to jump to • For example, it takes very little energy for electrons to jump from the partially f ...
Quarter Exam (Old Test)
... c. A compound consists of more than one phase. d. A compound can only be separated into its components by chemical means. ____ 29. What is the formula unit of sodium nitride? a. NaN b. NaN ...
... c. A compound consists of more than one phase. d. A compound can only be separated into its components by chemical means. ____ 29. What is the formula unit of sodium nitride? a. NaN b. NaN ...
Properties of blackbody radiation
... 1. Planck’s law of blackbody radiation This law, one of the earliest and greatest achievements of quantum physics, describes the energy emitted by a blackbody as a function of the wavelength of the radiation and the temperature of the blackbody. ...
... 1. Planck’s law of blackbody radiation This law, one of the earliest and greatest achievements of quantum physics, describes the energy emitted by a blackbody as a function of the wavelength of the radiation and the temperature of the blackbody. ...
IONIZATION METHODS IN MASS SPECTROMETRY
... allowed to crystallize so that it is comprised of microcrystals of a matrix into which the analytes are embedded. The target is placed, through a vacuum interlock, into the path of the laser beam in the ion source. An important practical advantage is the possibility of placing many samples in indivi ...
... allowed to crystallize so that it is comprised of microcrystals of a matrix into which the analytes are embedded. The target is placed, through a vacuum interlock, into the path of the laser beam in the ion source. An important practical advantage is the possibility of placing many samples in indivi ...
2011 Chem Facts Key
... 16. The Bohr Model of the atom placed electrons in “planet-like” orbits around the nucleus of an atom. 17. The current, wave-mechanical model of the atom has electrons in “clouds” (orbitals) around the nucleus. 18. Electrons can be excited to jump to higher energy levels. They emit energy as light ...
... 16. The Bohr Model of the atom placed electrons in “planet-like” orbits around the nucleus of an atom. 17. The current, wave-mechanical model of the atom has electrons in “clouds” (orbitals) around the nucleus. 18. Electrons can be excited to jump to higher energy levels. They emit energy as light ...
Problem Set 3: Bohr`s Atom
... A nano-scale P-N junction has only 100 atoms in its depletion region with each capable of producing only one electron-hole pair. In other words there are only 100 electrons available capable of jumping from valance level (band) to the conduction level. To start, all the electrons are in valence leve ...
... A nano-scale P-N junction has only 100 atoms in its depletion region with each capable of producing only one electron-hole pair. In other words there are only 100 electrons available capable of jumping from valance level (band) to the conduction level. To start, all the electrons are in valence leve ...
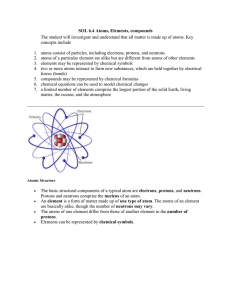
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
Time-resolved atomic inner-shell spectroscopy
... both multiphoton ionization and a perturbation to the studied electronic relaxation. The experimental results are summarized in a surface plot compiled from 20 spectra recorded at a sequence of pump–probe delays Dt (defined in Fig. 2b), each one integrated over 300,000 laser shots and normalized to ...
... both multiphoton ionization and a perturbation to the studied electronic relaxation. The experimental results are summarized in a surface plot compiled from 20 spectra recorded at a sequence of pump–probe delays Dt (defined in Fig. 2b), each one integrated over 300,000 laser shots and normalized to ...
Time-resolved atomic inner
... both multiphoton ionization and a perturbation to the studied electronic relaxation. The experimental results are summarized in a surface plot compiled from 20 spectra recorded at a sequence of pump–probe delays Dt (defined in Fig. 2b), each one integrated over 300,000 laser shots and normalized to ...
... both multiphoton ionization and a perturbation to the studied electronic relaxation. The experimental results are summarized in a surface plot compiled from 20 spectra recorded at a sequence of pump–probe delays Dt (defined in Fig. 2b), each one integrated over 300,000 laser shots and normalized to ...
Two valence electrons.
... they are almost completely inactive. All are colorless gases. Argon is the most abundant, making up almost one percent of the atmosphere. ...
... they are almost completely inactive. All are colorless gases. Argon is the most abundant, making up almost one percent of the atmosphere. ...
Chapter 4
... Radioactivity ■ In the late 1890’s Scientists noticed some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. This is because their nuclei is unstable ■ Rays and particles emitted are called radiation ■ Radioactive atoms undergo changes that alters their identity and allo ...
... Radioactivity ■ In the late 1890’s Scientists noticed some substances spontaneously emitted radiation in a process called radioactivity. This is because their nuclei is unstable ■ Rays and particles emitted are called radiation ■ Radioactive atoms undergo changes that alters their identity and allo ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 SECTION - A ALL
... 2. What are the important applications of an electron microscope? 3. Give the physical significance of the wave function. 4. What do you mean by tunneling through a potential barrier? 5. What is Hermitian operator? 6. Show that [Lx, Ly] = i ħ Lz. 7. What will be the speed of a photon in one referenc ...
... 2. What are the important applications of an electron microscope? 3. Give the physical significance of the wave function. 4. What do you mean by tunneling through a potential barrier? 5. What is Hermitian operator? 6. Show that [Lx, Ly] = i ħ Lz. 7. What will be the speed of a photon in one referenc ...
Study Guide Answers
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. ...
... classify as either metal, nonmetal, or metalloid: Ca, Cl, I, Ir, Si, and Ti. ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.