4.4 The Bohr Atom
... Evidently, from the Balmer formula and its extension to general integers m, n, these allowed non-radiating orbits, the stationary states, could be labeled 1, 2, 3, ... , n, ... and had energies -1, -1/4, -1/9, ..., -1/n2, ... in units of hcRH (using f = c and the Balmer equation above).” The main ...
... Evidently, from the Balmer formula and its extension to general integers m, n, these allowed non-radiating orbits, the stationary states, could be labeled 1, 2, 3, ... , n, ... and had energies -1, -1/4, -1/9, ..., -1/n2, ... in units of hcRH (using f = c and the Balmer equation above).” The main ...
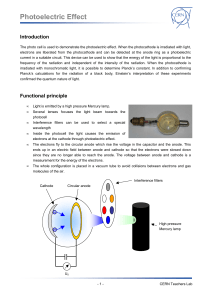
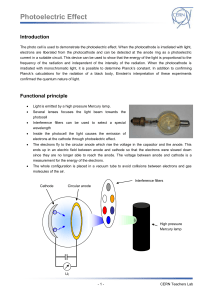
Photoelectric Effect
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
doc
... on the wavelength of the light. The photoelectric effect (and the limit voltage U0) should depend on the intensity, not on the frequency or wavelength of light. How we saw in this experiment, this is not true: the limit voltage is proportional to the wavelength and not to the intensity. The explanat ...
... on the wavelength of the light. The photoelectric effect (and the limit voltage U0) should depend on the intensity, not on the frequency or wavelength of light. How we saw in this experiment, this is not true: the limit voltage is proportional to the wavelength and not to the intensity. The explanat ...
Unit 1, Lecture 1
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
... The properties of electrons They are negatively charged. They have a spin (either up or down). The shapes of s and p orbitals s orbitals are spherically symmetric (“round”). p orbitals have two lobes with opposite sign along the axes. p orbitals are also triply degenerate. Atomic energy levels and e ...
7.4 The Wavelike properties of the Electron Models of
... • Experimental evidence (Davisson and Germer) – diffraction of electrons by crystal surfaces – diffraction patterns are consistent with the wavelength predicted by de Broglie’s relation ...
... • Experimental evidence (Davisson and Germer) – diffraction of electrons by crystal surfaces – diffraction patterns are consistent with the wavelength predicted by de Broglie’s relation ...
Multi-electron Atoms
... When a shell is full the next electron must occupy a higher state. E.g. lithium (Z = 3) has a full K-shell plus one electron in its less tightly-bound L-shell. Lithium, therefore, is chemically active as it can readily lose its outermost electron to form a Li+ ion, which has just two electrons filli ...
... When a shell is full the next electron must occupy a higher state. E.g. lithium (Z = 3) has a full K-shell plus one electron in its less tightly-bound L-shell. Lithium, therefore, is chemically active as it can readily lose its outermost electron to form a Li+ ion, which has just two electrons filli ...
Atomic Structure MC Review_ corrected
... Atomic Structure and Electron Configurations Multiple Choice PSI Chemistry Name:________________________ 1. Rutherford’s Nuclear Model of the atom A. is the currently accepted atomic model. B. explains the unique emission spectra of different elements. C. does not account for the stability of most a ...
... Atomic Structure and Electron Configurations Multiple Choice PSI Chemistry Name:________________________ 1. Rutherford’s Nuclear Model of the atom A. is the currently accepted atomic model. B. explains the unique emission spectra of different elements. C. does not account for the stability of most a ...
Intro to Atoms - Freehold Borough Schools
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
... protons and neutrons In the nucleus are: • Proton: small, positively charged particle in the nucleus of an atom ( + symbol) • Neutron: Neutral charged particle in the nucleus of an atom Outside the Nucleus: • Electron: tiny, negatively charged particle that moves around the nucleus of an atom ...
Atomic Structure PPQs 2
... State ONE similarity and ONE difference between these two isotopes in terms of the numbers of their fundamental particles. Similarity .......................................................................................................... Difference ................................................ ...
... State ONE similarity and ONE difference between these two isotopes in terms of the numbers of their fundamental particles. Similarity .......................................................................................................... Difference ................................................ ...
File
... increase C) increase and the volume of the gas sample to decrease D) increase and the volume of the gas sample to increase 106. A sample of helium gas has a volume of 900. milliliters and a pressure of 2.50 atm at 298 K. What is the new pressure when the temperature is changed to 336 K and the volum ...
... increase C) increase and the volume of the gas sample to decrease D) increase and the volume of the gas sample to increase 106. A sample of helium gas has a volume of 900. milliliters and a pressure of 2.50 atm at 298 K. What is the new pressure when the temperature is changed to 336 K and the volum ...
Chapter 28
... • When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electrons accelerate and gain energy • In quantum terms, electron energies increase if there are a high number of unoccupied energy levels for the electron to jump to • For example, it takes very little energy for electrons to jump from the partially f ...
... • When a voltage is applied to a conductor, the electrons accelerate and gain energy • In quantum terms, electron energies increase if there are a high number of unoccupied energy levels for the electron to jump to • For example, it takes very little energy for electrons to jump from the partially f ...
Regents_Chem_Core_for_review
... negatively charged electrons. (3.1b) I.3 Subatomic particles contained in the nucleus include protons and neutrons. (3.1c) I.4 The proton is positively charged, and the neutron has no charge. The electron is negatively charged. (3.1d) I.5 Protons and electrons have equal but opposite charges. The nu ...
... negatively charged electrons. (3.1b) I.3 Subatomic particles contained in the nucleus include protons and neutrons. (3.1c) I.4 The proton is positively charged, and the neutron has no charge. The electron is negatively charged. (3.1d) I.5 Protons and electrons have equal but opposite charges. The nu ...
Exam 2 Form N - TAMU Chemistry
... 10. Which of the following colors is the highest energy light? (see Figure.) a) orange b) yellow c) green d) blue e) they all have the same energy 11. Which of the following statements DOES NOT depend upon the quantization of energy? a) Light has the characteristics of both a wave and a particle. b) ...
... 10. Which of the following colors is the highest energy light? (see Figure.) a) orange b) yellow c) green d) blue e) they all have the same energy 11. Which of the following statements DOES NOT depend upon the quantization of energy? a) Light has the characteristics of both a wave and a particle. b) ...
Quantum Numbers
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
... • Excited state: Higher potential energy than ground state. • Photon: A particle of electromagnetic radiation having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy (i.e., packet of light) • Only certain wavelengths of light are emitted by hydrogen atoms when electric current is passed through—Why? Mulli ...
Review Vibrational energy of a quantum oscillator Diatomic Molecule
... equilibrium separation distance, and E0 is the energy of the system at r = req . Note that as the atoms get very far apart UM approaches zero, as it should in accordance with the principle of relativity. The energy spacing (energy difference between successive levels) is nearly constant for low ener ...
... equilibrium separation distance, and E0 is the energy of the system at r = req . Note that as the atoms get very far apart UM approaches zero, as it should in accordance with the principle of relativity. The energy spacing (energy difference between successive levels) is nearly constant for low ener ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... 4. What type of bond is formed by the transferring of electrons? ______________ Sharing electrons? ___________ 5. How does an element form a cation?___________________________ Anion? __________________________ 6. Why does Magnesium form a +2 charge? __________________________________________________ ...
... 4. What type of bond is formed by the transferring of electrons? ______________ Sharing electrons? ___________ 5. How does an element form a cation?___________________________ Anion? __________________________ 6. Why does Magnesium form a +2 charge? __________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 1 - Atoms: The Quantum World
... Note: In accordance with Hund’s rule, the two electrons in the 2p-subshell occupy separate orbitals with parallel spins. Any two of the three 2p-orbitals may be occupied and both spins could also be pointing down; such configurations are all degenerate. Example 1.12e Write the ground-state electron ...
... Note: In accordance with Hund’s rule, the two electrons in the 2p-subshell occupy separate orbitals with parallel spins. Any two of the three 2p-orbitals may be occupied and both spins could also be pointing down; such configurations are all degenerate. Example 1.12e Write the ground-state electron ...
Chapter 9 - Fayetteville State University
... are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs), the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I). 8) Groups: A sequence of elements of increasing atomic number in the periodic table that share similar chemical properties (Example: group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) 9) Metals: are characterized for having extra electrons outside the ...
... are the alkali metals (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs), the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I). 8) Groups: A sequence of elements of increasing atomic number in the periodic table that share similar chemical properties (Example: group 1A Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) 9) Metals: are characterized for having extra electrons outside the ...
Section 1 - Tutor
... (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The ground state electron has zero binding energy. (c) The ground state electron has zero ionization energy. (d) The ground state electron has zero spin angular momentum. (e) The ground state electron has zero orbital angular momentum. 27. ...
... (a) The ground state electron has zero kinetic energy. (b) The ground state electron has zero binding energy. (c) The ground state electron has zero ionization energy. (d) The ground state electron has zero spin angular momentum. (e) The ground state electron has zero orbital angular momentum. 27. ...
sample - Bright Red Publishing
... colours in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum (approximately 400–700 nm). When energy in the form of high voltage electricity is passed through a tube of a gas such as hydrogen at low pressure coloured light is produced. This light can be analysed by passing it through a prism or diffr ...
... colours in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum (approximately 400–700 nm). When energy in the form of high voltage electricity is passed through a tube of a gas such as hydrogen at low pressure coloured light is produced. This light can be analysed by passing it through a prism or diffr ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å falls normally on a thin wedge shaped film of µ=1.5, ...
... 2. Two lenses of focal lengths 8 cm and 6 cm are placed at a certain distance apart. Calculate the distance between the lenses if they form an achromatic combination. 3. Explain the formation of colours in thin film. 4. Light of wavelength 6000 Å falls normally on a thin wedge shaped film of µ=1.5, ...
Lecture 13 - UD Physics
... The expectation values Dik for all possible transitions between arbitrary levels i , k = 1, 2, . . . , n can be arranged in an n × n matrix. The Dik are therefore called electric-dipole matrix elements. If some of the matrix elements are zero, the corresponding transition does not occur. One says th ...
... The expectation values Dik for all possible transitions between arbitrary levels i , k = 1, 2, . . . , n can be arranged in an n × n matrix. The Dik are therefore called electric-dipole matrix elements. If some of the matrix elements are zero, the corresponding transition does not occur. One says th ...
Chemistry I Exam
... III. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium through which to travel. IV. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light through a vacuum. A. I and IV only B. I, II, and IV only C. II, III, and IV only D. II and III only ...
... III. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium through which to travel. IV. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light through a vacuum. A. I and IV only B. I, II, and IV only C. II, III, and IV only D. II and III only ...
Lecture 1 (Bohr model of the atom)
... • In this theory electrons are considered to be point objects in orbit around the nucleus • It gives a 1st order explanation of the spectral lines, & remains a useful treatment of electron behaviour • Next year you will gain enough QM knowledge to see how the true quantum description of such systems ...
... • In this theory electrons are considered to be point objects in orbit around the nucleus • It gives a 1st order explanation of the spectral lines, & remains a useful treatment of electron behaviour • Next year you will gain enough QM knowledge to see how the true quantum description of such systems ...
X-ray fluorescence

X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic ""secondary"" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by bombarding with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis and chemical analysis, particularly in the investigation of metals, glass, ceramics and building materials, and for research in geochemistry, forensic science and archaeology.